Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:93.95(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Sakakibara, Hiroshi; Aoki, Nobuhiro; Muto, Masahiro; Otabe, Jun; Takahashi, Kenji*; Fujita, Naoyuki*; Hiyama, Kazuhiko*; Suzuki, Hirokazu*; Kamogawa, Toshiyuki*; Yokosuka, Toru*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-020, 73 Pages, 2021/03
The decommissioning is currently in progress at the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. Fuel assemblies will be taken out of its core for the first step of the great task. Fuel assemblies stand on their own spike plugged into a socket on the core support plate and support with adjacent assemblies through their housing pads each other, resulting in steady core structure. For this reason, some substitutive assemblies are necessary for the purpose of discharging the fuel assemblies of the core. Monju side commissioned, therefore, Plutonium Fuel Development Center to manufacture the substitutive assemblies and the Center accepted it. This report gives descriptions of design, manufacture, and shipment in regard to the substitutive assemblies.
 processing of clustered DNA damage
processing of clustered DNA damageShikazono, Naoya; Akamatsu, Ken; Takahashi, Momoko*; Noguchi, Miho; Urushibara, Ayumi; O'Neill, P.*; Yokoya, Akinari
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 749(1-2), p.9 - 15, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:36.83(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)We examined the biological consequences of bi-stranded clustered damage sites, consisting of a combination of DNA lesions using a bacterial plasmid-based assay. The transformation efficiencies were significantly lower for the bi-stranded clustered GAP/AP lesions than for either a single GAP or a single AP site. When the two lesions were separated by 10-20 bp, the transformation efficiencies were comparable with those of the single lesions. This recovery of transformation efficiency for separated lesions requires DNA polymerase I (Pol I) activity. Analogously, the mutation frequency was enhanced in a bi-stranded cluster containing a GAP and an 8-oxoG, and Pol I was found to play an important role in minimising mutations induced as a result of clustered lesions. These results indicate that the biological consequences of clustered DNA damage strongly depend on Pol I activity.
Kakinouchi, Keisuke*; Nakamura, Tsutomu*; Tamada, Taro; Adachi, Hiroaki*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; Maruyama, Mihoko*; Takahashi, Yoshinori*; Takano, Kazufumi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Inoue, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 43(4), p.937 - 939, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A method for growing large protein crystals is described. In this method, a cut pipette tip is used to hang large-scale droplets (maximum volume 200  l) consisting of protein and precipitating agents. A crystal grows at the vapor-liquid interface; thereafter the grown crystal can be retrieved by droplet-droplet contact both for repeated macroseeding and for mounting crystals in a capillary. Crystallization experiments with peroxiredoxin of
l) consisting of protein and precipitating agents. A crystal grows at the vapor-liquid interface; thereafter the grown crystal can be retrieved by droplet-droplet contact both for repeated macroseeding and for mounting crystals in a capillary. Crystallization experiments with peroxiredoxin of 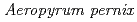 K1(thioredoxin peroxidase, ApTPx) and hen egg white lysozyme demonstrated that this large-scale hanging-drop method could produce a large-volume crystal very effectively. A neutron diffraction experiment confirmed that an ApTPx crystal (6.2 mm
K1(thioredoxin peroxidase, ApTPx) and hen egg white lysozyme demonstrated that this large-scale hanging-drop method could produce a large-volume crystal very effectively. A neutron diffraction experiment confirmed that an ApTPx crystal (6.2 mm ) obtained by this method diffracted to beyond 3.5
) obtained by this method diffracted to beyond 3.5  resolution.
resolution.
 resolution
resolutionShimizu, Noriko*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; Maruyama, Mihoko*; Takahashi, Yoshinori*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Hidaka, Koshi*; Hayashi, Yoshio*; Kimura, Toru*; Kiso, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Crystal Growth & Design, 10(7), p.2990 - 2994, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:72.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report crystal growth of human immunodeficiency virus 1 protease (HIV PR) in a complex with its inhibitor KNI-272 by six different methods. Comparative analysis indicates that top-seeded solution growth (TSSG) and TSSG combined with the floating and stirring technique (TSSG-FAST) are efficient strategies for rapidly obtaining large single crystals and effectively preventing polycrystallization of the seed crystal. Neutron diffraction analysis confirmed that the crystalobtained by TSSG is a high-quality single crystal. Furthermore, crystal shape was observed to be influenced by solution flow, suggesting that the degree of supersaturation significantly affects the crystal growth direction of HIV PR complex. This finding implies that the shape of the HIV PR complex crystal might be controlled by the solution flow rate.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Ago, Tomonori*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; Harada, Kentaro*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Honda, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.205 - 207, 2008/06
Future synchrotron light sources based on the energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) are expected to be capable of producing super-brilliant and/or ultra-short pulses of synchrotron radiation. Our Japanese collaboration team is making efforts for realizing an ERL-based hard X-ray source. We report recent progress in our R&D efforts.
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Murata, Miho*; Kimura, Takaumi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1246 - 1251, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:75.32(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Ichimasa, Michiko*; Awagakubo, Sayuri*; Takahashi, Miho*; Tauchi, Hiroshi*; Hayashi, Takumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Nishi, Masataka; Ichimasa, Yusuke*
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.759 - 762, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)There exists various kinds of HT oxidizing soil bacteria in the world, and we have conducted the investigation of HT oxidation activity of such bacteria. In the fusion facility where deuterium and tritium will be used as its fuel, the system is necessary to eliminate tritium from atmospheric air. General tritium elimination method is oxidation and dehumidification, and high temperature catalyst is used in the present system for oxidation. Application of the HT oxidation bioreactor, which can oxidize in room temperature, to this oxidation process has possibility to get higher tritium elimination efficiency, so we started to study the bioreactor. In the recent study, we can get high oxidation ratio of 85% in the processing conditions of 200 Bq/cm as tritium concentration in air, 100 cm
as tritium concentration in air, 100 cm /min as flow rate and once-through processing using the Caisson Assembly for Tritium Safety Study (CATS) in JAERI. This result encourages this development study.
/min as flow rate and once-through processing using the Caisson Assembly for Tritium Safety Study (CATS) in JAERI. This result encourages this development study.
 -silicate] species by FAB-MS
-silicate] species by FAB-MSTanaka, Miho*; Takahashi, Kazuya*; Urabe, Tatsuya*; Oikawa, Tomohiro*; Hasegawa, Atsushi*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
Alminosilicate ([Me -silicate] species) in hot spring water has been determined by FAB-MS.
-silicate] species) in hot spring water has been determined by FAB-MS.
Tanaka, Miho*; Takahashi, Kazuya*; Oikawa, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
Process of silica scale formation in cooling water for industrial use obtained from river and ground water has been investigated with the viewpoint of solution chemistry.
 model
modelTakahashi, Momoko; Noguchi, Miho; Hirakawa, Hirokazu*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*
no journal, ,
Ionizing radiation has been widely used as a tool for tumor treatment. However, there are still difficulties to treat the solid tumor with only irradiation. Several studies have been shown that the combination therapy using both X-irradiation and antitumor drug is more effective to tumor compared with X-irradiation only. Previously Noguchi et al. showed the Hsp90 inhibitor 17AAG induced tumor cell death effectively with X-irradiation. Hsp90 is the enzymes activated by cellular stress and activates several tumor-related genes. To clarify whether or not the combination therapy of carbon ion beam and 17AAG is effective to solid tumors, we tested the growth of solid tumor with the combination of X-irradiation and 17AAG  and compared the results from
and compared the results from  study.
study.
Okayasu, Ryuichi*; Hirakawa, Hirokazu*; Noguchi, Miho; Yu, D.*; Takahashi, Momoko; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Fujimori, Akira*
no journal, ,
17AAG, an Hsp90 inhibitor was shown to radiosensitize certain human tumor cells exposed to X-rays, while this sensitization was not clearly observed in normal human cells. The mechanism of this was suggested to come from inhibition of DNA double strand break (DSB) repair, particularly impairment of homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway by this drug (Noguchi et al 2006). Key proteins associated with HRR seem to be affected by this inhibitor. To our surprise, tumor radiosensitization with 17AAG was also observed in cells exposed to high LET carbon ions (70 kev/um). Independently we also found that knockdown of BRCA2, a key HRR protein significantly radiosensitized human tumor cells. These results indicate that there seem to be a radio-sensitization mechanism associated with the combination of HRR inhibition and high LET radiation, and this may occur particularly in S-phase cells. Furthermore, we also used mouse xenograft model to examine the combined effect of 17AAG and high LET carbon irradiation. For this purpose, SQ5 human lung tumor cells were implanted on the leg of nude mice and the tumor growth was observed in the combined treatment as compared with radiation or drug treatment alone. Our preliminary results indicate that tumor growth was more inhibited in the 17AAG and carbon irradiation than carbon or 17AAG treatment alone. These data suggest that an effective tumor control might be obtained by combining an HRR inhibitor with high LET carbon irradiation.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Fukuda, Miho*; Kambayashi, Shota*; Misono, Toshiharu; Dohi, Terumi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Suzuki, Takashi; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Sugihara, Naoko*; et al.
no journal, ,
While the amount of cesium-137 ( Cs: half-life 30.1 years) accumulated on the seabed due to the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (0.1-0.2 PBq) is only about 1 to 2% of the total amount of
Cs: half-life 30.1 years) accumulated on the seabed due to the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (0.1-0.2 PBq) is only about 1 to 2% of the total amount of  Cs transported to the ocean, it has been reported that it will remain for a long time in the coastal areas. On the other hand, long-term migration process of the sedimentary radiocesium and the impact on the ecosystem near the seafloor remain unknown. In this presentation, we will give an overview of the distribution and behavior of
Cs transported to the ocean, it has been reported that it will remain for a long time in the coastal areas. On the other hand, long-term migration process of the sedimentary radiocesium and the impact on the ecosystem near the seafloor remain unknown. In this presentation, we will give an overview of the distribution and behavior of  Cs, especially on the seafloor along the coast of Fukushima, and report the latest results on the processes I the seafloor that should be considered on decadal timescale.
Cs, especially on the seafloor along the coast of Fukushima, and report the latest results on the processes I the seafloor that should be considered on decadal timescale.
Sakakibara, Hiroshi; Aoki, Nobuhiro; Muto, Masahiro; Otabe, Jun; Takahashi, Kenji*; Fujita, Naoyuki*; Hiyama, Kazuhiko*; Suzuki, Hirokazu*; Kamogawa, Toshiyuki*; Yokosuka, Toru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aono, Tatsuo*; Nishikawa, Jun*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Takata, Hyoe*; Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Miura, Hikaru*; Kambayashi, Shota*; Fukuda, Miho*; Sakurada, Masanobu*; et al.
no journal, ,
From 2016 to 2020, the Tohoku Marine Ecosystem Research Vessel Shinsei-maru conducted four research cruises on the dynamics and bioavailability of radionuclides around off Fukushima. Seawater, sediments and organisms were collected mainly around off the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPS). The purpose of those cruises is to observe the flux of radionuclides released into the ocean by the FDNPS accident and to understand the bioavailability of radionuclides. In order to understand the contaminated levels of the marine environment, the concentration of radioactive cesium (Cs) in seawater and sediments around off Fukushima was investigated. As a result, the concentration range of dissolved Cs-137 in the surface seawater near the FDNPS from 2016 to 2018 was 10-23 mBq/L, but decreased to 7 mBq/L in 2020. In terms of points, the concentrations of dissolved Cs-137 tended to decrease with time. On the other hand, in sediments, the Cs-137 concentrations were higher in the surface layer (0-2 cm) than the deep layer from 2016 to 2017 and tended to decrease with depth, but after 2018, subsurface vertical maximum of Cs-137 concentrations was observed at some stations. Although these concentrations tended to increase in the subsurface layer, the concentrations in the sediment also tended to decrease with time. In this presentation, we report on the concentration variation of Cs-137 and their characteristics in seawater and sediments around off Fukushima.
Aono, Tatsuo*; Nishikawa, Jun*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Takata, Hyoe*; Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Miura, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Miho*; Kambayashi, Shota*; Sakurada, Masanobu*; et al.
no journal, ,
From 2016 to 2020, four research voyages were conducted to investigate the dynamics of radioactive materials in the waters around Fukushima. Seawater and sediment samples were collected in the waters off the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPS). The concentration of radioactive cesium (Cs) in seawater and sediment off the coast of Fukushima was surveyed to understand the status of the marine environment. As a result, no significant changes were observed in both seawater and sediment from 2016 to 2020.
Aono, Tatsuo*; Fukuda, Miho*; Sakurada, Masanobu*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Yamazaki, Shinnosuke*; Kambayashi, Shota*; Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Miura, Hikaru*; Nishikawa, Jun*; et al.
no journal, ,
From 2016 to 2020, R/V Shinsei-maru of JAMSTEC conducted four research cruises on the dynamics and bioavailability of radionuclides around off Fukushima. Seawater, sediments and organisms were collected mainly around off the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPS). The purpose of those cruises is to observe the flux of radionuclides released into the ocean by the FDNPS accident and to understand the bioavailability of radionuclides. In order to understand the contaminated levels of the marine environment, the concentration of radiocaesium (Cs) in seawater and sediments around off Fukushima was investigated.