Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Konishi, Teruaki*; Imaseki, Hitoshi*; Yasuda, Keisuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatori, Satoshi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(Suppl.A), p.A29 - A47, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:72.75(Biology)Takagi, Keiichi*; Tanaka, Yoshikazu*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Endo, Nobuyuki*
Heisei-18-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Kenkyu Seika Hokokushu, 9, P. 95, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Wang, X.*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Imaseki, Hitoshi*; Takagi, Keiichi*; Nakamura, Masanobu*; Kashino, Genro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takata, Hyoe*; Kuma, Kenshi*; Isoda, Yutaka*; Nishioka, Jun*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Chikira, Mitsuru*; Takagi, Shogo*; Kamei, Yoshihiko*; Sakaoka, Keiichiro*
no journal, ,
The authors discussed on the difference of behavior of iron between two basins (the Yamato Basin and Japan Basin) in the Japan Sea by measurements of iron (dissolved and labile dissolved phases) and nutrients in seawater. Concentration of labile dissolved iron in the surface water was about 1.0 nM and did not show difference between the basins. On the other hand, concentration of labile dissolved iron in the Japan Basin increased to 4.5 nM at 1-2 km depth and decreased to 4 nM in the bottom layer. In the Yamato Basin, concentration of labile dissolved iron in deep water increased uniformly and was about 6 nM at the bottom layer. The difference in distribution of iron in seawater indicates that the transport processes of biogenic elements in the deep layers are different between the basins of the Japan Sea.
Izumi, Yoshinobu*; Matsuo, Yoichiro*; Sakamoto, Ayako; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Kojima, Takao*; Shimizu, Kikuo*
no journal, ,
In cases of ion-beam irradiations, several features of deep interest can be observed, contrasting with the low-LET radiations such as  -rays. In order to elucidate the induction mechanisms of mutations peculiar to ion beams, carbon-ion beams with LETs of 13 keV/
-rays. In order to elucidate the induction mechanisms of mutations peculiar to ion beams, carbon-ion beams with LETs of 13 keV/ m - 107 keV/
m - 107 keV/ m and proton beam with LET of 0.45 keV/
m and proton beam with LET of 0.45 keV/ m were irradiated to budding yeast. Carbon-ion beams and proton beam irradiation were performed in TIARA or HIMAC, and WERC, respectively. After irradiations, survival ratios and mutation frequencies were analyzed as well as sequencing and gene expression analyses. In order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis caused by radiations, we used
m were irradiated to budding yeast. Carbon-ion beams and proton beam irradiation were performed in TIARA or HIMAC, and WERC, respectively. After irradiations, survival ratios and mutation frequencies were analyzed as well as sequencing and gene expression analyses. In order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis caused by radiations, we used 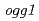 (BER-) which is deficient in the elimination of 8-oxodGTP and
(BER-) which is deficient in the elimination of 8-oxodGTP and 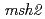 (MMR-) deficient in the mismatch-repair function. For comparison, we also used
(MMR-) deficient in the mismatch-repair function. For comparison, we also used 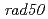 (NHEJ-) and
(NHEJ-) and 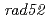 (HR-) that were deficient in the double-strand breaks (DSBs)-repair function.
(HR-) that were deficient in the double-strand breaks (DSBs)-repair function.