Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Hironobu; Takahashi, Kazuharu*; Fujishima, Atsushi
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-007, 35 Pages, 2009/07
We are carring out a geological survey to understand important geological structure as geological heterogeneity and migration pathway of material in the bedrock of around the URL area. This report summarizes method and the result of gas measurements, carried out in the Hokushin area and the Suwanosawa area, a period of the FY 2002 to FY 2006. We have investigated gas concentrations of CH and CO
and CO (methane and carbon dioxide) along the Omagari fault, and discussed correlations between the gas concentrations and the Omagari fault. The high amount of CO
(methane and carbon dioxide) along the Omagari fault, and discussed correlations between the gas concentrations and the Omagari fault. The high amount of CO gas concentration were observed around the Omagari Fault.
gas concentration were observed around the Omagari Fault.
Amo, Miki*; Suzuki, Noriyuki*; Shinoda, Toshio*; Ratnayake, N. P.*; Takahashi, Kazuharu
Organic Geochemistry, 38(7), p.1132 - 1145, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:37.67(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Late Miocene to Pliocene marine siliceous rocks in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan are rich in sterenes and steradienes. Diagenetic degradation and transformation of sterenes and steradienes in immature Horonobe marine siliceous rocks of Wakkanai and Koetoi Formations were studied using the borehole core samples from HDB-3 and HDB-4 drilled by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The paleo-temperatures of marine siliceous rocks were estimated to be in the range from 30 to 60  C considering the silica mineral transformation from Opal-A to Opal-CT during diagenesis and the present day geothermal gradient in Horonobe region. Concentrations of steradienes and sterenes decrease quickly in the temperature range from 45 to 60
C considering the silica mineral transformation from Opal-A to Opal-CT during diagenesis and the present day geothermal gradient in Horonobe region. Concentrations of steradienes and sterenes decrease quickly in the temperature range from 45 to 60  C. The significant increase of sterane concentration in the same temperature range shows that a part of steranes is derived from sterenes and steradienes. The sterane/sterene ratios of C
C. The significant increase of sterane concentration in the same temperature range shows that a part of steranes is derived from sterenes and steradienes. The sterane/sterene ratios of C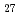 , C
, C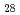 , and C
, and C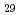 compounds change similarly with increasing maturity. The sterane/sterene ratio of Horonobe marine siliceous rocks can be a useful indicator of paleo-temperature. Either sterenes or steranes, the relative abundance of C
compounds change similarly with increasing maturity. The sterane/sterene ratio of Horonobe marine siliceous rocks can be a useful indicator of paleo-temperature. Either sterenes or steranes, the relative abundance of C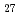 , C
, C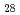 , and C
, and C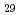 compounds is kept nearly similar all through the Horonobe boreholes, showing that their relative abundance is still applicable to the characterization of organic matter in immature sediments.
compounds is kept nearly similar all through the Horonobe boreholes, showing that their relative abundance is still applicable to the characterization of organic matter in immature sediments.
Ota, Kunio; Abe, Hironobu; Yamaguchi, Takehiro; Kunimaru, Takanori; Ishii, Eiichi; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tomura, Goji; Shibano, Kazunori; Hama, Katsuhiro; Matsui, Hiroya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2007-044, 434 Pages, 2007/03
The Horonobe URL Project started in 2000. Research and development activities are planned over three phases, that will span a total duration of about 20 years: the 1st surface-based investigarion phase (6 years), the 2nd URL construction phase (8 years) and rhe 3rd operation phase (12 years). Geological, geophysical, geo-mechanical, hydrogeological, and hydro-geochemical investigations have been carried out during the surface-based investigation.
Takahashi, Kazuharu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Ishii, Eiichi
JNC TN5400 2005-011, 27 Pages, 2005/08
This article presents the results of the estimated amount of erosion and uplifting based on mineralogy and organic geochemical characters of the Neogene siliceous rock (Wakkanai and Koetoi Formations) in Horonobe. As a result of the transformational change of silica minerals, it was clarified that the erosion amount was about 0.66 [m ky ] or more at the large uplift site, and was about 0.21 [m ky
] or more at the large uplift site, and was about 0.21 [m ky ] or more at the small uplift site at Hokushin region, Horonobe area. In this case of the correlation with the palaeo-geothermal temperature and the sterane/sterene ratio, the ratio is effective measure to estimate the burial depth and erosion amount. We think that the estimation of the amount of erosion and uplifting became possible in high a resolution by the organic geochemical character.
] or more at the small uplift site at Hokushin region, Horonobe area. In this case of the correlation with the palaeo-geothermal temperature and the sterane/sterene ratio, the ratio is effective measure to estimate the burial depth and erosion amount. We think that the estimation of the amount of erosion and uplifting became possible in high a resolution by the organic geochemical character.
Takahashi, Kazuharu
JNC TN5400 2005-010, 72 Pages, 2005/08
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) is carrying out with underground research laboratory (URL) project on the sedimentary rock in Horonobe, Hokkaido. This project is planned over 20 years. Surface-based investigation (Phase 1) has been conducted for the present. The character of the lithofacies, hardness, color, porosity, elemental composition, microfossil age, and organic composition of Masuporo, Wakkanai, Koetoi, Yuchi, and Sarabetsu Formations has been obtained by geological and drilling surveys at the Phase 1 investigation. In this report, I arranged the results of the measurements and of the analysis. As a result, the data of geological and drilling surveys has been similar character on each formation.
Funaki, Hironori; Ishii, Eiichi; Yasue, Kenichi; Takahashi, Kazuharu
JNC TN5400 2004-006, 53 Pages, 2005/03
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) is proceeding with underground research laboratory (URL) project for the sedimentary rock in Horonobe, Hokkaido. This project is an investigation project which is planned over 20 years. Surface-based investigations (Phase 1) have been conducted for the present. The purposes of the Phase 1 are to construct the geological environment model (geological-structural, hydrogeological, and hydrochemical models) and to confirm the applicability of investigation technologies for the geological environment. The geological-structural model comprises the base for the hydrogeological and hydrochemical models. We constructed the geological-structural model by mainly using data obtained from literature studies.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Takahashi, Kazuharu; Ishii, Eiichi; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Sasaki, Manabu; Kunimaru, Takanori; Matsui, Hiroya
JNC TN5400 2003-002, 61 Pages, 2003/08
The working program for deep borehole investigations (HDB-6,7,8 boreholes).
Takahashi, Kazuharu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Amo, Miki*; Suzuki, Noriyuki*
no journal, ,
This article presents the adapted results of the estimation method of erosion and uplifting based on mineralogy and organic geochemical characters of the Neogene siliceous rock (Wakkanai and Koitoi Formations) in Horonobe in succession to last year's article(Takahashi et al., 2005a).
Amo, Miki*; Suzuki, Noriyuki*; Shinoda, Toshio*; Ratnayake, N. P.*; Takahashi, Kazuharu
no journal, ,
Diagenetic degradation and transformation of steroid and acyclic isoprenoid hydrocarbons in immature Horonobe diatomaceous mudstones of Wakkanai and Koetoi Formations were studied using the borehole core samples from HDB-3 and HDB-4. Late Miocene to Pliocene marine diatomaceous mudstones in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan are rich in steroid hydrocarbon such as sterenes, steradienes and sterane and isoprenoid hydrocarbons such as pristenes, phytenes, pristane and phytane. The present study attempts to constrain the diagenetic pathway of these compounds in a thick sedimentary sequence of immature mudstones. Detailed geochemical analyses for Horonobe diatomaceous mudstones revealed the timing of transformation and the compositional change of isoprenoid hydrocarbons during diagenesis. Potential maturity parameters based on ratios of sterenes to steranes, pristene to pristane, and phytene to phytane are proposed in the present study. Possible potentials of these compounds as indicators of depositional environment for immature sediments are also investigated in the present study.
Takahashi, Kazuharu; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Amo, Miki*; Suzuki, Noriyuki*
no journal, ,
This article presents the results of the estimated amount of erosion and uplifting based on mineralogy and organic geochemical characters of the Neogene siliceous rock (Wakkanai and Koetoi Formations) in Horonobe in succession to last year's article (Takahashi et al., 2005a).
Kunimaru, Takanori; Ota, Kunio; Abe, Hironobu; Yamaguchi, Takehiro; Ishii, Eiichi; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tomura, Goji; Shibano, Kazunori; Hama, Katsuhiro; Matsui, Hiroya; et al.
no journal, ,
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. The project consists of two major research areas, "Geoscientific Research" and "R&D on Geological Disposal", and proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigation", "Phase II: Construction" and "Phase III: Operation", over a period of 20 years. The present report summarises the results of the Phase I geoscientific research carried out from March 2001 to March 2005. Integration of work from different disciplines into a "geosynthesis" ensures that the Phase I goals have been successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to be addressed in the Phase II/III investigations.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Hanakawa, Toshiyuki; Ota, Kunio; Abe, Hironobu; Yamaguchi, Takehiro; Kunimaru, Takanori; Ishii, Eiichi; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tomura, Goji; Shibano, Kazunori; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niwa, Masakazu; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Kurosawa, Hideki; Shimada, Koji; Moriya, Toshifumi*; Takahashi, Kazuharu*
no journal, ,
It is suggested that fracture zones formed by fault activities have an effect on hydrologic feature of surrounding rocks. Spatial distribution and features of fracture zones in surveyed areas are informative for site selection and design of geological repositories. Here we show a case study in the Atotsugawa Fault, northern Gifu Prefecture. Field mapping in the study area indicates that the number of fracture zone is sharply reduced, and width of each fracture zones falls within 2 m, with distance of more than 500 m from the surface trace of the Atotsugawa Fault.
Matsui, Hiroya; Takahashi, Kazuharu*; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,
JAEA has been studied the development of grouting technology in deep geological environment as a contract study from MTTI. As a part of this project, the investigation of distributed grout material in the vicinity of a fracture. In this investigation, a core with fracture filled in grout material was sampled and sliced. Then, sliced rock was analyzed by XRF, EPMA and three dimensional shape of filled grout in the fracture was reconstructed. The results suggested that ordinary portland cement can penetrate in a fracture with several ten micro meter aperture and averaged aperture of analyzed fracture is about 4.5 mm. Also, the methodology to understand the grout distribution in fracture scale was proposed.