Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takagi, Hirotaka*; Takagi, Rina*; Minami, Susumu*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Michito*; Yanagi, Yuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Khanh, N.*; Karube, Kosuke*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:99.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
Kosugi, Yoshihisa*; Goto, Matato*; Tan, Z.*; Kan, Daisuke*; Isobe, Masahiko*; Yoshii, Kenji; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Fujita, Asaya*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12682_1 - 12682_8, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:41.33(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Caloric effects of solids provide more efficient and environment-friendly innovative refrigeration systems compared to the widely-used conventional vapor compressive cooling systems. Exploring novel caloric materials is challenging but critically important in developing future technologies. Here we discovered that the quadruple perovskite structure ferrimagnet BiCu Cr
Cr O
O shows a large multicaloric effect at the first-order charge transition occurred around 190 K. Large latent heat and the corresponding isothermal entropy changes 28.2 J K
shows a large multicaloric effect at the first-order charge transition occurred around 190 K. Large latent heat and the corresponding isothermal entropy changes 28.2 J K kg
kg can be fully utilized by applying both magnetic fields (magnetocaloric effect) and pressure (barocaloric effect). Adiabatic temperature changes reach 3.9 K for the 50 kOe magnetic field and 4.8 K for the 4.9 kbar pressure, and thus highly efficient thermal controls are achieved by multiple ways.
can be fully utilized by applying both magnetic fields (magnetocaloric effect) and pressure (barocaloric effect). Adiabatic temperature changes reach 3.9 K for the 50 kOe magnetic field and 4.8 K for the 4.9 kbar pressure, and thus highly efficient thermal controls are achieved by multiple ways.
Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Iwasaki, Daisuke*; Higashino, Yuji*; Yoshimi, Chiaki*; Nakagawa, Koya*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(11), p.115103_1 - 115103_10, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:59.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we systematically investigate three-dimensional(3D) momentum-resolved electronic structures of Ruddlesden-Popper-type iridium oxides Sr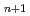 Ir
Ir O
O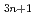 using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO
using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO -plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled
-plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled 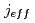 = 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO
= 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO and
and 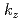 -dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr
-dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr Ir
Ir O
O . To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
. To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
Uematsu, Daisuke*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Arima, Takahisa*; Ishikawa, Jun*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Yoshida, Masahiro*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ishii, Kenji
Physical Review B, 92(9), p.094405_1 - 094405_6, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:67.70(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Katayama, Naoyuki*; Uchida, Masaya*; Hashizume, Daisuke*; Niitaka, Seiji*; Matsuno, Jobu*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Takeshita, Nao*; Gauzzi, A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(14), p.146405_1 - 146405_4, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:89.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate LiVS and LiVSe
and LiVSe with a triangular lattice as itinerant analogues of LiVO
with a triangular lattice as itinerant analogues of LiVO known for the formation of a valence-bond solid (VBS) state out of an S = 1 frustrated magnet. LiVS
known for the formation of a valence-bond solid (VBS) state out of an S = 1 frustrated magnet. LiVS , which is located at the border between a metal and a correlated insulator, shows a first order transition from a paramagnetic metal to a VBS insulator at T
, which is located at the border between a metal and a correlated insulator, shows a first order transition from a paramagnetic metal to a VBS insulator at T
 305 K upon cooling. The presence of a VBS state in the close vicinity of insulator-metal transition may suggest the importance of itinerancy in the formation of a VBS state. We argue that the high temperature metallic phase of LiVS
305 K upon cooling. The presence of a VBS state in the close vicinity of insulator-metal transition may suggest the importance of itinerancy in the formation of a VBS state. We argue that the high temperature metallic phase of LiVS has a pseudogap, likely originating from the VBS fluctuation. LiVSe
has a pseudogap, likely originating from the VBS fluctuation. LiVSe was found to be a paramagnetic metal down to 2 K.
was found to be a paramagnetic metal down to 2 K.
Tokura, Akio*; Maeda, Fumihiko*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takagi, Daisuke*; Homma, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yoshio*; Kobayashi, Yoshihiro*
Carbon, 46(14), p.1903 - 1908, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:51.84(Chemistry, Physical)We have investigated the adsorption of atomic hydrogen on vertically aligned carbon nanotube using  synchrotron-radiation-based core-level photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy. From C1s spectra, we identified a peak component due to CH bonds of carbon atoms in single-walled carbon nanotubes. We also found the suppression of
synchrotron-radiation-based core-level photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy. From C1s spectra, we identified a peak component due to CH bonds of carbon atoms in single-walled carbon nanotubes. We also found the suppression of  -plasmon excitation, indicating that the hydrogen adsorption deforms the bonding structure. Raman spectra of the single-walled carbon nanotubes indicated that the radial-breathing-mode intensities decreased due to the adsorption-induced bonding-structure deformation. Moreover, the decrease for single-walled carbon nanotubes with small-diameter was more severe than that for large-diameter. Our results strongly suggest that the hydrogen adsorption, which induces the structure deformation from sp
-plasmon excitation, indicating that the hydrogen adsorption deforms the bonding structure. Raman spectra of the single-walled carbon nanotubes indicated that the radial-breathing-mode intensities decreased due to the adsorption-induced bonding-structure deformation. Moreover, the decrease for single-walled carbon nanotubes with small-diameter was more severe than that for large-diameter. Our results strongly suggest that the hydrogen adsorption, which induces the structure deformation from sp to sp
to sp bonding, depends on the diameter of SWCNTs.
bonding, depends on the diameter of SWCNTs.
Tokura, Akio*; Maeda, Fumihiko*; Takagi, Daisuke*; Homma, Yoshikazu*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Watanabe, Yoshio*; Kobayashi, Yoshihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tokura, Akio*; Maeda, Fumihiko*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takagi, Daisuke*; Homma, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yoshio*; Kobayashi, Yoshihiro*
no journal, ,
We have investigated the adsorption of atomic hydrogen on vertically aligned SWNT film. The effects of hydrogen adsorption were investigated by photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy. By fitting C 1s core level spectrum, we found the component attributed to hydrogenation of carbon. The suppression of  plasmons was also found. These results indicate that hydrogen adsorption induced bonding structure deformation. Raman spectra demonstrate that the radial-breathing-mode intensity of small-diameter SWNTs is more severely decreased than that of large-diameter SWNTs. The G-band/D-band ratio also decreased after the irradiation. These results indicate the disordering of graphene on small-diameter SWNTs is induced more easily. Our results indicate that the adsorption coefficient of hydrogen atoms for SWNTs with small diameter is higher than that for SWNTs with large diameter.
plasmons was also found. These results indicate that hydrogen adsorption induced bonding structure deformation. Raman spectra demonstrate that the radial-breathing-mode intensity of small-diameter SWNTs is more severely decreased than that of large-diameter SWNTs. The G-band/D-band ratio also decreased after the irradiation. These results indicate the disordering of graphene on small-diameter SWNTs is induced more easily. Our results indicate that the adsorption coefficient of hydrogen atoms for SWNTs with small diameter is higher than that for SWNTs with large diameter.