Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scattering
He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scatteringRyoki, Akiyuki*; Watanabe, Fumi*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Oku, Takayuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakamura, Yo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 160(11), p.114907_1 - 114907_9, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:42.16(Chemistry, Physical)Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Fukahori, Takuya*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Takahashi, Akiyuki*; Shimodaira, Masaki; Ueda, Takashi*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Takahashi, Yukio*; Ohata, Mitsuru*
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Kumagai, Tomohisa*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Miura, Naoki*; Marie, S.*; Almahdi, R.*; Mano, Akihiro; Li, Y.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Wada, Yoshitaka*; Hwang, J.-H.*; et al.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011509_1 - 011509_18, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.77(Engineering, Mechanical)To predict fracture behavior for ductile materials, some ductile fracture simulation methods different from classical approaches have been investigated based on appropriate models of ductile fracture. For the future use of the methods to overcome restrictions of classical approaches, the applicability to the actual components is of concern. In this study, two benchmark problems on the fracture tests supposing actual components were provided to investigate prediction ability of simulation methods containing parameter decisions. One was the circumferentially through-wall and surface cracked pipes subjected to monotonic bending, and the other was the circumferentially through-wall cracked pipes subjected to cyclic bending. Participants predicted the ductile crack propagation behavior by their own approaches, including FEM employed GTN yielding function with void ratio criterion, are FEM employed GTN yielding function, FEM with fracture strain or energy criterion modified by stress triaxiality, XFEM with J or delta J criterion, FEM with stress triaxiality and plastic strain based ductile crack propagation using FEM, and elastic-plastic peridynamics. Both the deformation and the crack propagation behaviors for monotonic bending were well reproduced, while few participants reproduced those for cyclic bending. To reproduce pipe deformation and fracture behaviors, most of groups needed parameters which were determined toreproduce pipe deformation and fracture behaviors in benchmark problems themselves and it is still difficult to reproduce them by using parameters only from basic materials tests.
Hirota, Takatoshi*; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Hojo, Kiminobu*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Takahashi, Akiyuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Ueda, Takashi*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Ohata, Mitsuru*; et al.
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/07
Saito, Kimiaki; Mikami, Satoshi; Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinase, Sakae; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tetsuro*; Seki, Akiyuki; Sanada, Yukihisa; Wainwright-Murakami, Haruko*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 44(4), p.128 - 148, 2019/12
Shintaku, Yuichi*; Shinozaki, Yuto*; Fujiwara, Takaki*; Takahashi, Akiyuki*; Kikuchi, Masanori
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 85(876), p.19-00141_1 - 19-00141_15, 2019/08
The contribution of this paper is to develop two kinds of numerical simulation method for fatigue crack propagation with plastic-induced crack closure under different cyclic loading conditions. One of the developed methods is Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS) using S-version FEM that allow us to simulate by combining with global mesh only representing whole structure and local mesh including crack. After stress intensity factor is calculated by S-version FEM, crack opening level due to plastic-induced crack closure is determined by elastic-plastic analysis using local mesh which is enough subdivided to realize small plastic zone around crack tip. The crack growth rate considering effect of plastic-induced crack closure is predicted by modified Paris' law in which the stress intensity factor range under cyclic loading is converted into the effective value by the crack opening level. Then, the local mesh is updated by new crack shape determined from crack growth rate. By repeating these processes, our developed method can provide us to simulate fatigue crack propagation with plastic-induced crack closure directly. Another method is simplified one that the effective stress intensity factor range is approximately determined by the relationship between the maximum stress intensity factor and crack opening level as a result of preanalysis using two-dimensional DNS. By comparison of experimental results, it can be confirmed that our developed methods predict propagation of surface crack in specimen under bending and tensile loading conditions.
 -ray emitting radioactive nuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
-ray emitting radioactive nuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentSaito, Kimiaki; Tanihata, Isao*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Saito, Takashi*; Shimoura, Susumu*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Onda, Yuichi*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Ikeuchi, Yoshihiro*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.308 - 319, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:237 Percentile:98.59(Environmental Sciences)Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Saito, Kimiaki; Tanaka, Kei*; Takahashi, Yutaka*; Takemura, Kazuhiro*; Tsuzawa, Masaharu*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.47 - 50, 2014/04
The radionuclide distribution database and map system, which provide basic information for evaluations and countermeasures of the Fukushima nuclear accident, are explained. Due to massive earthquake and tsunami, Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant has been damaged and had spread out radioactive materials around the Fukushima site. It is necessary to collect, analyze, and provide the information of radioactivity correctly and immediately. We developed two providing systems to identify the current distribution of released radionuclides and support decontamination activities.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Shigemori, Yuji*; Seki, Akiyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-008, 127 Pages, 2009/07
A radiation transport calculation can derive dose distribution in a heavily exposed person for the medical treatment at the case of an accident. Since the accident cannot be prospected, many complicated procedures are needed to make the input file soon after the accident and to inform radiation dose based upon the output files with much information concerning the calculation. Thus, (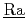 )diation (
)diation (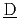 )ose (
)ose (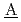 )ssessment system for (
)ssessment system for (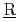 )adiation (
)adiation (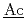 )cident (RADARAC) was developed to derive effectively radiation dose by the MCNPX or the MCNP code. RADARAC consists of RADARAC_INPUT and RADARAC_DOSE. A user can interactively set up necessary resources to make input files with three programs in RADARAC_INPUT. The results of radiation doses are indicated with tables, graphs and figures depicting dose distribution by RADARAC_DOSE. It is confirmed that RADARAC can make input files with a few thousand lines and indicate more than 20,000 data dose within a few minutes.
)cident (RADARAC) was developed to derive effectively radiation dose by the MCNPX or the MCNP code. RADARAC consists of RADARAC_INPUT and RADARAC_DOSE. A user can interactively set up necessary resources to make input files with three programs in RADARAC_INPUT. The results of radiation doses are indicated with tables, graphs and figures depicting dose distribution by RADARAC_DOSE. It is confirmed that RADARAC can make input files with a few thousand lines and indicate more than 20,000 data dose within a few minutes.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Shigemori, Yuji*; Seki, Akiyuki
Hozengaku, 8(1), p.56 - 61, 2009/04
Failure of safety management system can bring about a heavily exposed person in maintenance of a radiation facility, though such a case is very rare. A method using radiation transport code has advantages in an assessment of dose distribution inside a human body. Complicated procedures, however, are needed to prepare an input-file and to derive radiation dose based upon descriptions of an output-file in a numerical analysis using a radiation transport code. Thus, a system was developed to set up necessary information for an input file and to give radiation dose from an output file by a dialogue method using graphical user interfaces. Dose assessment can be effectively carried out for a radiological accident with this system.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Shigemori, Yuji*; Seki, Akiyuki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 133(1), p.35 - 43, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.92(Environmental Sciences)A system has been developed to assess radiation dose distribution inside a body of exposed persons in a radiological accident by utilizing radiation transport calculation codes - MCNP and MCNPX. The system mainly consists of two parts, pre-processor and post-processor of the radiation transport calculation. Programs for the pre-processor are used to set up a "problem-dependent" input file, which defines the accident condition and dosimetric quantities to be estimated. The developed program for the post-processor part can effectively indicate dose information based upon the output file of the code. All of the programs in the dosimetry system can be executed with a generally used personal computer and accurately give the dose profile to an exposed person in a radiological accident without complicated procedures. An experiment using a physical phantom was carried out to verify the availability of the dosimetry system with the developed programs in a  -ray irradiation field. The dosimetry system with the developed programs can appropriately assess dose distribution inside or on the human body, if the user exactly define the source and human models and their geometric relationship.
-ray irradiation field. The dosimetry system with the developed programs can appropriately assess dose distribution inside or on the human body, if the user exactly define the source and human models and their geometric relationship.
Seki, Akiyuki; Suzuki, Kenta; Takahashi, Yoshitomo; Matsubara, Takeshi; Suto, Shigeo; Saito, Kimiaki; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency developed a tool which automatically collects the monitoring data published by the related organizations separately. The data was formatted in a common style and published on the same website called "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data". Since a lot of environmental monitoring results have been accumulated in the past five years since the accident, new contents, which help us understand the change of the distribution of radionuclide by analyzing their time histories, were released on the website.
Seki, Akiyuki; Suzuki, Kenta; Takahashi, Yoshitomo; Matsubara, Takeshi; Suto, Shigeo; Saito, Kimiaki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Murakami, Haruko*
no journal, ,
After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, a lot of monitoring studies had been conducted to collect the precious data which are important for the estimation and prediction of the radionuclide distribution. However, those monitoring databases were not convenient for users because their formats were not unified and they are provided as PDF files. Moreover those databases ware published on the independent websites operated by each organization. JAEA developed the database which provides the monitoring data in an unique format on the same website. The database provides not only numerical data but also visualization data following users' needs.
Kikuchi, Masamitsu; Oishi, Tetsuya; Takahashi, Kenichi; Murakami, Hiroyuki; Seki, Akiyuki; Kubota, Jinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Shigemori, Yuji*; Seki, Akiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Saito, Kimiaki; Tanaka, Kei*; Takahashi, Yutaka*; Takemura, Kazuhiro*; Tsuzawa, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Radioactive database and contamination map for the accident of Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant are described. It is necessary to obtain precise data on the contamination conditions. Both systems have been developed to provide information to identify the current distribution of released materials and to support decontamination planning. The former is designed to provide quantitative data for detailed analysis, while another to provide intuitive images for the qualitative estimation. They contain air dose rates at around 2,200 locations within approximately 100 km from the plant, and radionuclide concentration data at each location. The vehicle-borne survey results are also included for the purpose of ascertaining the distribution of radioactive substances around roads in detail. All the data have been measured during the first investigation conducted in June, and the second in December 2011. The systems will become open to the public at the site of JAEA soon.
Seki, Akiyuki; Suzuki, Kenta*; Takahashi, Yoshitomo*; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Suto, Shigeo*; Saito, Kimiaki; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
JAEA had collected and published radioactive monitoring data provided individually by government offices and local governments and so on. The amount of those data which were unified in same display format and accuracy had become enormous by six years after the accident had passed. To understand how much the radionuclide distribution changed, new contents which were prepared in maps and graphs were added in the site for publishing.
Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Saito, Kimiaki; Tanaka, Kei*; Takahashi, Yutaka*; Takemura, Kazuhiro*; Tsuzawa, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
The construction of the database and map systems, which provide basic information for evaluations and countermeasures of the Fukushima nuclear accident, are explained. Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant had been damaged and spread out radioactive materials around there on March 2011. There are still a lot of requests to know the distribution of radioactive material from government, local government, residents, and/or researchers. In order to meet those requests, we developed two systems to provide those data to the public. One of the systems is a database system which is designed to provide quantitative data for detailed analysis. Another is a map system which provides intuitive images for the qualitative estimation.
Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Saito, Osamu; Saito, Kimiaki; Tanaka, Kei*; Takahashi, Yutaka*; Takemura, Kazuhiro*; Tsuzawa, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
The system for saving and providing the data which are related to the radionuclides in Fukushima prefecture and the neighboring prefectures has been developed. The data mainly include the dose-rate and the analysis result of the soil and water samples. The Center for Computational Science and e-Systems developed the system under the study on distribution of radioactive substances around Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant founded by MEXT. Proceeding with the installation of the data which are collected by MEXT and Fukushima prefecture, the system are being enhanced more.