Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Imai, Makoto*; Sataka, Masao*; Matsuda, Makoto; Okayasu, Satoru; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Komaki, Kenichiro*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 354, p.172 - 176, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)Both equilibrium and non-equilibrium charge-state distributions were studied experimentally for 2.0 MeV/u carbon ions after passing through carbon foils. Measured charge-state distribution established the equilibrium at a target thickness of 10  g/cm
g/cm and this remained unchanged until a maximum target thickness of 98
and this remained unchanged until a maximum target thickness of 98  g/cm
g/cm . The equilibrium charge-state distribution, the equilibrium mean charge-state, and the width and skewness of the equilibrium distribution were compared with predictions using existing semi-empirical formulae as well as simulation results, including the ETACHA code. It was found that charge-state distributions, mean charge states, and distribution widths for C
. The equilibrium charge-state distribution, the equilibrium mean charge-state, and the width and skewness of the equilibrium distribution were compared with predictions using existing semi-empirical formulae as well as simulation results, including the ETACHA code. It was found that charge-state distributions, mean charge states, and distribution widths for C , C
, C , and C
, and C incident ions merged into quasi-equilibrium values at a target thickness of 5.7
incident ions merged into quasi-equilibrium values at a target thickness of 5.7  g/cm
g/cm in the pre-equilibrium region and evolved simultaneously to the "real equilibrium" values for all of the initial charge states, including C
in the pre-equilibrium region and evolved simultaneously to the "real equilibrium" values for all of the initial charge states, including C and C
and C ions. Two kinds of simulation, ETACHA and solution of rate equations taking only single electron transfers into account, were used, and both of them reproduced the measured charge evolution qualitatively. The quasi-equilibrium behavior could be reproduced with the ETACHA code, but not with solution of elementary rate equations.
ions. Two kinds of simulation, ETACHA and solution of rate equations taking only single electron transfers into account, were used, and both of them reproduced the measured charge evolution qualitatively. The quasi-equilibrium behavior could be reproduced with the ETACHA code, but not with solution of elementary rate equations.

Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Takahiro, Katsumi*
Thin Solid Films, 562, p.648 - 652, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Liquid organic-hydrides such as cyclohexane which can release-absorbing hydrogen in reversible have been proposed approvable carriers to store and transport hydrogen. However, organic-hydrides are known as highly flammable in air. To realize practical use of this hydrogen production process, the monitoring of leakage of organic-hydride gas is strongly required. In the present work, we have examined the plasmonic sensing ability of Au nanoparticle (NP) arrays for dilute cyclohexane. Au NP arrays were prepared on SiO by a sputter deposition technique. The change in an extinction spectrum of Au NP arrays before and after exposure of cyclohexane vapor enabled us to detect it. The Au NP array prepared with 4.4
by a sputter deposition technique. The change in an extinction spectrum of Au NP arrays before and after exposure of cyclohexane vapor enabled us to detect it. The Au NP array prepared with 4.4  10
10 Au atoms/cm
Au atoms/cm deposited at 300
deposited at 300 C was and demonstrated a high sensitivity for cyclohexane at RT. The experimentally detectable concentration of cyclohexane was as low as 0.5 vol%, much lower than its explosion limit (1.3 vol%).
C was and demonstrated a high sensitivity for cyclohexane at RT. The experimentally detectable concentration of cyclohexane was as low as 0.5 vol%, much lower than its explosion limit (1.3 vol%).
 /Si by ion implantation
/Si by ion implantationTakahiro, Katsumi*; Ninakuchi, Yuki*; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Sasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nishiyama, Fumitaka*
Applied Surface Science, 258(19), p.7322 - 7326, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.97(Chemistry, Physical)A nanometer-sized metallic particle embedded in a transparent dielectric exhibits a nonlinear susceptibility, and going to be applied to nonlinear optical devices. In the present study, well-ordered arrangements of Ag nanoparticles have been found for Ag-implanted SiO . Thermally grown SiO
. Thermally grown SiO on Si were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to fluences of 0.37-1.2
on Si were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to fluences of 0.37-1.2  10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveal the presence of a two-dimensional array of Ag nanoparticles of 25-40 nm in diameter located at a depth of
. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveal the presence of a two-dimensional array of Ag nanoparticles of 25-40 nm in diameter located at a depth of  130 nm, together with the self-organization of tiny Ag nanoparticles aligned along the SiO
130 nm, together with the self-organization of tiny Ag nanoparticles aligned along the SiO /Si interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirm the stability of these Ag nanoparticles embedded in the SiO
/Si interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirm the stability of these Ag nanoparticles embedded in the SiO /Si is found to be stable against oxidation and sulfidation when stored in ambient conditions for more than one and a half year.
/Si is found to be stable against oxidation and sulfidation when stored in ambient conditions for more than one and a half year.
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Saito, Masahiro*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Plasmonics, 6(3), p.535 - 539, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.09(Chemistry, Physical)Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) have optical absorption bands due to localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) in visible range. The LSPR of Ag-NPs is being used for optical gas sensors. However, there have been differences in LSPR absorption band between most of the experimental data and calculations. We have demonstrated that plasma treatments for Ag NPs to clear the effect of contamination on surface of Ag NPs for LSPR absorption band. The results show that Ar plasma treatments to Ag NPs bring blue-shift and narrowing in their LSPR absorption band. Raman scattering analysis result that hydrocarbons adsorbed on silver surfaces were removed effectively by plasma exposure. It was found that the decrease in Raman line intensity for hydrocarbons was correlated well with the blue-shift. Our findings indicate that one of the most important factors for difference in LSPR absorption band between the experimental data and calculations is due to the impurity adsorption on silver surfaces.

Takahiro, Katsumi*; Oizumi, Shinnosuke*; Morimoto, Keiichi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
Applied Surface Science, 256(4), p.1061 - 1064, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:36.52(Chemistry, Physical)Takahiro, Katsumi*; Ozaki, Koichi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
Applied Surface Science, 256(4), p.972 - 975, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:47.64(Chemistry, Physical)Nagata, Shinji*; Sasase, Masato*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Inoue, Aichi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Shikama, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 267(8-9), p.1514 - 1517, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)In this study, effects of the ion implantation on the phase transformation and nano-crystalline formation were examined in Zr-based metallic glasses. Samples were 2 mm thick plates and thin films of Zr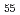 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu prepared by casting in a copper mold and by using RF magnetron sputtering, respectively. Ions of Mg, P, Au and Bi with 100-500 keV were implanted in the samples up to 2
prepared by casting in a copper mold and by using RF magnetron sputtering, respectively. Ions of Mg, P, Au and Bi with 100-500 keV were implanted in the samples up to 2  10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm at room temperature. Nano-crystalline structure was found in implanted samples by TEM observation, while the long-range order in the structure was not found for the X-ray diffraction patterns. The electron diffraction patterns indicated the formation of fcc-Zr
at room temperature. Nano-crystalline structure was found in implanted samples by TEM observation, while the long-range order in the structure was not found for the X-ray diffraction patterns. The electron diffraction patterns indicated the formation of fcc-Zr Cu in the P, Au, and Bi implanted region. Changes of the binding energy of the core level electron and valence band structure suggested the formation of Au-Zr or Au-Cu alloys in the Au ion implanted region.
Cu in the P, Au, and Bi implanted region. Changes of the binding energy of the core level electron and valence band structure suggested the formation of Au-Zr or Au-Cu alloys in the Au ion implanted region.
Nagata, Shinji*; Konishi, Yoshitada*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; To, Kentaro*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Shikama, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.519 - 522, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:49.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)Effects of MeV ion irradiation on electrical characteristics of perfluorosulphonic polymer membrane have been studied. The DC electrical conductivity in dry condition increased of three orders of magnitude as a consequence of irradiation with MeV region H and He ion irradiation at a fluence of 2  10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The optical absorption in the ultra-violet region increased in the ion irradiated membrane due to the formation of fluorocarbon and peroxy radicals. The ion irradiation may form fluorocarbon and peroxy compounds and improve the transport property of protons in the membrane.
. The optical absorption in the ultra-violet region increased in the ion irradiated membrane due to the formation of fluorocarbon and peroxy radicals. The ion irradiation may form fluorocarbon and peroxy compounds and improve the transport property of protons in the membrane.
Nagata, Shinji*; Higashi, Seijiro*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; To, Kentaro*; Shikama, Tatsuo*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Ozaki, Koichi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Inoue, Aichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.420 - 423, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:71.93(Instruments & Instrumentation)Structural modification and primary precipitates in the Zr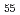 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu alloy films (50-100
alloy films (50-100  m thickness) caused by radiation with 300-500 keV H, Ag, Cu and Au ions has been studied. The results of XRD indicated that a metastable primary phase was formed in the alloy by the heat treatment after ion irradiation, but no difference was observed just after the ion irradiation at room temperature. Furthermore, higher incident Au ion fluence effectively suppressed thermal precipitation of the Zr
m thickness) caused by radiation with 300-500 keV H, Ag, Cu and Au ions has been studied. The results of XRD indicated that a metastable primary phase was formed in the alloy by the heat treatment after ion irradiation, but no difference was observed just after the ion irradiation at room temperature. Furthermore, higher incident Au ion fluence effectively suppressed thermal precipitation of the Zr Ni type crystalline phase in the alloy. The deposited energy dependence of the precipitation behavior indicated an increase of the nucleation sites by the implanted metal atoms, simultaneously with a decrease of the growth rate by higher energy deposition density.
Ni type crystalline phase in the alloy. The deposited energy dependence of the precipitation behavior indicated an increase of the nucleation sites by the implanted metal atoms, simultaneously with a decrease of the growth rate by higher energy deposition density.
Imai, Makoto*; Sataka, Masao; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Komaki, Kenichiro*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 256(1), p.11 - 15, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Oizumi, Shinnosuke*; Terai, Atsushi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sasase, Masato*
Journal of Applied Physics, 100(8), p.084325_1 - 084325_6, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:68.21(Physics, Applied)X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) has been applied for size estimation of Au clusters formed by ion implantation into glassy carbon. The 4f and 5d XPS spectra reveal the presence of the cluster 0.7-2.5nm in diameter, depending on the Au concentration. The elationship between XPS 4f-binding energy shift and 5d splitting is determined for the Au clusters embedded in the carbon and found to be significantly different from the previous data for the ones supported on a carbon substrate. We suppose that this difference results from the effect of the environment around a cluster on Coulomb charging during photoemission at the final state.
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Terai, Atsushi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Nagata, Shinji*; Nishiyama, Fumitaka*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 45(3A), p.1823 - 1825, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.66(Physics, Applied)It is found that the surface charging during Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) of insulating sapphire samples enables us to measure the charge-state distribution of probing ions backscattered at the sapphire surface. For Cu/Au-deposited Al O
O samples, two components, higher and lower-energy ones, were resolved on both Cu and Au peaks in the RBS random spectrum. For single-crystalline Al
samples, two components, higher and lower-energy ones, were resolved on both Cu and Au peaks in the RBS random spectrum. For single-crystalline Al O
O samples, a double-peak structure was clearly observed on both Al and O surface peaks in the RBS aligned spectrum. The charge-state distribution can be obtained from the intensity of each component. The results obtained here are compared with previous data for the equilibrium charge-state distribution.
samples, a double-peak structure was clearly observed on both Al and O surface peaks in the RBS aligned spectrum. The charge-state distribution can be obtained from the intensity of each component. The results obtained here are compared with previous data for the equilibrium charge-state distribution.
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Terai, Atsushi*; Oizumi, Shinnosuke*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.445 - 447, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy have been applied to investigate amorphization processes by ion irradiation for various carbon materials, including highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), isotropic graphite, glassy carbon (GC) and C crystalline film. It is found that the asymmetry of the XPS C 1s line increases as the irradiation dose increases. The origin of the asymmetry appeared on the C 1s line is discussed. It is concluded that the asymmetry of the C 1s line is not correlated with the increase in the size of a graphitic layer, but is related with the structural disorders, such as a bond angle disorder.
crystalline film. It is found that the asymmetry of the XPS C 1s line increases as the irradiation dose increases. The origin of the asymmetry appeared on the C 1s line is discussed. It is concluded that the asymmetry of the C 1s line is not correlated with the increase in the size of a graphitic layer, but is related with the structural disorders, such as a bond angle disorder.
Nasu, Shoichi*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yoshii, Kiichiro*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Kikuchi, Naoto*; Kusano, Eiji*; Moto, Shintaro*; Yamaguchi, Sadae*; Ohashi, Kentaro*; Noda, Kenji; et al.
Funtai Oyobi Fummatsu Yakin, 52(6), p.427 - 429, 2005/06
no abstracts in English
Imai, Makoto*; Sataka, Masao; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Komaki, Kenichiro*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 230(1-4), p.63 - 67, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.75(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
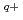 with He
with HeKawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Imai, Makoto*; Sataka, Masao; Komaki, Kenichiro*; Shibata, Hiromi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 205, p.528 - 532, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.70(Instruments & Instrumentation)Auger and Coster-Kronig electron spectra from highly excited states produced by low-energy highly charged ions with gas targets have been investigated both theoretically and experimentally. In this case, the highly excited states were formed by electron capture processes. We have studied collision processes of high-energy highly charged ions with a gas target using zero-degree electron spectroscopy at the tandem accelerator of JAERI, Tokai. In the present, we have measured Auger and C-K electron spectra from highly excited states produced by 1-3 MeV/u O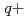 (q=3-5) + He collisions, where the highly excited states in Oq+ ions were formed by electron excitation. We have compared and discussed the Auger and C-K electron spectra obtained by electron-capture and electron-excitation processes. It is found that the C-K spectra for high-energy Oq+ ions show relatively low-l states and the Auger spectra also have different structures from those for low-energy highly charged Oq+ ions.
(q=3-5) + He collisions, where the highly excited states in Oq+ ions were formed by electron excitation. We have compared and discussed the Auger and C-K electron spectra obtained by electron-capture and electron-excitation processes. It is found that the C-K spectra for high-energy Oq+ ions show relatively low-l states and the Auger spectra also have different structures from those for low-energy highly charged Oq+ ions.
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Takeshima, Naoki*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2001-039, TIARA Annual Report 2000, p.188 - 189, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yamaguchi, Sadae*; Naramoto, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.143 - 145, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Morimoto, Keiichi*; Yasuda, Kenji*; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /Si by ion implantation
/Si by ion implantationNinakuchi, Yuki*; Saito, Masahiro*; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Nishiyama, Fumitaka*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Sasase, Masato*; Takahiro, Katsumi*
no journal, ,
In the course of Ag implantation into thermally grown SiO films, we found well-ordered Ag nanoparticles in the vicinity of SiO
films, we found well-ordered Ag nanoparticles in the vicinity of SiO /Si interface. SiO
/Si interface. SiO films of 300 nm thick were grown on single crystalline Si(111) substrates. The SiO
films of 300 nm thick were grown on single crystalline Si(111) substrates. The SiO /Si samples were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to a fluence of 1
/Si samples were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to a fluence of 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The Ag-implanted SiO
. The Ag-implanted SiO /Si samples were characterized by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and cross sectional transmission electron microscopy (XTEM). The Ag concentration depth profiles obtained by RBS and XPS were non-Gaussian, indicating that Ag atoms diffused significantly. XTEM revealed that well-arranged Ag nanoparticles of 30 nm and 2 nm in diameter were distributed near the projected range and the SiO
/Si samples were characterized by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and cross sectional transmission electron microscopy (XTEM). The Ag concentration depth profiles obtained by RBS and XPS were non-Gaussian, indicating that Ag atoms diffused significantly. XTEM revealed that well-arranged Ag nanoparticles of 30 nm and 2 nm in diameter were distributed near the projected range and the SiO /Si interface, respectively.
/Si interface, respectively.