Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toyoda, Shin*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Yamaguchi, Ichiro*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Hirota, Seiko*; Oka, Toshitaka; Shimazaki, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Hideyuki*; Tani, Atsushi*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Interlaboratory comparison studies are important for radiation dosimetry in order to demonstrate how the technique is universally available. The set of standard samples are examined in each participating laboratory in the present study. After a set of standard samples together with the samples with unknown doses, which were prepared in the same laboratory as the standard samples, are measured at a participating laboratory, those samples are sent to another participating laboratory for next measurement. There is some small difference observed in the sensitivity (the slope of the dose response line) of the standard samples while the differences in the obtained doses for the samples with unknown doses are rather systematic, implying that the difference is mostly due to the samples but not to measurements.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Terunuma, Akihiro; Mimura, Ryuji; Nagashima, Hisao; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hirokawa, Katsunori*; Uta, Masato; Ishimori, Yuu; Kuwabara, Jun; Okamoto, Hisato; Kimura, Yasuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-008, 98 Pages, 2016/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency formulated the plan to achieve the medium-term target in the period of April 2010 to March 2015(hereinafter referred to as "the second medium-term plan"). JAEA determined the plan for the business operations of each year (hereinafter referred to as "the year plan"). This report is that the Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Waste Management has summarized the results of the decommissioning technology development and decommissioning of nuclear facilities which were carried out in the second medium-term plan.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.682 - 683, 2014/08
X-rays originate form electronic transitions from valence bands (VB, bonding electron states) to inner-shell electron levels inform us energy states of bonding electrons. We have developed the SXES spectrometers attaching to TEM, EPMA, and SEM. A spectrometer has an energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing gratings. Applications of TEM-SXES instrument to C have revealed characteristic energy distribution of bonding electrons. Carbon K-emission spectra of C
have revealed characteristic energy distribution of bonding electrons. Carbon K-emission spectra of C  crystals showed that both the peak structures in
crystals showed that both the peak structures in  - and
- and  -bands and the characteristic dip structure between the
-bands and the characteristic dip structure between the  - and
- and  -bonding states in monomer-C
-bonding states in monomer-C disappear in the most polymerized-C
disappear in the most polymerized-C crystals. Bulk specimens were examined by applying SXES to a SEM. Al L-emission spectra of intermetallic compounds of Al
crystals. Bulk specimens were examined by applying SXES to a SEM. Al L-emission spectra of intermetallic compounds of Al Au, AlCo, and aluminum showed different intensity distributions due to different band structures originating from different crystal structures.
Au, AlCo, and aluminum showed different intensity distributions due to different band structures originating from different crystal structures.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.684 - 685, 2014/08
A novel wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) having a X-ray energy range of 50-210 eV has been developed. One feature is that the SXES is parallel detection of the signals so that it can be used like a conventional energy dispersive spectrometer. The other is a high energy resolution, which is about 0.2 eV at Al-L comparable to those revealed by XPS and EELS. These features enable us to obtain meaningful information about chemical bonding in various bulk samples. The SXES can detect Li-K emission spectrum. In the case of an anode electrode of a lithium ion battery (LIB), two types of lithium peaks are observed: one lower energy peak at 50 eV and the other higher energy peak at 54 eV. It was found that the former peak corresponds to the amount of charging, whereas the latter corresponds to the metallic state of lithium.
Terauchi, Masami*; Koshiya, Shogo*; Sato, Futami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(3), p.692 - 697, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:90.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Electron beam induced soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) by using a grating spectrometer has been introduced to a conventional scanning electron microscope (SEM) for characterizing desired specimen areas of bulk materials. The spectrometer was designed as a grazing-incidence flat-field optics by using aberration corrected (varied-line-spacing) gratings and a multi-channel-plate detector combined with a charge-coupled-device camera, which has already applied for a transmission electron microscope. The best resolution was confirmed as 0.13 eV at Mg L-emission (50 eV), which value is comparable to that of recent dedicated electron energy-loss spectroscopy instruments. This SXES-SEM instrument presents density of states of simple metals of bulk Mg and Li. Apparent band structure effects have been observed in Si L-emission of Si-wafer, P L-emission of GaP-wafer, and Al L-emissions of intermetallic compounds of AlCo, AlPd, Al Pt, and Al
Pt, and Al Au.
Au.
Toyoda, Minoru*; Kaira, Kyoichi*; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Ishioka, Noriko; Shino, Masato*; Sakakura, Koichi*; Takayasu, Yukihiro*; Takahashi, Katsumasa*; Tominaga, Hideyuki*; Oriuchi, Noboru*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(10), p.2506 - 2513, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:106 Percentile:95.14(Oncology)Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.77 - 80, 2013/09
We have been developing a soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instrument for electron microscopes (TEM, EPMA/SEM) with an extension of detectable energy range to 50-4000 eV. An introduction of valence electron spectroscopy with microscopy will supply fruitful information on bonding electrons, which cannot be obtained by EELS and EDS. For extend the lowest (or highest) detection energy upto 50 eV (or 4000 eV), a new laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating, JS50XL, (or JS4000) has designed and manufactured. JS50XL and JS4000 having 1200 and 2400 lines/mm as well as coated by Au and a new multilayer-structure of W/B C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terauchi, Masami*; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.13 - 15, 2013/09
A very unique high performance soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) has successfully been developed which can be attached not only to transmission electron microscopes (TEMs), but also to scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) as well as electron probe microanalyzers (EPMAs). To extend the analyzed energy ranges, a newly designed laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating JS50XL, for a lower energy range, 50-170 eV, and a multilayered VLS grating JS4000, for a higher energy range, 2000-4000 eV, have been developed and installed to this spectrometer. Application software has also been developed for a commercial use of SXES in several fields such as battery materials, steel and alloys, and electron devices. The appearance of this spectrometer attached to EPMA and a few results acquired are shown in the following figures. This development has been conducted as one of the projects of Collaborative Development of Innovative Seeds (Practicability verification stage) by Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8848, p.884812_1 - 884812_14, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.03(Optics)We have developed an objective soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph to be able to attach to electron microscopes. This spectrograph has two attractive features. One is that it is designed to cover a wide energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing holographic gratings optimized for 50-200 eV, 155-350 eV, 300-2200 eV, and 2000-4000 eV. They can be accommodated in the single spectrograph. The other is a newly invented W/B C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of
C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of 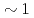 % at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
% at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 19(Suppl.2), p.1258 - 1259, 2013/08
A new wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (WD-SXES) consisting of newly developed diffraction gratings has been developed for soft X-ray emission spectroscopy. The WD-SXES with two types of diffraction gratings nominally covering an energy range between 50 and 210 eV has been installed to electron probe X-ray microanalyzers, JEOL JXA-8100, for commercial use. The energy resolution of this WD-SXES is nominally 0.3 eV, which is one order of magnitude better than that of conventional WDSs with layered dispersion elements. It is to be noted that the corresponding edge of Al B is shifted to higher energy side by about 1 eV. One of the energy range was selected from 72 to 73.5 eV whereas the other was from 73.5 to 75 eV. The contrast in the former map is reversed in the later map as expected even though the energy difference between two maps is only 1.5 eV. The study confirms the high potential for the characterization especially for chemical state mapping.
B is shifted to higher energy side by about 1 eV. One of the energy range was selected from 72 to 73.5 eV whereas the other was from 73.5 to 75 eV. The contrast in the former map is reversed in the later map as expected even though the energy difference between two maps is only 1.5 eV. The study confirms the high potential for the characterization especially for chemical state mapping.
Terauchi, Masami*; Koshiya, Shogo*; Sato, Futami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 19(Suppl.2), p.1278 - 1279, 2013/08
We have been developed and tested soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instruments by attaching to TEM and EPMA. The spectrometer has an energy range form 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing (aberration corrected) gratings. This SXES spectrometer inform us energy states of valence electrons (bonding electrons) form an identified specimen area by electron microscopy, which cannot be obtained by EELS and EDS. This provides not only the probing method for the energy states of valence electrons but also a sensitive tool for elemental and chemical identification. The spectrometer has applied also to a SEM (JEOL JSM-6480LV). As SEM can use a larger probe current and excitation volume of specimen than those of TEM, the detection time is about one order shorter than that of TEM. The energy resolution evaluated at AL-L edge is 0.16 eV. The spectrum of LaB
edge is 0.16 eV. The spectrum of LaB shows apparent intensity corresponds to B-K Fermi edge, showing chemical state of boron.
shows apparent intensity corresponds to B-K Fermi edge, showing chemical state of boron.
 and Sn-L
and Sn-L emissions of indium tin oxide
emissions of indium tin oxideTerauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy, 62(3), p.391 - 395, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.48(Microscopy)A new multilayer-coated varied line-spaced grating, JS4000, was fabricated and tested for extending the upper limit of a grating X-ray spectrometer for electron microscopy. This grating was designed for 2-3.8 keV at a grazing incidence angle of 1.35 deg. It was revealed that this new multilayer structure enables us to take soft-X-ray emission spectra continuously from 1.5 keV to 4 keV at the same optical setting. The full-width at half maximum of Te-L
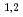 (3.8 keV) emission peak was 27 eV. Sn-L
(3.8 keV) emission peak was 27 eV. Sn-L (3444 eV) and In-L
(3444 eV) and In-L
 (3487 eV) peaks, which cannot be resolved by a widely used energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
(3487 eV) peaks, which cannot be resolved by a widely used energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; Terauchi, Masami*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 425(15), p.152008_1 - 152008_4, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:79.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a flat-field spectrograph equipped with a wide-band multilayer grating and prefocusing mirror for the 2-4 keV range. To realize a spectrograph without any mechanical movement, the multilayer has a newly invented layer structure to uniformly enhance the diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the grating (or prefocusing mirror) at a fixed angle of incidence in the whole energy region. The multilayer structure consisting of W and B C layers has been deposited by ion beam sputtering method on a varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating. Also the same multilayer has been done on a spherical substrate. The average diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the multilayer grating (or spherical mirror) is in excess of 3% at 88.65
C layers has been deposited by ion beam sputtering method on a varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating. Also the same multilayer has been done on a spherical substrate. The average diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the multilayer grating (or spherical mirror) is in excess of 3% at 88.65 (or 4% at 88.00
(or 4% at 88.00 ) in the 2.1-3.8 keV range. The throughput of the spectrograph with multilayer optics can be evaluated to be 2-5000 times higher than that with conventional optics coated by a gold layer.
) in the 2.1-3.8 keV range. The throughput of the spectrograph with multilayer optics can be evaluated to be 2-5000 times higher than that with conventional optics coated by a gold layer.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.33 - 37, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.86(Physics, Applied)Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; et al.
JEOL News, 47(1), p.23 - 28, 2012/07
A new WDS spectrometer for a transmission electron microscope has been constructed. This spectrometer can cover an energy region from 50 eV to 3800 eV by using four aberration-corrected gratings for flat-field optics. By using a newly designed and manufactured grating of JS50XL for 50-200 eV, soft-X-ray emission spectra of simple metals of Mg, Li, Al and Be were measured. Those intensity profiles correspond to partial density of states of valence electrons (bonding electrons) and also showed clear Fermi edges (top of the occupied state). At the Fermi edge of Mg-L emission (49.5 eV), an energy resolution was evaluated to be 0.16 eV. Si-L emission spectra of Si and TiSi show a difference in those intensity distributions, indicating different valence-electron states for those materials. A comparison of B-K emission spectra of CaB
show a difference in those intensity distributions, indicating different valence-electron states for those materials. A comparison of B-K emission spectra of CaB and LaB
and LaB , which were obtained by using another grating of JS200N, is shown.
, which were obtained by using another grating of JS200N, is shown.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Applied Optics, 51(13), p.2351 - 2360, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:52.47(Optics)Laminar and blazed types holographic varied-line-spacing spherical gratings for use in a versatile soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph attached to an electron microscope are designed, fabricated, and evaluated. The absolute diffraction efficiencies of laminar (or blazed) master and replica gratings at 86.00 incidence evaluated by synchrotron radiation show over 5% (or 8%) in the 50-200 eV range with the maxima of 22% (or 26-27%). Also the resolving power evaluated by a laser produced plasma source is in excess of 700 at the energy near the
incidence evaluated by synchrotron radiation show over 5% (or 8%) in the 50-200 eV range with the maxima of 22% (or 26-27%). Also the resolving power evaluated by a laser produced plasma source is in excess of 700 at the energy near the  emission spectrum of lithium (
emission spectrum of lithium ( 55 eV) for all gratings. Moreover, the
55 eV) for all gratings. Moreover, the  emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution is successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution is successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
 emission spectrum of Li
emission spectrum of LiImazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Memoirs of the SR Center Ritsumeikan University, (14), p.131 - 144, 2012/05
We have developed a wavelength-dispersive soft X-ray spectrograph covering an energy region of 50-4000 eV to attach to a conventional electron microscope. The energy range was properly divided into four ranges of 50-200 eV, 155-350 eV, 300-2200 eV, and 2000-4000 eV, and a versatile spectrograph equipped with interchangeable multiple gratings optimized in the respective energy ranges has been developed. In particular, the grating that covers the 50-200 eV range can be used for the measurement of the  emission spectrum (
emission spectrum ( 55 eV) of lithium. The diffraction efficiency evaluated by synchrotron radiation and resolving power measured by laser produced plasma sources are over 5% and in excess of 700, respectively. The
55 eV) of lithium. The diffraction efficiency evaluated by synchrotron radiation and resolving power measured by laser produced plasma sources are over 5% and in excess of 700, respectively. The  emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution has been successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution has been successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.