Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:88.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takahashi, Nobuo; Kubota, Shintaro; Takiya, Hiroaki; Sakaba, Ryosuke*; Sato, Koichi; Shichi, Ryo
JAEA-Testing 2021-002, 106 Pages, 2022/01
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has various nuclear facilities such as reactor facilities and reprocessing facilities. Some aged facilities will be decommissioned after their original functions ended, and it is necessary to evaluate their decommissioning cost to formulate the initial decommissioning plans and the final decommissioning plans. We have developed an evaluation method called DECOST that can efficiently calculate the decommissioning cost in a short time based on factors such as features and similarity of the facilities and dismantling methods. The decommissioning of nuclear facilities has been implemented and new achievements and findings have been reported since the development of DECOST. These findings were reflected in DECOST. In consideration of the needs of DECOST users, DECOST has been improved so that the cost of dismantling the facility can be divided into the cost of releasing the controlled area and the cost of dismantling the facility building after the release of the controlled area. This report shows the improvement of DECOST, the concept of resetting the evaluation coefficient used in the cost evaluation formula, and the validity of the evaluation coefficient after resetting. In addition, the evaluation procedure of the improved DECOST is described, since the evaluation items and evaluation contents were partially changed due to the improvement.
Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Matsubara, Natsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-069, 163 Pages, 2021/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2019 to March 2020. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Takahashi, Nobuo; Suekane, Yurika; Sakaba, Ryosuke*; Kurosawa, Takuya*; Sato, Koichi; Meguro, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Testing 2018-002, 45 Pages, 2018/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has many nuclear facilities such as research reactors, nuclear fuel facilities and research facilities. Although these facilities will be decommissioned due to the termination of the purpose of use of the facility and aging, it is necessary to evaluate the decommissioning cost of these facilities prior to the decommissioning. We have developed an evaluation method called DECOST code that can efficiently calculate the decommissioning cost in a short time based on factors such as features, similarity, and dismantling methods. This report is as a manual of the DECOST code prepared for improving convenience. Here, the evaluation formulae used for DECOST are presented and the method of using them is explained for each kind of nuclear facilities to be evaluated. In addition, the preparation method of facility information and dismantled waste amount that are need for evaluation is also shown.
 superstructure of monolayer MoS
superstructure of monolayer MoS and MoSe
and MoSe on Au(111)
on Au(111)Yasuda, Satoshi; Takahashi, Ryosuke*; Osaka, Ryo*; Kumagai, Ryota*; Miyata, Yasumitsu*; Okada, Susumu*; Hayamizu, Yuhei*; Murakoshi, Kei*
Small, 13(31), p.1700748_1 - 1700748_8, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:70.23(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)MoS and MoSe
and MoSe monolayers are grown on Au surface by chemical vapor deposition and it is demonstrated that the contact with a crystalline Au(111) surface gives rise to only out-of-plane strain in both MoS
monolayers are grown on Au surface by chemical vapor deposition and it is demonstrated that the contact with a crystalline Au(111) surface gives rise to only out-of-plane strain in both MoS and MoSe
and MoSe layers, whereas no strain generation is observed on polycrystalline Au or SiO
layers, whereas no strain generation is observed on polycrystalline Au or SiO /Si surfaces. Scanning tunneling microscopy analysis provides information regarding consequent specific adsorption sites between lower S (Se) atoms in the S-Mo-S (Se-Mo-Se) structure and Au atoms via unique moir
/Si surfaces. Scanning tunneling microscopy analysis provides information regarding consequent specific adsorption sites between lower S (Se) atoms in the S-Mo-S (Se-Mo-Se) structure and Au atoms via unique moir superstructure formation for MoS
superstructure formation for MoS and MoSe
and MoSe layers on Au(111). This observation indicates that the specific adsorption sites give rise to out-of-plane strain in the TMDC layers. Furthermore, it also leads to effective modulation of the electronic structure of the MoS
layers on Au(111). This observation indicates that the specific adsorption sites give rise to out-of-plane strain in the TMDC layers. Furthermore, it also leads to effective modulation of the electronic structure of the MoS or MoSe
or MoSe layer.
layer.
Oshima, Katsumi; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Terakado, Masayuki; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi
JAEA-Technology 2015-061, 65 Pages, 2016/03
In JAEA, an ITER relevant control system for ITER gyrotron was developed according to Plant Control Design Handbook. This control system was developed based on ITER CODAC Core System and implemented state machine control of gyrotron operation system, sequential timing control of gyrotron oscillation startup, and data acquisition. The operation of ITER 170 GHz gyrotron was demonstrated with ITER relevant power supply configuration. This system is utilized for gyrotron operation test for ITER procurement. This report describes the architecture of gyrotron operation system, its basic and detailed design, and recent operation results.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oda, Yasuhisa; Wada, Kenji; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
Proceedings of 40th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2015/08
A gyrotron for electron cyclotron heating and current drive (ECH/CD) has been developed for JT-60SA (Super-Advanced). In high-power, long-pulse operations, oscillations of 1 MW/100 s have been demonstrated at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz, for the first time. These results fully satisfied the requirements for JT-60SA. Moreover, it was experimentally shown that the higher power operation at each frequency is expected to be acceptable for this gyrotron from the viewpoint of heat load at the cavity resonator, collector, and stray radiation absorbers. An oscillation at 82 GHz, which is an additional frequency, has been demonstrated up to 2 s at the output power of 0.4 MW, so far. High power experiments toward higher power of 1.5 MW (110/138 GHz) and 1 MW (82 GHz) are ongoing.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Yokokura, Kenji; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063008_1 - 063008_8, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:77.57(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A gyrotron enabling high-power, long-pulse oscillations at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz has been developed for electron cyclotron heating (ECH) and current drive (CD) in JT-60SA. Oscillations of 1 MW for 100 s have been demonstrated at both frequencies, for the first time as a gyrotron operating at two frequencies. The optimization of the anode voltage, or the electron pitch factor, using a triode gun was a key to obtain high power and high efficiency at two frequencies. It was also confirmed that the internal losses in the gyrotron were sufficiently low for expected long pulse operation at the higher power level of  1.5 MW. Another important result is that an oscillation at 82 GHz, which enables to use fundamental harmonic waves in JT-60SA while the other two frequencies are used as second harmonics waves, was demonstrated up to 0.4 MW for 2 s. These results of the gyrotron development significantly contribute to enhancing operation regime of the ECH/CD system in JT-60SA.
1.5 MW. Another important result is that an oscillation at 82 GHz, which enables to use fundamental harmonic waves in JT-60SA while the other two frequencies are used as second harmonics waves, was demonstrated up to 0.4 MW for 2 s. These results of the gyrotron development significantly contribute to enhancing operation regime of the ECH/CD system in JT-60SA.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Oshima, Katsumi; Nakamoto, Takashi*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(7), p.365 - 373, 2014/07
no abstracts in English
Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Long pulse operation of the dual frequency gyrotron was started for JT-60SA ECH system. Pulse length of 2 s at 0.4 MW output, and 1 s at 0.7 MW were obtained at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz, so far. Typical oscillation efficiency is about 30%. Diffraction loss was acceptable for long pulse 1 MW output. The first high power test of the "power and beam profile monitor" featuring a fast movable Si N
N disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Hiranai, Shinichi; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
no journal, ,
An original design of the toroidal injection angle range of electron cyclotron waves in JT-60SA was -15 degree to +15 degree for effective use of 110 GHz wave. However, the modification of the toroidal angle range has been discussed since the frequency of 138 GHz is considered to be a second frequency by the use of a dual frequency gyrotron. We report newly calculated available steering range of the launcher on both poloidal and toroidal angles with and without tilting angle of the second mirror, which is considered to obtain large toroidal injection angle. Moreover calculated beam divergences for various curvature radiuses of the first and second mirrors are shown. The decision of the target injection angle range for JT-60SA initial plasma will be made by the JT-60SA physics team by taking into account the above calculation results.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Oshima, Katsumi; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Purohito, D.*; Henderson, M.*
no journal, ,
Oda, Yasuhisa; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Oshima, Katsumi; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Purohito, D.*; Henderson, M.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Takahashi, Koji; et al.
no journal, ,
Developments of a dual frequency (110 GHz and 138 GHz) electron cyclotron heating and current drive system for JT-60SA are required. In a long pulse operation of a dual-frequency gyrotron, oscillations of 1 MW for 10 s at both frequencies were obtained, so far. Out gas in the gyrotron has been decreased shot by shot, and conditioning of the gyrotron is in progress. Oscillation efficiencies of higher than 30% were obtained for both frequencies. Measured internal diffraction loss was almost the same level of the previously developed 110 GHz long pulse gyrotron. From the above results, it is expected that further pulse length expansion is possible by continuing conditioning operations. Moreover, optical characteristics of an antenna, which is used to inject high-power millimeter waves into tokamak, was confirmed for dual frequency operation. It was found that the beam width for the 138 GHz wave is narrower than that for the 110 GHz wave.
Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Aoki, Takashi; Oshima, Katsumi; Tsubota, Naoaki; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Moriyama, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Sawahata, Masayuki; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Wada, Kenji; Sato, Yoshikatsu; Hinata, Jun; Yokokura, Kenji; Hoshino, Katsumichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Long pulse operation of the dual frequency gyrotron was started for JT-60SA ECH system. Pulse lengths of 10 s with output power of 1MW were obtained at both 110 GHz and 138 GHz, so far. Typical oscillation efficiency is approximately 30%. Diffraction loss was acceptable for long pulse 1 MW output. The first high power test of the "power / beam profile monitor" featuring a fast movable Si 3N
3N disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
disk in the waveguide slit was successfully demonstrated.
Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
TE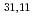 mode gyrotron has advantages for multi-frequency oscillation. Triple frequency of 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz pass through a diamond disk window without a reflection lose and are radiated toward the same direction without moving a final mirror in the gyroton. In short pulse experiments (
mode gyrotron has advantages for multi-frequency oscillation. Triple frequency of 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz pass through a diamond disk window without a reflection lose and are radiated toward the same direction without moving a final mirror in the gyroton. In short pulse experiments ( 5s), the output power, the oscillation efficiency and the electric efficiency for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation achieved 1.2 MW/27%/43%, 810 kW/25%/40% and 720 kW/25%/38%. In long pulse operation, pulse length reached 100s with 870 kW output power for 170 GHz oscillation. HE11 mode purity measured at the MOU exit was 94.5%, 93% and 92% for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation. By building precisely a transmission line, the purity of 91%, 88% and 95%, respectively is obtained at the exit of the long transmission line (35 m).
5s), the output power, the oscillation efficiency and the electric efficiency for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation achieved 1.2 MW/27%/43%, 810 kW/25%/40% and 720 kW/25%/38%. In long pulse operation, pulse length reached 100s with 870 kW output power for 170 GHz oscillation. HE11 mode purity measured at the MOU exit was 94.5%, 93% and 92% for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation. By building precisely a transmission line, the purity of 91%, 88% and 95%, respectively is obtained at the exit of the long transmission line (35 m).
Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
TE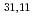 mode gyrotron has advantages for multi-frequency oscillation. Oscillations of 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz at TE
mode gyrotron has advantages for multi-frequency oscillation. Oscillations of 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz at TE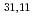 , TE
, TE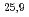 and TE
and TE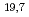 modes, respectively are excited by varying the magnetic field strength. In high power experiments, the output power, the oscillation efficiency and the electric efficiency for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation achieved 1.2 MW / 27% / 43%, 810 kW / 25% / 40% and 720 kW / 25% / 38%. In long pulse operation, 900 kW / 100 s, 800 kW / 224 s and 650 kW / 433 s for 170 GHz oscillation are obtained. HE
modes, respectively are excited by varying the magnetic field strength. In high power experiments, the output power, the oscillation efficiency and the electric efficiency for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation achieved 1.2 MW / 27% / 43%, 810 kW / 25% / 40% and 720 kW / 25% / 38%. In long pulse operation, 900 kW / 100 s, 800 kW / 224 s and 650 kW / 433 s for 170 GHz oscillation are obtained. HE mode purity of 91%, 88% and 95% for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation is obtained at the exit of a 40 m transmission line.
mode purity of 91%, 88% and 95% for 170 GHz, 137 GHz and 104 GHz oscillation is obtained at the exit of a 40 m transmission line.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Oshima, Katsumi; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English