Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kosugi, Yoshihisa*; Goto, Matato*; Tan, Z.*; Kan, Daisuke*; Isobe, Masahiko*; Yoshii, Kenji; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Fujita, Asaya*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12682_1 - 12682_8, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Caloric effects of solids provide more efficient and environment-friendly innovative refrigeration systems compared to the widely-used conventional vapor compressive cooling systems. Exploring novel caloric materials is challenging but critically important in developing future technologies. Here we discovered that the quadruple perovskite structure ferrimagnet BiCu Cr
Cr O
O shows a large multicaloric effect at the first-order charge transition occurred around 190 K. Large latent heat and the corresponding isothermal entropy changes 28.2 J K
shows a large multicaloric effect at the first-order charge transition occurred around 190 K. Large latent heat and the corresponding isothermal entropy changes 28.2 J K kg
kg can be fully utilized by applying both magnetic fields (magnetocaloric effect) and pressure (barocaloric effect). Adiabatic temperature changes reach 3.9 K for the 50 kOe magnetic field and 4.8 K for the 4.9 kbar pressure, and thus highly efficient thermal controls are achieved by multiple ways.
can be fully utilized by applying both magnetic fields (magnetocaloric effect) and pressure (barocaloric effect). Adiabatic temperature changes reach 3.9 K for the 50 kOe magnetic field and 4.8 K for the 4.9 kbar pressure, and thus highly efficient thermal controls are achieved by multiple ways.
Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Iwasaki, Daisuke*; Higashino, Yuji*; Yoshimi, Chiaki*; Nakagawa, Koya*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(11), p.115103_1 - 115103_10, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:61.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we systematically investigate three-dimensional(3D) momentum-resolved electronic structures of Ruddlesden-Popper-type iridium oxides Sr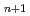 Ir
Ir O
O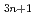 using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO
using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO -plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled
-plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled 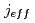 = 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO
= 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO and
and 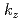 -dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr
-dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr Ir
Ir O
O . To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
. To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
Uematsu, Daisuke*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Arima, Takahisa*; Ishikawa, Jun*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Yoshida, Masahiro*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ishii, Kenji
Physical Review B, 92(9), p.094405_1 - 094405_6, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:66.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsuno, Jobu*; Ihara, Kota*; Yamamura, Shugen*; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Ishii, Kenji; Shankar, V.*; Kee, H.-Y.*; Takagi, Hidenori*
Physical Review Letters, 114(24), p.247209_1 - 247209_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:148 Percentile:97.75(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
O
Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Niitaka, Seiji*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakajima, Kenji; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Physical Review Letters, 113(23), p.236402_1 - 236402_5, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Spin fluctuations were studied over a wide momentum (
 ) and energy (
) and energy ( ) space in the frustrated
) space in the frustrated 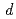 -electron heavy-fermion metal LiV
-electron heavy-fermion metal LiV O
O by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. We observed the overall
by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. We observed the overall 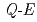 evolutions near the characteristic
evolutions near the characteristic 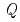 = 0.6
= 0.6 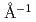 peak and found another weak broad magnetic peak around 2.4
peak and found another weak broad magnetic peak around 2.4 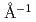 . The data are described by a simple response function, a partially delocalized magnetic form factor, and antiferromagnetic short-range spatial correlations, indicating that heavy-fermion formation is attributable to spin-orbit fluctuations with orbital hybridization.
. The data are described by a simple response function, a partially delocalized magnetic form factor, and antiferromagnetic short-range spatial correlations, indicating that heavy-fermion formation is attributable to spin-orbit fluctuations with orbital hybridization.
 Ir
Ir O
O
Takayama, Tomohiro*; Yaresko, A.*; Matsumoto, Akiyo*; Nuss, J.*; Ishii, Kenji; Yoshida, Masahiro*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Takagi, Hidenori*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 4, p.6818_1 - 6818_6, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:81.59(Multidisciplinary Sciences) IrO
IrO studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringIshii, Kenji; Jarrige, I.; Yoshida, Masahiro; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ohashi, Kei*; Takayama, Tomohiro*; Matsuno, Jobu*; Takagi, Hidenori*
Physical Review B, 83(11), p.115121_1 - 115121_5, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:90.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N
NIikubo, Satoshi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Takenaka, Koshi*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 251, p.012014_1 - 012014_4, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:80.96(Biophysics)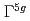 antiferromagnetic moment in the giant negative thermal expansion material Mn
antiferromagnetic moment in the giant negative thermal expansion material Mn Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N (
N (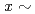 0.5)
0.5)Kodama, Katsuaki; Iikubo, Satoshi*; Takenaka, Koshi*; Takigawa, Masashi*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Physical Review B, 81(22), p.224419_1 - 224419_8, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:81.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Katayama, Naoyuki*; Uchida, Masaya*; Hashizume, Daisuke*; Niitaka, Seiji*; Matsuno, Jobu*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Takeshita, Nao*; Gauzzi, A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(14), p.146405_1 - 146405_4, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:88.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate LiVS and LiVSe
and LiVSe with a triangular lattice as itinerant analogues of LiVO
with a triangular lattice as itinerant analogues of LiVO known for the formation of a valence-bond solid (VBS) state out of an S = 1 frustrated magnet. LiVS
known for the formation of a valence-bond solid (VBS) state out of an S = 1 frustrated magnet. LiVS , which is located at the border between a metal and a correlated insulator, shows a first order transition from a paramagnetic metal to a VBS insulator at T
, which is located at the border between a metal and a correlated insulator, shows a first order transition from a paramagnetic metal to a VBS insulator at T
 305 K upon cooling. The presence of a VBS state in the close vicinity of insulator-metal transition may suggest the importance of itinerancy in the formation of a VBS state. We argue that the high temperature metallic phase of LiVS
305 K upon cooling. The presence of a VBS state in the close vicinity of insulator-metal transition may suggest the importance of itinerancy in the formation of a VBS state. We argue that the high temperature metallic phase of LiVS has a pseudogap, likely originating from the VBS fluctuation. LiVSe
has a pseudogap, likely originating from the VBS fluctuation. LiVSe was found to be a paramagnetic metal down to 2 K.
was found to be a paramagnetic metal down to 2 K.
 Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N with negative thermal expansion
N with negative thermal expansionMatsuno, Jobu*; Takenaka, Koshi*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro
Applied Physics Letters, 94(18), p.181904_1 - 181904_3, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:82.5(Physics, Applied)Local structure analysis of Cu and Ge atoms in the negative thermal expansion material Mn Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N was conducted using X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. The temperature dependence of the interatomic distance was found to reflect the macroscopic negative thermal expansion both for Cu-Mn and Ge-Mn shells, although the magnitude of the relative change was much larger for Ge-Mn than Cu-Mn. An enhanced anomaly of the Debye-Waller factor was observed for the Ge-Mn shell in the temperature region of the negative expansion, indicating the presence of static local disorder around Ge impurities. These local structure anomalies strongly suggest that the local and inhomogeneous strain around Ge is essential in broadening the discontinuous volume contraction.
N was conducted using X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. The temperature dependence of the interatomic distance was found to reflect the macroscopic negative thermal expansion both for Cu-Mn and Ge-Mn shells, although the magnitude of the relative change was much larger for Ge-Mn than Cu-Mn. An enhanced anomaly of the Debye-Waller factor was observed for the Ge-Mn shell in the temperature region of the negative expansion, indicating the presence of static local disorder around Ge impurities. These local structure anomalies strongly suggest that the local and inhomogeneous strain around Ge is essential in broadening the discontinuous volume contraction.
 Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N
NIikubo, Satoshi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Takenaka, Koshi*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Takigawa, Masashi*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Physical Review Letters, 101(20), p.205901_1 - 205901_4, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:169 Percentile:96.65(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Giant negative thermal expansion is achieved in antiperovskite manganese nitrides when the sharp volume change associated with magnetic ordering is broadened by substitution. In this Letter, we address the unique role of the "magic" element, Ge, for such broadening in Mn Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N. We present evidence for a local lattice distortion well described by the low-temperature tetragonal (
N. We present evidence for a local lattice distortion well described by the low-temperature tetragonal (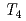 ) structure of Mn
) structure of Mn GeN for a range of
GeN for a range of  , where the overall structure remains cubic. This structural instability shows a strong correlation with the broadness of the growth of the ordered magnetic moment and, hence, is considered to trigger the broadening of the volume change.
, where the overall structure remains cubic. This structural instability shows a strong correlation with the broadness of the growth of the ordered magnetic moment and, hence, is considered to trigger the broadening of the volume change.
 O
O
Matsuda, Masaaki; Chung, J.-H.*; Park, S.*; Sato, Taku*; Matsuno, Kenichiro*; Katori, Hiroko*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Tsunoda, Yorihiko*; et al.
Europhysics Letters, 82(3), p.37006_1 - 37006_5, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:71.09(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recently, two consecutive phase transitions were observed, upon cooling, in an antiferromagnetic spinel GeNi O
O at
at 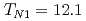 K and
K and 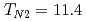 K, respectively. Using unpolarized and polarized elastic neutron scattering we show that the two transitions are due to the existence of frustrated minority spins in this compound. Upon cooling, at
K, respectively. Using unpolarized and polarized elastic neutron scattering we show that the two transitions are due to the existence of frustrated minority spins in this compound. Upon cooling, at 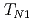 the spins on the
the spins on the  111
111 kagom
kagom planes order ferromagnetically in the plane and antiferromagnetically between the planes (phase I), leaving the spins on the
planes order ferromagnetically in the plane and antiferromagnetically between the planes (phase I), leaving the spins on the  111
111 triangular planes that separate the kagom
triangular planes that separate the kagom planes frustrated and disordered. At the lower
planes frustrated and disordered. At the lower 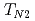 , the triangular spins also order in the
, the triangular spins also order in the  111
111 plane (phase II). We also present a scenario involving exchange interactions that qualitatively explains the origin of the two purely magnetic phase transitions.
plane (phase II). We also present a scenario involving exchange interactions that qualitatively explains the origin of the two purely magnetic phase transitions.
 Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N related to the magnetic structure; Neutron powder diffraction measurements
N related to the magnetic structure; Neutron powder diffraction measurementsIikubo, Satoshi; Kodama, Katsuaki; Takenaka, Koshi*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Physical Review B, 77(2), p.020409_1 - 020409_4, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:109 Percentile:94.61(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic structures in an antiperovskite system Mn Cu
Cu Ge
Ge N with a large magneto-volume effect above
N with a large magneto-volume effect above  =0.15 have been studied by neutron powder diffraction measurement. The present neutron study revealed that not only a cubic crystal structure, but also a
=0.15 have been studied by neutron powder diffraction measurement. The present neutron study revealed that not only a cubic crystal structure, but also a 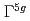 antiperovskite spin structure, is a key ingredient of the large magneto-volume effect in this itinerant electron system. The large magneto-volume effect is possibly ascribed to the geometrical frustration originating from the corner-shared octahedra of the antiperovskite sturucture.
antiperovskite spin structure, is a key ingredient of the large magneto-volume effect in this itinerant electron system. The large magneto-volume effect is possibly ascribed to the geometrical frustration originating from the corner-shared octahedra of the antiperovskite sturucture.
 Na
Na CuO
CuO Cl
Cl
Hanaguri, Tetsuo*; Kosaka, Yuki*; Davis, J. C.*; Lupien, C.*; Yamada, Ikuya*; Azuma, Masaki*; Takano, Mikio*; Oishi, Kazuki; Ono, Masaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*
Nature Physics, 3(12), p.865 - 871, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:141 Percentile:95.65(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Na
Na CuO
CuO Cl
Cl
Hanaguri, Tetsuo*; Kosaka, Yuki*; Davis, J. C.*; Lupien, C.*; Yamada, Ikuya*; Azuma, Masaki*; Takano, Mikio*; Oishi, Kazuki; Takagi, Hidenori*
Physica C, 460-462, p.954 - 955, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.7(Physics, Applied)We performed high-resolution scanning tunneling microscopy/spectroscopy on an optimally-doped Ca Na
Na CuO
CuO Cl
Cl crystal. The so-called checkerboard local-density-of-state modulation manifests in the spectroscopic map of the optimally-doped sample. In addition, spatially-inhomogeneous energy gap is observed. The gap tends to be buried at elevated temperatures and correlates with the checkerboard modulation. These results suggest that the gap is related to superconductivity which coexists with the checkerboard modulation.
crystal. The so-called checkerboard local-density-of-state modulation manifests in the spectroscopic map of the optimally-doped sample. In addition, spatially-inhomogeneous energy gap is observed. The gap tends to be buried at elevated temperatures and correlates with the checkerboard modulation. These results suggest that the gap is related to superconductivity which coexists with the checkerboard modulation.
 O
O
Matsuda, Masaaki; Takeda, Masayasu; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Osawa, Akira*; Leli vre-Berna, E.*; Chung, J.-H.*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Lee, S.-H.*
vre-Berna, E.*; Chung, J.-H.*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Lee, S.-H.*
Physical Review B, 75(10), p.104415_1 - 104415_6, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:81.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A frustrated spinel CdCr O
O undergoes a three-dimensional spin-Peierls transition at
undergoes a three-dimensional spin-Peierls transition at 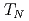 = 7.8 K from a cubic paramagnetic to a tetragonal N
= 7.8 K from a cubic paramagnetic to a tetragonal N el state. The N
el state. The N el state has a spiral magnetic structure with a characteristic wave vector of
el state has a spiral magnetic structure with a characteristic wave vector of 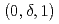 when the
when the  axis elongated. Here we report our spherical neutron polarimetry experiments to investigate the spiral spin structure in detail. Our results indicate that the spins lie in the
axis elongated. Here we report our spherical neutron polarimetry experiments to investigate the spiral spin structure in detail. Our results indicate that the spins lie in the 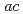 plane perpendicular to the direction of the spiral modulation. We also found that the spiral structure in the
plane perpendicular to the direction of the spiral modulation. We also found that the spiral structure in the 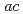 plane is elliptical with the
plane is elliptical with the  -component larger by
-component larger by  24% than the
24% than the  -component, suggesting a strong coupling between the magnetic structure and structural distortion. Unpolarized neutron diffraction under an external magnetic field has also been performed. The magnetic field dependence suggests existence of magnetic anisotropy in the N
-component, suggesting a strong coupling between the magnetic structure and structural distortion. Unpolarized neutron diffraction under an external magnetic field has also been performed. The magnetic field dependence suggests existence of magnetic anisotropy in the N el state, which is consistent with our previous inelastic studies.
el state, which is consistent with our previous inelastic studies.
 O
O
Chung, J.-H.*; Matsuda, Masaaki; Lee, S.-H.*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Sato, Taku*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Hong, K.-P.*; Park, S.*
Physical Review Letters, 95(24), p.247204_1 - 247204_4, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:140 Percentile:95.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Azuma, Masaki*; Saito, Takashi*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Yoshida, Hirofumi*; Takano, Mikio*; Kosaka, Yuki*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 14(44), p.11321 - 11324, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.72(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 O
O studied by polarized neutron techniques
studied by polarized neutron techniquesMatsuda, Masaaki; Osawa, Akira*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Chung, J.-H.*; Lee, S.-H.*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
CdCr O
O has the spinel structure, in which geometrical frustration exists between the Cr
has the spinel structure, in which geometrical frustration exists between the Cr moments located at the corners of the tetrahedron. It shows an incommensurate antiferromagnetic ordering below
moments located at the corners of the tetrahedron. It shows an incommensurate antiferromagnetic ordering below 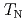 =7.8K with a characteristic wave vector of
=7.8K with a characteristic wave vector of 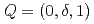 (
(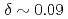 ). We first performed a 1D polarized neutron analysis and determined that the Cr
). We first performed a 1D polarized neutron analysis and determined that the Cr moments has a planer anisotropy in the
moments has a planer anisotropy in the 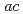 plane, indicating that the magnetic structure is spiral. Finally, the 3D polarized neutron analysis using a CRYOPAD on TAS-1 at JRR-3 determined that the magnetic structure is elliptical spiral in the
plane, indicating that the magnetic structure is spiral. Finally, the 3D polarized neutron analysis using a CRYOPAD on TAS-1 at JRR-3 determined that the magnetic structure is elliptical spiral in the 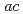 plane with ellipsoid slightly elongated along the
plane with ellipsoid slightly elongated along the  axis. The origin of the structure will be discussed.
axis. The origin of the structure will be discussed.