Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 -Co compound/Ni bilayer structure
-Co compound/Ni bilayer structureMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Avramov, P.; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*
Chemical Physics Letters, 511(1-3), p.68 - 72, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:15.54(Chemistry, Physical)X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy was employed to investigate the electronic and magnetic structures of the bilayers of a C -Co compound and Ni. A few -several nm thick C
-Co compound and Ni. A few -several nm thick C -Co compound layers on the Ni(111) surface are found to show intense XMCD signals attributed to the localized Co d-spins only with the remanent magnetization of Ni layer. It is suggested that the region of the C
-Co compound layers on the Ni(111) surface are found to show intense XMCD signals attributed to the localized Co d-spins only with the remanent magnetization of Ni layer. It is suggested that the region of the C -Co compound within 3 nm from the interface is ferromagnetically coupled with Ni due to the indirect exchange interaction mediated by C
-Co compound within 3 nm from the interface is ferromagnetically coupled with Ni due to the indirect exchange interaction mediated by C , probably relevant to the interlayer charge transfer.
, probably relevant to the interlayer charge transfer.
 -Co films with giant tunnel magnetoresistance
-Co films with giant tunnel magnetoresistanceMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Mitani, Seiji*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Maeda, Yoshihito
Chemical Physics Letters, 470(4-6), p.244 - 248, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:49.68(Chemistry, Physical)Electronic and spin states of the codeposited C -Co films with large tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) effect were investigated with the X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectroscopies. It is revealed that a C
-Co films with large tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) effect were investigated with the X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectroscopies. It is revealed that a C -Co compound generated in the C
-Co compound generated in the C -Co films shows the clear MCD signal attributed to the spin-polarized Co 3d states hybridized with C
-Co films shows the clear MCD signal attributed to the spin-polarized Co 3d states hybridized with C
 orbitals. The magnetic response of these Co 3d-derived states agrees well with temperature dependence of the observed MR ratios of the granular C
orbitals. The magnetic response of these Co 3d-derived states agrees well with temperature dependence of the observed MR ratios of the granular C -Co films. This suggests the incorporation of the spin-polarized Co 3d-derived states of the C
-Co films. This suggests the incorporation of the spin-polarized Co 3d-derived states of the C -Co compound into the observed TMR effect.
-Co compound into the observed TMR effect.
Sakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
Anomalously large tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) effects were found for the granular structured C60-Co films consisting of a C60-Co compound matrix and Co nanoparticles dispersed therein. The observed MR ratios of 90% at the maximum are significantly higher than the MR ratios of the inorganic granular films. Our recent X-ray magnetic circular dichroism study revealed that the C60-Co compound in the C60-Co films shows the paramagnetic behaviors due to the spin-polarized states (Co d-spin) derived from the Co 3d orbitals. We found that the T-dependence of the zero-bias MR ratio is represented by considering the similar T-dependence of the spin-polarization(P) of tunneling electrons to the observed T-dependence of the magnetization of the Co d-spin in the C60-Co compound, and by assuming P=100% at low temperature. This result suggests the incorporation of the spin-polarized Co 3d-derived states of the C60-Co compound into the spin-transport process in the granular C60-Co films.
 -Co thin films with giant tunnel magnetoresistance
-Co thin films with giant tunnel magnetoresistanceMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co films
-Co filmsSakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Entani, Shiro; Sugai, Isamu*; Takanashi, Koki; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
In the present study, we examine the bias-voltage (V) and temperature (T) dependences of the spin-dependent transport properties of the granular C -Co films (C
-Co films (C Co
Co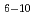 ) in the current perpendicular to plane (CPP) geometry for the origin of the large TMR effect. At low T, the CPP samples show much higher MR than the upper limit of TMR (MR = 50%) derived from the Julliere's model. From the I-V characteristics, we evaluated the degree of the higher order tunneling process, as a possible cause of the MR enhancement above MR = 50%, to be 3-7 at low temperatures, which changes depending on the sample composition and device structure. After considering this MR enhancement effect, we can evaluate the spin-polarization of the tunneling electrons generated at the C
) in the current perpendicular to plane (CPP) geometry for the origin of the large TMR effect. At low T, the CPP samples show much higher MR than the upper limit of TMR (MR = 50%) derived from the Julliere's model. From the I-V characteristics, we evaluated the degree of the higher order tunneling process, as a possible cause of the MR enhancement above MR = 50%, to be 3-7 at low temperatures, which changes depending on the sample composition and device structure. After considering this MR enhancement effect, we can evaluate the spin-polarization of the tunneling electrons generated at the C -Co compound/Co interface. The evaluated values are remarkably high, i.e., P
-Co compound/Co interface. The evaluated values are remarkably high, i.e., P  75% at zero temperature, compared to Co crystal (P = 30%).
75% at zero temperature, compared to Co crystal (P = 30%).
Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Hirao, Norie; Baba, Yuji; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
Recently, we have found that the codeposited C60-Co films where Co nanoparticles are dispersed into the matrix of the C60-Co compound show large tunnel magnetoresistanene (TMR) effects at low temperatures. The observed MR ratios cannot be explained by a spin-polarization of crystalline Co, so it is expected that the C60-Co compound mediates an enhancing effects to the spin-dependent transport in the films. In the present work, we have investigated the spin states of the C60-Co films by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy. As the results, MCD spectra of the C60-Co compound show the sensitivity to the sample temperature, which is consistent to the temperature dependence of MR ratios. This indicates clearly that spin-polarized states of the C60-Co compound influences the degree of spin-dependent transport in the films.
 -Co thin films studied by XPS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
-Co thin films studied by XPS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroismMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Hirao, Norie; Baba, Yuji; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
 -Co thin films studied by XPS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
-Co thin films studied by XPS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroismMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co hybrid films
-Co hybrid filmsSakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sugai, Isamu*; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
In the present study, the V and T dependences of the TMR effect are investigated intensively for the co-deposited C -Co films with different compositions. The mechanism of the giant TMR effect is discussed taking our recent results for the microstructures of the granular films (i.e., a hybrid structure of the covalent C
-Co films with different compositions. The mechanism of the giant TMR effect is discussed taking our recent results for the microstructures of the granular films (i.e., a hybrid structure of the covalent C -Co compound and Co nanoparticles dispersed therein) and the electronic and spin states of the C
-Co compound and Co nanoparticles dispersed therein) and the electronic and spin states of the C -Co compound studied by XPS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy into account.
-Co compound studied by XPS and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy into account.
 -Co compounds affecting giant tunneling magnetoresistance effect
-Co compounds affecting giant tunneling magnetoresistance effectMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Mitani, Seiji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co films
-Co filmsMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Mitani, Seiji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co thin films
-Co thin filmsMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Mitani, Seiji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Entani, Shiro; Sugai, Isamu*; Takanashi, Koki; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We investigated the bias-voltage (V) and temperature (T) dependences of the spin-dependent transport properties of the granular C60-Co films in the current perpendicular to plane (CPP) geometry. At low T, each sample shows much higher MR than the upper limit of TMR (MR=50%) derived from the Julliere's model. From the I-V characteristics, we evaluated the degree of the higher order tunneling process, as a possible cause of the MR enhancement above MR=50%, to be 3-7 (T=2K), which changes depending on the sample composition and device structure. By considering this enhancement effect, we can estimate the spin-polarization at the C60-Co compound/Co interface. The estimated values are remarkably high, i.e., P=75% at zero temperature, compared to Co crystal(P=30%), and almost independent of the samples. The detailed results on the transport properties and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy were presented in the conference.
 -Co compound in granular C
-Co compound in granular C -Co films with giant TMR effect
-Co films with giant TMR effectMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
Recently, we have found that the granular C -Co films have revealed the presence of the localized spin-polarized states in the C
-Co films have revealed the presence of the localized spin-polarized states in the C -Co compound, and it was suggested that such localized states are closely correlated with the large tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) effect. Detailed analysis of the C
-Co compound, and it was suggested that such localized states are closely correlated with the large tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) effect. Detailed analysis of the C -Co compound is essential for the understanding of the electronic origin of the TMR effect. In the present study, we investigated electronic and spin states of the C
-Co compound is essential for the understanding of the electronic origin of the TMR effect. In the present study, we investigated electronic and spin states of the C -Co compound with different Co content, x (C
-Co compound with different Co content, x (C Co
Co , x
, x  5) using X-ray absorption (XAS) and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectroscopies.
5) using X-ray absorption (XAS) and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectroscopies.
Sakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Otomo, Manabu; Entani, Shiro; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Otomo, Manabu; Entani, Shiro; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co hybrid films
-Co hybrid filmsSakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sugai, Isamu*; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co thin films
-Co thin filmsSakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sugai, Isamu*; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Maeda, Yoshihito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English