Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -nonyl N,N-dimethylammonio)-propyl sulfate, present in isotropic solutions above its upper critical solution temperature
-nonyl N,N-dimethylammonio)-propyl sulfate, present in isotropic solutions above its upper critical solution temperatureTanji, Tamao*; Kusunoki, Yuto*; Nakagawa, Taichi; Takase, Tsugiko*; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hinze, W. L.*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Langmuir, 41(21), p.13184 - 13191, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Yanagisawa, Kayo; Yokota, Hiromi*; Fujimoto, Katsushige*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Bunseki Kagaku, 73(9), p.515 - 522, 2024/09
On-line isotope dilution-laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (on-line ID-LA-ICP-MS) is capable of quantification for each point ablated by laser, then the quantitative mapping of elements can be also conducted by reconstruction of the obtained each point data. The volume of data obtained as flow peaks in this system as a flow injection analysis, will be multiplied by each data such as number of m/z, scan time, time resolution and measurement position, and the total amount of data is enormous, resulting in a large human power and time consumption for data processing. In this paper, an original application software using Python to improve the efficiency of data processing in on-line ID-LA-ICP-MS was developed. To discriminate between the time-to-peak intensity and the background noise, an automatic peak detection using penalized asymmetric least squares was developed.
Matsueda, Makoto; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Bunseki (Internet), 2024(6), p.195 - 200, 2024/06
The analytical demand for radioisotopes (RI) contained in radioactive waste from the decommissioning of nuclear power plants, research activities and nuclear accidents is increasing. However, traditional analytical methods of RI are mostly complicated and time-consuming, it is necessary to be rapid, simple and automatic methods. This paper describes the rapid analytical techniques of inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in recent years, which current technology, challenges and perspective for the future.
Nakagawa, Taichi; Suzuki, Reika*; Matsueda, Makoto; Terashima, Motoki; Hinze, W. L.*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 31(2), p.49 - 56, 2024/00
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Ishiniwa, Hiroko*; Wada, Toshihiro*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analyst, 148(18), p.4291 - 4299, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.29(Chemistry, Analytical)Quantitative imaging of trace elements was successfully performed by online isotope dilution laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (online LA-ICP-IDMS). The sample aerosols produced by LA are mixed online with the mist created from an isotopically enriched spike solution via an in-house cyclonic spray chamber, which has a gas port on the top. Quantification was continuously achieved in each spot; subsequently, quantitative imaging was realized. Fe and Sr were selected as the model elements, and their spot quantifications based on online-isotope dilution. The method was applied to actual biological hard tissues, and the results were compared with electron probe microanalyzer data.
 -CO
-CO mixed-gas reaction in inductively coupled plasma tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry
mixed-gas reaction in inductively coupled plasma tandem quadrupole mass spectrometryMatsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 38(11), p.1371 - 1376, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.77(Chemistry, Analytical)The  I analysis using ICP-MS is challenging caused by xenon-129 (
I analysis using ICP-MS is challenging caused by xenon-129 ( Xe) and
Xe) and  IH
IH generated from excess stable isotope
generated from excess stable isotope  I. In this study, mass discrimination between iodine-129 (
I. In this study, mass discrimination between iodine-129 ( I) and interfering substances was achieved by inductively coupled plasma-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) with a dynamic reaction cell introduced a mixture gas of O
I) and interfering substances was achieved by inductively coupled plasma-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) with a dynamic reaction cell introduced a mixture gas of O and CO
and CO . As a result, the ratio of (background noise intensity at m/z 129)/
. As a result, the ratio of (background noise intensity at m/z 129)/ I was 3.8
I was 3.8  10
10 and 10 mBq/L of
and 10 mBq/L of  I was analyzed without chemical separation in the presence of 100 mg/L stable
I was analyzed without chemical separation in the presence of 100 mg/L stable  I. Spiked tests with actual rainwater were performed, and obtained values were agreed with the spiked amounts.
I. Spiked tests with actual rainwater were performed, and obtained values were agreed with the spiked amounts.
Yamashita, Kiyoto; Yokoyama, Aya*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*; Maki, Shota; Yokosuka, Kazuhiro; Fukui, Masahiro; Iemura, Keisuke
JAEA-Technology 2022-020, 106 Pages, 2022/10
Radioactive solid wastes generated by Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station disaster may contain high levels of salt from the tsunami and seawater deliberately released into the area. It is assumed that polyvinyl chloride (PVC) products may be used for decommissioning work and for containment of radioactive wastes in the future. Among the method of handling them, incineration is one method that needs to be investigated as it is good method for reduction and stabilization of wastes. But in order to dispose of Trans-Uranic (TRU) solid waste containing chlorides, it is necessary to select the structure and materials of the facility based on the information such as the movement of nuclides and chlorides in the waste gas treating system and the corrosion of equipment due to chlorides. Therefore, we decided to get various data necessary to design a study of the incineration facilities. And we decided to examine the transfer behavior of chlorides to the waste gas treatment system, the corrosion-resistance of materials in the incineration facilities, and the distribution survey of plutonium in them obtained using the Plutonium-contaminated Waste Treatment Facility (PWTF), Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, which is a unique incinerating facility in Japan. This report describes the transfer behavior of chlorides in the waste gas treatment system, the evaluation of corrosion-resistance materials and the distribution survey of plutonium in the incineration facilities obtained by these tests using the Plutonium-contaminated Waste Treatment Facility, Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 38(8), p.1105 - 1114, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.86(Chemistry, Analytical)We demonstrate the sensitivity enhancement in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) by combining ultrasonic nebulization via the nitrogen mixed gas effect. We showed the effect of nitrogen gas concentration (0-5%) in the nebulizer gas on the signal sensitivity for 63 elements using commercially available (concentric and ultrasonic) nebulizers. In addition, the limit of detection was calculated in each case. Finally, we compared the sensitivity (i.e., the slope of the calibration curve), background noise intensity, and three-dimensional intensity distribution in the plasma to elucidate the effects of the concurrent use of mixed gas plasmas and nebulization methods.
 Reactions to Achieve Mass-spectrometric Discrimination in Simultaneous Plutonium-isotope Speciation with Inductively Coupled Plasma-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Reactions to Achieve Mass-spectrometric Discrimination in Simultaneous Plutonium-isotope Speciation with Inductively Coupled Plasma-Tandem Mass SpectrometryMatsueda, Makoto; Kawakami, Tomohiko*; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Iijima, Kazuki; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Chemistry Letters, 51(7), p.678 - 682, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.73(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)New methodology for a simultaneous isotope speciation of various Pu isotopes without complicated isobaric interferences is developed by using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). In analyzing ICP tandem MS (ICP-MS/MS), CO gas reactions in a dynamic reaction cell (DRC) almost eliminated the background noise intensity produced by isobaric interference from isotopes originating from actinides such as Am, Cm, and U at the locations (m/z) of significant Pu isotopes (
gas reactions in a dynamic reaction cell (DRC) almost eliminated the background noise intensity produced by isobaric interference from isotopes originating from actinides such as Am, Cm, and U at the locations (m/z) of significant Pu isotopes ( Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu).
Pu).
 Sr using
Sr using  Sr/
Sr/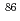 Sr isotope dilution method
Sr isotope dilution methodYanagisawa, Kayo*; Odashima, Mizuki*; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Talanta, 244, p.123442_1 - 123442_7, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.11(Chemistry, Analytical)The determination of a low concentration of  Sr was achieved by the combination of online SPE-ICP-QMS and ID method using
Sr was achieved by the combination of online SPE-ICP-QMS and ID method using  Sr/
Sr/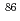 Sr ratio. No requirement of radioactive standard material and the preparation process of the calibration curve was in the quantification process and data acquisition can be in one-shot sample injection. The proposed method allowed the rapid (within 15 min/sample) quantification of
Sr ratio. No requirement of radioactive standard material and the preparation process of the calibration curve was in the quantification process and data acquisition can be in one-shot sample injection. The proposed method allowed the rapid (within 15 min/sample) quantification of  Sr in the presence of significant interferences such as isobaric
Sr in the presence of significant interferences such as isobaric  Zr and other elements. The LOD for
Zr and other elements. The LOD for  Sr was 5.6 Bq/L for a 10 mL injection and this could be improved by simply increasing the sample volume injected.
Sr was 5.6 Bq/L for a 10 mL injection and this could be improved by simply increasing the sample volume injected.
Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Abe, Hironobu; Kitamura, Akihiro; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(29), p.19281 - 19290, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Online solid-phase extraction-inductively coupled plasma-quadrupole mass spectrometry with oxygen dynamic reaction cell (online SPE-ICP-MS-DRC) was shown to be a thorough automatic analytical system, circumventing the need for human handling. At three stepwise separations (SPE-DRC-Q mass filters), we showed that interference materials allowed the coexistence of abundance ratios of 1.5 10
10 for
for  Tc/Mo. Using this optimized system, a detection limit of
Tc/Mo. Using this optimized system, a detection limit of  Tc was 9.3 pg/L (5.9 mBq/L) for a 50 mL injection and sequential measurements were undertaken at a cycle of 24 min/sample.
Tc was 9.3 pg/L (5.9 mBq/L) for a 50 mL injection and sequential measurements were undertaken at a cycle of 24 min/sample.
Matsueda, Makoto; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Bunseki, 2021(4), p.160 - 161, 2021/04
no abstracts in English
 Sr using automatic solid-phase extraction inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr using automatic solid-phase extraction inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryYanagisawa, Kayo*; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 36(9), p.1131 - 1135, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.20(Chemistry, Analytical)In this paper, we propose an online water infusion system for rapid quantification of radioactive strontium-90 ( Sr) with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled solid-phase extraction and O
Sr) with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled solid-phase extraction and O dynamic reaction (cascade ICP-MS). The proposed system automatically provides a higher dilution ratio, which is at most 3.3 times the ratio obtained by the previous method, without increasing the analysis time (within 15 min). A detection limit of 2.7 Bq/kg wet (0.54 pg/kg wet) was achieved. The recovery test results were consistent with two different spiked values.
dynamic reaction (cascade ICP-MS). The proposed system automatically provides a higher dilution ratio, which is at most 3.3 times the ratio obtained by the previous method, without increasing the analysis time (within 15 min). A detection limit of 2.7 Bq/kg wet (0.54 pg/kg wet) was achieved. The recovery test results were consistent with two different spiked values.
Takagai, Yoshitaka*; Furukawa, Makoto*; Kameo, Yutaka; Matsueda, Makoto; Suzuki, Katsuhiko*
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(4), p.223 - 231, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.53(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Takagai, Yoshitaka*; Furukawa, Makoto*; Kameo, Yutaka; Suzuki, Katsuhiko*
Isotope News, (721), p.2 - 7, 2014/05
no abstracts in English
Takagai, Yoshitaka*; Furukawa, Makoto*; Kameo, Yutaka; Suzuki, Katsuhiko*
Analytical Methods, 6(2), p.355 - 362, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:97.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Radioactive strontium-90 ( Sr) scattered by nuclear power plant accident was specifically determined by conventional inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass-spectrometry (ICP-QMS) preceded by on-line chelate column separation and oxygen reaction. After implementing the cascade-step, the detection limit (DL) of quantitative ICP-QMS of
Sr) scattered by nuclear power plant accident was specifically determined by conventional inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass-spectrometry (ICP-QMS) preceded by on-line chelate column separation and oxygen reaction. After implementing the cascade-step, the detection limit (DL) of quantitative ICP-QMS of  Sr from spiked water samples was 2.85 Bq/L (equivalent to 0.56 ppq). Analysis of microwave-digested soil yielded a DL of 4.73 Bq/kg (equivalent to 0.93 ppq). The
Sr from spiked water samples was 2.85 Bq/L (equivalent to 0.56 ppq). Analysis of microwave-digested soil yielded a DL of 4.73 Bq/kg (equivalent to 0.93 ppq). The  Sr from environmental contaminated soil samples ranged from 63 Bq/kg to 89 Bq/kg, with no statistical difference between the proposed and general methods at 98% confidence level.
Sr from environmental contaminated soil samples ranged from 63 Bq/kg to 89 Bq/kg, with no statistical difference between the proposed and general methods at 98% confidence level.
 U and
U and  U nuclide using a microwave digestion associated with ICP-MS and the large areal soil survey related to Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster
U nuclide using a microwave digestion associated with ICP-MS and the large areal soil survey related to Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear DisasterTakagai, Yoshitaka*; Furukawa, Makoto*; Nagahashi, Yoshitaka*; Takase, Tsugiko*; Shikino, Osamu*; Kameo, Yutaka
Bunseki Kagaku, 60(12), p.947 - 957, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:38.84(Chemistry, Analytical)Isotope ratio analysis for  U and
U and  U in soil samples using a microwave digestion procedure associated with ICP-MS was proposed and demonstrated. In the microwave digestion procedure, the dissolution of natural uranium in silicate (in rocks) was reduced by using a mixture of nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide (to measure the radioactive uranium from a disaster). Upon ICP-MS, the isotope ratio of the certificated geochemical reference material was realized to precisely correct the isotope ratio in real soil samples. In addition, cell-pass voltages can be available to make calibrations and/or to correct the mass bias in the mass-spectrometer. By these effects, the isotope ration of uranium can be measured with an accuracy of 0.37% without using a radioactive standard source.
U in soil samples using a microwave digestion procedure associated with ICP-MS was proposed and demonstrated. In the microwave digestion procedure, the dissolution of natural uranium in silicate (in rocks) was reduced by using a mixture of nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide (to measure the radioactive uranium from a disaster). Upon ICP-MS, the isotope ratio of the certificated geochemical reference material was realized to precisely correct the isotope ratio in real soil samples. In addition, cell-pass voltages can be available to make calibrations and/or to correct the mass bias in the mass-spectrometer. By these effects, the isotope ration of uranium can be measured with an accuracy of 0.37% without using a radioactive standard source.  U and
U and  U were quantitatively determined, and those detection limits were both 0.010
U were quantitatively determined, and those detection limits were both 0.010  g/kg. In the case of an emergency, like a nuclear hazard, the proposed method is useful to immediately gather a large amount of information in large area as compared with a common method such as a complete dissolution process associated with an
g/kg. In the case of an emergency, like a nuclear hazard, the proposed method is useful to immediately gather a large amount of information in large area as compared with a common method such as a complete dissolution process associated with an  -ray spectrometer or ICP-MS. In addition, the survey of how radioactive uranium spreads was conducted from 7 to 80 km around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (Fukushima-DNPP) (115 points in Fukushima prefecture). As a result, the values of the uranium isotope ratio for those soils were similar to the natural abundance, although the various concentrations of uranium were detected from sampling points.
-ray spectrometer or ICP-MS. In addition, the survey of how radioactive uranium spreads was conducted from 7 to 80 km around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (Fukushima-DNPP) (115 points in Fukushima prefecture). As a result, the values of the uranium isotope ratio for those soils were similar to the natural abundance, although the various concentrations of uranium were detected from sampling points.
Suzuki, Reika*; Nakagawa, Taichi; Matsueda, Makoto; Takase, Tsugiko*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Abe, Yuta; Terashima, Motoki; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Reika*; Nakagawa, Taichi; Matsueda, Makoto; Abe, Yuta; Hirata, Takafumi*; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Taichi; Suzuki, Reika*; Matsueda, Makoto; Terashima, Motoki; Iijima, Kazuki; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English