Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Yusuke; Shimaike, Masamitsu; Matsumoto, Takashi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Morimoto, Yasuyuki
Nuclear Technology, 209(5), p.777 - 786, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)At the Ningyo-Toge Center, technical development related to uranium refining conversion and enrichment has been completed, and decommissioning of these facilities has begun. The error between the quantity of dismantled materials estimated from the facility design drawings and the actual quantity of dismantled materials was minimal when averaging over the entire Uranium Refining and Conversion Plant and Uranium Enrichment Engineering Facility, which results indicated that the preliminary estimate of the quantity of dismantled materials for decommissioning was reasonable. Most of the dismantled materials, which have no contamination history and are properly managed were able to be carried out to recyclers as non-radioactive waste (NR). In addition, the possibility of evaluating the uranium concentration of clearance level in dismantled objects was confirmed through gamma-ray measurement tests using mock-up waste.
Yamane, Ikumi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nishiwaki, Hiroki; Matsumoto, Takashi; Ogawa, Jumpei; Nomura, Mitsuo; Arima, Tatsumi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-038, 18 Pages, 2022/02
We have dismantled uranium enrichment facilities in Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center since their operation finished in 2001, and the total amount of metallic wastes is estimated to be about 130 thousand tons. Eighty percent of them can be disposed as nonradioactive waste (NR), but there are some steel parts possibly uranium-contaminated. We need removing painted surface of such steels and radiologically surveying to dispose them as NRs. Though painted surfaces have been conventionally removed through hand working with grinders, this manual work requires installation of green house, protective clothing, and full-face mask, in order to prevent dispersion and inhalation of airborne dusts. We desire further developments of surface cleaning techniques to reduce time, cost, workload, and secondary waste generation caused by excessive grinding. Therefore, in this study, we focused on the laser cleaning technology used for the separation and removal of paint films at construction sites. In order to improve the coating separation and removal technology for NR objects, we evaluated the coating separation and removal performance of NR steel surface by laser cleaning system, observed the coating scattering behavior by high-speed camera and investigated the coating recovery method, evaluated the laser separation and removal performance of steel surface powder, and thermodynamically evaluated the uranium compounds on steel surface. We additionally evaluated the feasibility of laser cleaning techniques in our works basing on these results, and discussed future work plans for further developments of laser cleaning techniques.
Takahashi, Nobuo; Kubota, Shintaro; Takiya, Hiroaki; Sakaba, Ryosuke*; Sato, Koichi; Shichi, Ryo
JAEA-Testing 2021-002, 106 Pages, 2022/01
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has various nuclear facilities such as reactor facilities and reprocessing facilities. Some aged facilities will be decommissioned after their original functions ended, and it is necessary to evaluate their decommissioning cost to formulate the initial decommissioning plans and the final decommissioning plans. We have developed an evaluation method called DECOST that can efficiently calculate the decommissioning cost in a short time based on factors such as features and similarity of the facilities and dismantling methods. The decommissioning of nuclear facilities has been implemented and new achievements and findings have been reported since the development of DECOST. These findings were reflected in DECOST. In consideration of the needs of DECOST users, DECOST has been improved so that the cost of dismantling the facility can be divided into the cost of releasing the controlled area and the cost of dismantling the facility building after the release of the controlled area. This report shows the improvement of DECOST, the concept of resetting the evaluation coefficient used in the cost evaluation formula, and the validity of the evaluation coefficient after resetting. In addition, the evaluation procedure of the improved DECOST is described, since the evaluation items and evaluation contents were partially changed due to the improvement.
Takahashi, Nobuo; Suekane, Yurika; Sakaba, Ryosuke*; Kurosawa, Takuya*; Sato, Koichi; Meguro, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Testing 2018-002, 45 Pages, 2018/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has many nuclear facilities such as research reactors, nuclear fuel facilities and research facilities. Although these facilities will be decommissioned due to the termination of the purpose of use of the facility and aging, it is necessary to evaluate the decommissioning cost of these facilities prior to the decommissioning. We have developed an evaluation method called DECOST code that can efficiently calculate the decommissioning cost in a short time based on factors such as features, similarity, and dismantling methods. This report is as a manual of the DECOST code prepared for improving convenience. Here, the evaluation formulae used for DECOST are presented and the method of using them is explained for each kind of nuclear facilities to be evaluated. In addition, the preparation method of facility information and dismantled waste amount that are need for evaluation is also shown.
Matsumoto, Takashi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Hayashibara, Kenichi; Ishimori, Yuu; Mita, Yutaka; Kakiya, Hideyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2016-020, 80 Pages, 2016/11
The Enrichment Engineering Facility of the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center was constructed in order to establish the technological basis of plant engineering for uranium enrichment in Japan. Uranium enrichment tests, using natural and reprocessed uranium, were carried out from 1979 to 1989 with two types of centrifuges in the facility. According to the decommissioning plan of the facility, UF handling equipment and supplemental equipment in these plants are intended to be dismantled by 2019 in order to make vacant spaces for future projects use, for example, inventory investigation, precipitation treatment, etc. This report shows the current state of the decommissioning project in the second-half of the fiscal year of 2014.
handling equipment and supplemental equipment in these plants are intended to be dismantled by 2019 in order to make vacant spaces for future projects use, for example, inventory investigation, precipitation treatment, etc. This report shows the current state of the decommissioning project in the second-half of the fiscal year of 2014.
Terunuma, Akihiro; Mimura, Ryuji; Nagashima, Hisao; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hirokawa, Katsunori*; Uta, Masato; Ishimori, Yuu; Kuwabara, Jun; Okamoto, Hisato; Kimura, Yasuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-008, 98 Pages, 2016/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency formulated the plan to achieve the medium-term target in the period of April 2010 to March 2015(hereinafter referred to as "the second medium-term plan"). JAEA determined the plan for the business operations of each year (hereinafter referred to as "the year plan"). This report is that the Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Waste Management has summarized the results of the decommissioning technology development and decommissioning of nuclear facilities which were carried out in the second medium-term plan.
Matsumoto, Takashi; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Takahashi, Nobuo; Takata, Masaharu; Yoshida, Hideaki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Ishimori, Yuu
JAEA-Technology 2015-036, 60 Pages, 2016/01
The Enrichment Engineering Facilities of the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center was constructed in order to establish the technical basis of the uranium enrichment plant in Japan. Uranium enrichment tests, using natural and reprocessed uranium, were carried out from 1979 to 1990 at two types of plants in the facilities. UF handling equipment and Supplemental equipment in these plants are intended to be dismantled by 2019 in order to make places for future projects, for example, inventory investigation, precipitation treatment, etc. This report shows the basic plan of this decommissioning project and presents the current state of dismantling in the first-half of the fiscal year of 2014, with indicating its schedule, procedure, situation, results, and so on. The dismantled materials generated amounted to 37 mesh containers and 199 drums, and the secondary waste generated amounted to 271.4 kg.
handling equipment and Supplemental equipment in these plants are intended to be dismantled by 2019 in order to make places for future projects, for example, inventory investigation, precipitation treatment, etc. This report shows the basic plan of this decommissioning project and presents the current state of dismantling in the first-half of the fiscal year of 2014, with indicating its schedule, procedure, situation, results, and so on. The dismantled materials generated amounted to 37 mesh containers and 199 drums, and the secondary waste generated amounted to 271.4 kg.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Kawase, Masato; Ouchi, Nobuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.012020_1 - 012020_6, 2015/09
Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Suwa, Tomone; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Ozeki, Hidemasa; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Isono, Takaaki; Matsui, Kunihiro; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.4200904_1 - 4200904_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:20.23(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is responsible for procuring all amounts of Central Solenoid (CS) Conductors for ITER, including CS jacket sections. The conductor is cable-in-conduit conductor (CICC) with a central spiral. A total of 576 Nb Sn strands and 288 copper strands are cabled around the central spiral. The maximum operating current is 40 kA at magnetic field of 13 T. CS jacket section is circular in square type tube made of JK2LB, which is high manganese stainless steel with boron added. Unit length of jacket sections is 7 m and 6,300 sections will be manufactured and inspected. Outer/inner dimension and weight are 51.3/35.3 mm and around 90 kg, respectively. Eddy Current Test (ECT) and Phased Array Ultrasonic Test (PAUT) were developed for non-destructive examination. The defects on inner and outer surfaces can be detected by ECT. The defects inside jacket section can be detected by PAUT. These technology and the inspected results are reported in this paper.
Sn strands and 288 copper strands are cabled around the central spiral. The maximum operating current is 40 kA at magnetic field of 13 T. CS jacket section is circular in square type tube made of JK2LB, which is high manganese stainless steel with boron added. Unit length of jacket sections is 7 m and 6,300 sections will be manufactured and inspected. Outer/inner dimension and weight are 51.3/35.3 mm and around 90 kg, respectively. Eddy Current Test (ECT) and Phased Array Ultrasonic Test (PAUT) were developed for non-destructive examination. The defects on inner and outer surfaces can be detected by ECT. The defects inside jacket section can be detected by PAUT. These technology and the inspected results are reported in this paper.
 Sn cable assembled with conduit for ITER central solenoid
Sn cable assembled with conduit for ITER central solenoidNabara, Yoshihiro; Suwa, Tomone; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Kajitani, Hideki; Ozeki, Hidemasa; Sakurai, Takeru; Iguchi, Masahide; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.4200305_1 - 4200305_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.682 - 683, 2014/08
X-rays originate form electronic transitions from valence bands (VB, bonding electron states) to inner-shell electron levels inform us energy states of bonding electrons. We have developed the SXES spectrometers attaching to TEM, EPMA, and SEM. A spectrometer has an energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing gratings. Applications of TEM-SXES instrument to C have revealed characteristic energy distribution of bonding electrons. Carbon K-emission spectra of C
have revealed characteristic energy distribution of bonding electrons. Carbon K-emission spectra of C  crystals showed that both the peak structures in
crystals showed that both the peak structures in  - and
- and  -bands and the characteristic dip structure between the
-bands and the characteristic dip structure between the  - and
- and  -bonding states in monomer-C
-bonding states in monomer-C disappear in the most polymerized-C
disappear in the most polymerized-C crystals. Bulk specimens were examined by applying SXES to a SEM. Al L-emission spectra of intermetallic compounds of Al
crystals. Bulk specimens were examined by applying SXES to a SEM. Al L-emission spectra of intermetallic compounds of Al Au, AlCo, and aluminum showed different intensity distributions due to different band structures originating from different crystal structures.
Au, AlCo, and aluminum showed different intensity distributions due to different band structures originating from different crystal structures.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.684 - 685, 2014/08
A novel wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) having a X-ray energy range of 50-210 eV has been developed. One feature is that the SXES is parallel detection of the signals so that it can be used like a conventional energy dispersive spectrometer. The other is a high energy resolution, which is about 0.2 eV at Al-L comparable to those revealed by XPS and EELS. These features enable us to obtain meaningful information about chemical bonding in various bulk samples. The SXES can detect Li-K emission spectrum. In the case of an anode electrode of a lithium ion battery (LIB), two types of lithium peaks are observed: one lower energy peak at 50 eV and the other higher energy peak at 54 eV. It was found that the former peak corresponds to the amount of charging, whereas the latter corresponds to the metallic state of lithium.
Izumo, Sari; Usui, Hideo; Kubota, Shintaro; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Kawagoshi, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Technology 2014-021, 79 Pages, 2014/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed PROject management data evaluation code for DIsmantling Activities (PRODIA) to make an efficient decommissioning for nuclear facilities. PRODIA is a source code which provides estimated value such as manpower needs, costs, etc., for dismantling by evaluation formulas according to the type of nuclear facility. Evaluation formulas of manpower needs for dismantling of equipments about reprocessed uranium conversion in Uranium Refining and Conversion Plant are developed in this report. In the result, 7 formulas for prepare process, 24 formulas for dismantling process and 8 formulas for clean-up process are derived. It is confirmed that an unified evaluation formula can be used instead of 8 formulas about dismantling process of steel equipment for uranium conversion process, and 3 types of simplified formula can be used for preparation process and clean-up process respectively.
Terauchi, Masami*; Koshiya, Shogo*; Sato, Futami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(3), p.692 - 697, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:90.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Electron beam induced soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) by using a grating spectrometer has been introduced to a conventional scanning electron microscope (SEM) for characterizing desired specimen areas of bulk materials. The spectrometer was designed as a grazing-incidence flat-field optics by using aberration corrected (varied-line-spacing) gratings and a multi-channel-plate detector combined with a charge-coupled-device camera, which has already applied for a transmission electron microscope. The best resolution was confirmed as 0.13 eV at Mg L-emission (50 eV), which value is comparable to that of recent dedicated electron energy-loss spectroscopy instruments. This SXES-SEM instrument presents density of states of simple metals of bulk Mg and Li. Apparent band structure effects have been observed in Si L-emission of Si-wafer, P L-emission of GaP-wafer, and Al L-emissions of intermetallic compounds of AlCo, AlPd, Al Pt, and Al
Pt, and Al Au.
Au.
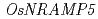 -knockdown rice is a promising candidate for Cd phytoremediation in paddy fields
-knockdown rice is a promising candidate for Cd phytoremediation in paddy fieldsTakahashi, Ryuichi*; Ishimaru, Yasuhiro*; Shimo, H.*; Bashir, K.*; Senoura, Takeshi*; Sugimoto, Kazuhiko*; Ono, Kazuko*; Suzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Ishii, Satomi; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 9(6), p.e98816_1 - e98816_7, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:86.7(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kawase, Masato*; Takahashi, Hiroki; Kato, Yuko; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ouchi, Nobuo
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.731 - 734, 2014/06
The data acquisition in J-PARC LINAC/RCS are two methods of data archiving of polling data via EPICS Channel Access and synchronized waveform data. The synchronized waveform data are collected by several Wave Endless Recorders (WER). The WER counts the trigger number and holds waveform data in a ring buffer memory. We developed a Trigger Counter in order to manage the trigger number of each WER and synchronize the trigger number of each WER via LAN. At present, in order to install the waveform data synchronization system, we carried out verification using the timing test bench. This report presents about the waveform data synchronization system and future plan of the data acquisition system.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.77 - 80, 2013/09
We have been developing a soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instrument for electron microscopes (TEM, EPMA/SEM) with an extension of detectable energy range to 50-4000 eV. An introduction of valence electron spectroscopy with microscopy will supply fruitful information on bonding electrons, which cannot be obtained by EELS and EDS. For extend the lowest (or highest) detection energy upto 50 eV (or 4000 eV), a new laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating, JS50XL, (or JS4000) has designed and manufactured. JS50XL and JS4000 having 1200 and 2400 lines/mm as well as coated by Au and a new multilayer-structure of W/B C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terauchi, Masami*; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.13 - 15, 2013/09
A very unique high performance soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) has successfully been developed which can be attached not only to transmission electron microscopes (TEMs), but also to scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) as well as electron probe microanalyzers (EPMAs). To extend the analyzed energy ranges, a newly designed laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating JS50XL, for a lower energy range, 50-170 eV, and a multilayered VLS grating JS4000, for a higher energy range, 2000-4000 eV, have been developed and installed to this spectrometer. Application software has also been developed for a commercial use of SXES in several fields such as battery materials, steel and alloys, and electron devices. The appearance of this spectrometer attached to EPMA and a few results acquired are shown in the following figures. This development has been conducted as one of the projects of Collaborative Development of Innovative Seeds (Practicability verification stage) by Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Izumo, Sari; Usui, Hideo; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Takahashi, Nobuo; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2013) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Engineering, Environmental)Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8848, p.884812_1 - 884812_14, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.03(Optics)We have developed an objective soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph to be able to attach to electron microscopes. This spectrograph has two attractive features. One is that it is designed to cover a wide energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing holographic gratings optimized for 50-200 eV, 155-350 eV, 300-2200 eV, and 2000-4000 eV. They can be accommodated in the single spectrograph. The other is a newly invented W/B C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of
C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of 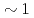 % at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
% at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.