Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 crystals
crystalsTakatori, Sayuri*; Pimon, M.*; Pollitt, S.*; Bartokos, M.*; Beeks, K.*; Gr neis, A.*; Hiraki, Takahiro*; Homma, Tetsuo*; Hosseini, N.*; Leitner, A.*; et al.
neis, A.*; Hiraki, Takahiro*; Homma, Tetsuo*; Hosseini, N.*; Leitner, A.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 27(4), p.043024_1 - 043024_10, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recent reports on laser excitation of the low-energy thorium-229 ( Th) nuclear isomeric state in calcium fluoride single crystals render this system a promising candidate for a solid-state nuclear clock. However, experimental characterization of the microscopic ion arrangement around the doped
Th) nuclear isomeric state in calcium fluoride single crystals render this system a promising candidate for a solid-state nuclear clock. However, experimental characterization of the microscopic ion arrangement around the doped  Th and its electronic charge state, crucial for the precise control of the clock transition and assessing the solid-state clock's performance, remains an unresolved task. This study uses X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy of
Th and its electronic charge state, crucial for the precise control of the clock transition and assessing the solid-state clock's performance, remains an unresolved task. This study uses X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy of  Th:CaF
Th:CaF to investigate the charge state and coordination environment of doped
to investigate the charge state and coordination environment of doped  Th. The results indicate that
Th. The results indicate that  Th is doped with a 4+ valence at the substitutional site of the Ca
Th is doped with a 4+ valence at the substitutional site of the Ca ion, with charge compensated provided by two F
ion, with charge compensated provided by two F ions located at interstitial sites adjacent to
ions located at interstitial sites adjacent to  Th.
Th.
Yomogida, Takumi; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chikyu Kagaku, 59(1), p.1 - 10, 2025/03
X-ray absorption fine structure XAFS spectroscopy techniques, which are applicable to almost all elements, provide information on elemental valence and local structure with high elemental selectivity and high sensitivity. It has become an indispensable method in space geochemistry and environmental chemistry. This review presents examples of the application of fluorescence XAFS methods to elements that are difficult to detect by conventional methods, and examples where new chemical species information has been obtained by increasing the energy resolution of the X-ray fluorescence (XRF) detection system to obtain XAFS.
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(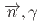 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Science of the Total Environment, 964, p.178585_1 - 178585_13, 2025/02
There are many unresolved issues in the adsorption reactions of clay minerals. One of the reasons is the existence of multiple adsorption sites. It is known that the contribution of each adsorption site depends on the concentration of adsorbed ions, and there is a challenge in comprehensively correlate the results of atomic-level simulations that employ limited number of atoms and inevitably deal high-concentration samples with actual environmental samples where concentrations are orders of magnitude lower. In this study, we combined experiments using synchrotron radiation and first-principles calculations to comprehensively elucidate the systematic changes in the local structure of adsorption sites and adsorbed ions based on the adsorption concentration at the atomic level, and demonstrated that the interaction between adsorbed ions and clay minerals involves ionic bonding.
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Yomogida, Takumi
Treatise on Geochemistry, 3rd edition, Vol.6, p.105 - 150, 2025/00
With the recent development of measurement techniques, new approaches to the environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been applied for various research targets. In this review article, several topics within the last 10-15 years in the field of environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been discussed. In particular, this article mainly focused on two topics, (i) studies on the migration of radionuclides emitted by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident in 2011 and (ii) the development of X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy and its application to the geochemical processes of radionuclides.
Nagasawa, Makoto*; Shimizu, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Tokunaga, Kohei; Mukai, Hiroki*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemical Geology, 670, p.122431_1 - 122431_25, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Yamaguchi, Akiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Okumura, Masahiko
Isotope News, (796), p.21 - 23, 2024/12
Clay minerals are abundant in soils and control the environmental behavior of various elements because they adsorb many cations. Since the strength of adsorption of clay minerals depends on the adsorption structure at the molecular level, a systematic understanding of what determines the adsorption structure at the molecular level is important. In this study, we systematically elucidated the adsorption structures of many cations, including radium, using extensive X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements and first-principles simulations. The results show that the size and hydration enthalpy of adsorbed ions are important in determining the adsorption structure.
Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10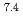 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 
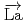 +
+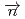
Okudaira, Takuya*; Nakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044606_1 - 044606_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear) -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 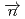 +
+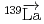 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.90(Physics, Nuclear)Yomogida, Takumi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Yamada, Shinya*; Tatsuno, Hideyuki*; Noda, Hirofumi*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Takatori, Sayuri*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
Analyst, 149(10), p.2932 - 2941, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:34.56(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we successfully applied a transition-edge sensor (TES) spectrometer as a detector for microbeam X-ray measurements from a synchrotron X-ray light source to determine uranium (U) distribution at the micro-scale and its chemical species in biotite obtained from the U mine. It is difficult to separate the fluorescent X-ray of the U L
 line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K
line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
 and Rb K
and Rb K were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Isotope News, (789), p.20 - 23, 2023/10
Radium is a radioactive element produced from uranium and thorium and is important for environmental contamination issues around uranium mines and for geological disposal. In addition, radium is used in radiometric dating and cancer therapy, making it important not only in environmental chemistry but also in many other fields, including geochemistry and nuclear medicine. However, because radium is a radioactive element with no stable isotopes, spectroscopic measurement of radium is difficult, and little information at the molecular level has been obtained so far. In this study, we have clarified the molecular-level information of hydrated radium for the first time in the world by combining extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements and first-principles molecular dynamics simulations.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:65.24(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English

 -, SeO
-, SeO
 -, and SeO
-, and SeO
 -coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphate
-coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphateTokunaga, Kohei; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(8), p.3166 - 3175, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.75(Engineering, Environmental)Coprecipitation of radionuclides with barite has been studied to remove radionuclides from radioactive liquid waste because of its excellent removal efficiency; however, little information exists concerning the stability of the ions coprecipitated with barite. This study systematically investigated the stability of iodate, selenite, and selenate coprecipitated with barite via leaching tests. These oxyanions were gradually leached from the oxyanion-bearing barite into ultrapure water over time. Leaching of the oxyanions significantly increased in leaching solutions containing NaCl (pH5.3), NaNO (pH5.9), and Na
(pH5.9), and Na SO
SO (pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH
(pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH PO
PO solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO
solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 23, p.14 - 19, 2023/00
 -edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
-edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
Yomogida, Takumi; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Kumagai, Yuta; Higashi, Kotaro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kirishima, Akira*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(50), p.20206 - 20210, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:58.38(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)FeUO was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L
was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L -edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
-edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
 rays in the
rays in the 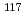 Sn(
Sn( )
)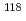 Sn reaction
Sn reactionEndo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.