Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detectorMorishita, Yuki; Sagawa, Naoki; Takada, Chie; Momose, Takumaro; Takasaki, Koji
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(13), p.1376 - 1383, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)It is very important to evaluate the diameters (activity median aerodynamic diameter) of Plutonium dioxide (PuO ) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO
) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of
particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of  PuO
PuO and the case of PuO
and the case of PuO (including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO
(including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
 Fe
Fe GeO
GeO with andalusite structure
with andalusite structureKakimoto, Kazuo*; Takada, Saki*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Hatakeyama, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054704_1 - 054704_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kobayashi, Masaki*; Anh, L. D.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Kaneta-Takada, Shingo*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Shibata, Goro*; Tanaka, Arata*; Tanaka, Masaaki*; Oya, Shinobu*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 15(6), p.064019_1 - 064019_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.71(Physics, Applied)Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Hojo, Kiminobu*; Hayashi, Shotaro*; Nishi, Wataru*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi*; Nagai, Masaki*; Okamoto, Toshiki*; Takada, Yasukazu*; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(4), p.16-00083_1 - 16-00083_16, 2016/08
Performance demonstration certification of non-destructive inspection for cast stainless steel (CASS) has been planned but the target flaw depth to be detected has not been determined yet in Japan. The target flaw size is closely connected to the allowable flaw size which is determined by flaw evaluation of the rules on fitness-for-service. For rational mitigation of the acceptable flaw size, application of probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is one of the useful countermeasures compared with deterministic approach. In this paper, benchmark problems for a CASS pipe were proposed with intention applying and verifying PFM codes. As the fracture modes, fatigue crack extension, plastic collapse and ductile crack initiation were assumed. Six organizations participated in the benchmark analysis and failure probabilities from them were compared. As a result the failure probability of each problem showed good agreement and the code for application of CASS issue has been verified.
 -ray for improvement neutron emission profile measurement
-ray for improvement neutron emission profile measurementUchida, Yuki*; Takada, Eiji*; Fujisaki, Akihiro*; Isobe, Mitsutaka*; Ogawa, Kunihiro*; Shinohara, Koji; Tomita, Hideki*; Kawarabayashi, Jun*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(11), p.11E118_1 - 11E118_4, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fujii, Hirofumi*; Hara, Kazuhiko*; Hashimoto, Shugo*; Ito, Fumiaki*; Kakuno, Hidekazu*; Kim, S.*; Kochiyama, Mami; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Suzuki, Atsuto*; Takada, Yoshihisa*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2013(7), p.073C01_1 - 073C01_20, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:76.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shinohara, Masanori; Motegi, Toshihiro; Saito, Kenji; Haga, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Takada, Kiyoshi*; Higashimura, Keisuke*; Fujii, Junichi*; Ukai, Takayuki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-032, 29 Pages, 2012/11
An event, in which one of WRMs were disabled to detect the neutron flux in the reactor core, occurred during the period of reactor shut down of HTTR in March, 2010. The actual life time of WRM was unexpectedly shorter than the past developed life time. Investigation of the cause of the outage of WRM toward the recovery of the life time up to the past developed life is one of the issues to develop the technology basis of HTGR. Then, two experimental investigations were carried out to reveal the cause of the malfunction by specifying the damaged part causing the event in the WRM. One is an experiment using a mock-up sample test which strength degradation on assembly accuracy and heat cycle to specify the damaged part in the WRM. The other is a destructive test in FMF to specify the damaged part in the WRM. This report summarized the results of the destructive test and the experimental investigation using the mock-up to reveal the cause of malfunction of WRM.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(2), p.264 - 271, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:55.77(Biology)Deposit energy distribution in microscopic site is basic information for understanding of biological effects of energetic heavy ion beams. To estimate RBE, lineal energy,  , can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of
, can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of  distributions,
distributions, 
 (
( ), for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He, 290 MeV/u C, 490 MeV/u Si and 500 MeV/u Ar. Data of
), for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He, 290 MeV/u C, 490 MeV/u Si and 500 MeV/u Ar. Data of 
 (
( ) were also obtained in the wide range of LET. The dose-means of
) were also obtained in the wide range of LET. The dose-means of  ,
, 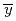
 , were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated
, were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated 
 (
( ) and
) and 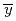
 agree fairly well with those measured. The values of
agree fairly well with those measured. The values of 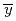
 are larger than those of LET less than
are larger than those of LET less than  10 keV/
10 keV/ m because of the discrete energy deposition by delta rays, while the relation is reversed above 10 keV/
m because of the discrete energy deposition by delta rays, while the relation is reversed above 10 keV/ m. The results indicate that care should be taken in the difference between
m. The results indicate that care should be taken in the difference between 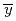
 and LET when the values of RBE of energetic heavy ions are estimated.
and LET when the values of RBE of energetic heavy ions are estimated.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
KEK Proceedings 2011-8, p.100 - 108, 2011/12
Deposit energy distribution in microscopic site is basic information for understanding of biological effects of energetic heavy ion beams. To estimate RBE, lineal energy, y, can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of y distributions, 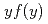 , for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He and 490 MeV/u Si ion beams. Data of
, for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He and 490 MeV/u Si ion beams. Data of 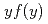 and the dose-means of
and the dose-means of  ,
, 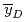 , were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated
, were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated 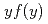 and
and 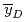 agree fairly well with those measured, as well as the already reported result of 290 MeV/u carbon beam.
agree fairly well with those measured, as well as the already reported result of 290 MeV/u carbon beam.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-136, p.219 - 220, 2011/11
Measurements of lineal energy distribution were employed using 160 MeV proton and 490 MeV/u Si. The calculated 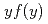 by PHITS and
by PHITS and 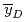 agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of
agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of 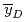 was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
Takahashi, Eiichi*; Kato, Susumu*; Furutani, Hirohide*; Sasaki, Akira; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*; Takada, Kenji*; Matsumura, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Hiroyasu*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 44(30), p.302001_1 - 302001_4, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.23(Physics, Applied)A recently developed ultrafast camera that can acquire 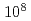 frames per second was used to investigate positive streamer discharge. It enabled single-shot evaluation of streamer evolution without the need to consider shot-to-shot reproducibility. This camera was used to investigate streamers in argon. Growing branches, the transition when a streamer forms a return stroke, and related phenomena were clearly observed.
frames per second was used to investigate positive streamer discharge. It enabled single-shot evaluation of streamer evolution without the need to consider shot-to-shot reproducibility. This camera was used to investigate streamers in argon. Growing branches, the transition when a streamer forms a return stroke, and related phenomena were clearly observed.
 carbon beam
carbon beamTsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.450 - 454, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.65(Environmental Sciences)A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter, wall-less TEPC, has been designed and used for the measurement of the y distributions for energetic heavy ions in order to verify a biological dose calculation model incorporated in the PHITS code. It is found that the dose-mean value of y obtained by the wall-less TEPC is 50 - 60% of the LET of the argon ions in water, since the delta-rays with relatively low y can be measured.
 C beam
C beamTsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 55(17), p.5089 - 5101, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:60.77(Engineering, Biomedical)The frequency distribution of the lineal energy of 290 MeV/u carbon beam was measured using a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (wall-less TEPC) in a cylindrical volume with simulated diameter 0.72  m in verifying the accuracy of a dose calculation model. The measured lineal energy distribution as well as its dose-mean value agreed fairly well with the corresponding data from microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code within the experimental uncertainty. It is found that a wall-less TEPC is needed to measure the precise energy deposition spectra of the delta rays produced secondarily by energetic heavy ion beams. The measured data also indicate that more than 11% of the energy escaped from the path of the trajectory of the carbon beam.
m in verifying the accuracy of a dose calculation model. The measured lineal energy distribution as well as its dose-mean value agreed fairly well with the corresponding data from microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code within the experimental uncertainty. It is found that a wall-less TEPC is needed to measure the precise energy deposition spectra of the delta rays produced secondarily by energetic heavy ion beams. The measured data also indicate that more than 11% of the energy escaped from the path of the trajectory of the carbon beam.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-134 (CD-ROM), p.227 - 228, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
KEK Proceedings 2009-12, p.36 - 44, 2010/01
Knowledge of energy deposition at micrometer dimensions along heavy ion tracks is essential to understand the biological effects of radiation. Wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (wall-less TEPC) was produced for the purpose of measurement of lineal energy distribution including secondary-produced high-energy electrons, delta-rays. The measurement using the wall-less TEPC was performed at Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator at NIRS, Japan. It is found that lineal energy distributions could be measured for primary carbon beam with energy of 400MeV per nucleon and delta-rays. Detail of the experiment, energy calibration and estimation of delta-rays production will be presented.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
NIRS-M-226, HIMAC-132, p.264 - 265, 2009/06
A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter was designed and applied to measuring deposit energy distribution of heavy ion beams, including the contribution of delta-rays produced along heavy ion tracks. Lineal energy distributions were obtained for 400 MeV/u carbon and 490 MeV/u silicon beams.
Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Ito, Kimio; Momose, Takumaro; Miyabe, Kenjiro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 127(1-4), p.411 - 414, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.34(Environmental Sciences)Practical action levels for beginning chelation therapy to remove plutonium in the body are now under discussion in Japan since there has been no experience in administrating agents to a subject in accidental intake in Japan although a first commercial reprocessing plant is about to start operation. Recently, International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) proposed some medical intervention levels for chelation therapy on ICRP Publication 96. These levels are determined based on internal dose however common monitoring methods such as lung counting or excreta analysis are not necessarily suitable in terms of both sensitivity and promptness. As an alternative, the authors paid attention to nose swabs and introduced the practical action levels.
Kurihara, Osamu; Hato, Shinji; Kanai, Katsuta; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Ito, Kimio; Ikeda, Hiroshi*; Oeda, Mikihiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*; Fukutsu, Kumiko*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(10), p.1337 - 1346, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the case of internal contamination of radionuclides, it is necessary to perform internal dose assessment for radiation protection. For this purpose, the ICRP has given the dose coefficients and the retention and excretion rates for various radionuclides. However, these dosimetric quantities are calculated only in typical conditions, therefore, are not necessarily covered enough in the case of dose assessment in which specific information on the incident or/and individual biokinetic characteristics should be taken into account retrospectively. This paper describes a developed PC-based package of software REIDAC to meet the needs in retrospective dose assessment. REIDAC was verified by comparisons with dosimetric quantities given on the ICRP publications and several examples of practical use were also shown.
 Am lung monitoring system using an imaging plate
Am lung monitoring system using an imaging plateHirota, Masahiro*; Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Momose, Takumaro; Deji, Shizuhiko*; Ito, Shigeki*; Saze, Takuya*; Nishizawa, Kunihide*
Health Physics, 93(1), p.28 - 35, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.41(Environmental Sciences)A new  Am lung monitoring system without shielding was devised by using an imaging plate system. The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's realistic torso phantom containing a
Am lung monitoring system without shielding was devised by using an imaging plate system. The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's realistic torso phantom containing a  Am lung was covered by imaging plates sealed in lightproof bags. The imaging plate system displayed
Am lung was covered by imaging plates sealed in lightproof bags. The imaging plate system displayed  Am lung images characteristic of the lung shape of the torso phantom. The imaging plate system's lower detection limits of 14 Bq for 60 min exposure and 6 Bq for 300 min were the same levels as those of the phoswich detectors and the germanium detectors placed in shielded rooms. The imagingplate system for 60 min exposure detected about 2% of the annual limit of 740 Bq for
Am lung images characteristic of the lung shape of the torso phantom. The imaging plate system's lower detection limits of 14 Bq for 60 min exposure and 6 Bq for 300 min were the same levels as those of the phoswich detectors and the germanium detectors placed in shielded rooms. The imagingplate system for 60 min exposure detected about 2% of the annual limit of 740 Bq for  Am inhalation. A lung monitoring system using imaging plates is applicable for
Am inhalation. A lung monitoring system using imaging plates is applicable for  Am lung monitoring.
Am lung monitoring.