Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamano, Hidemasa; Emura, Yuki; Takai, Toshihide; Kubo, Shigenobu; Quaini, A.*; Fossati, P.*; Delacroix, J.*; Journeau, C.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
This report mainly introduces trends in fast reactor development in Japan in addition to introducing overseas development trends for major developing countries. The paper describes major severe accident study results focusing on kinetics of interaction in core material mixtures, physical properties of core material mixtures, high temperature thermodynamic data for the uranium oxide (UO )-iron (Fe)-boron carbide (B
)-iron (Fe)-boron carbide (B C) system, experimental studies on B
C) system, experimental studies on B C-stainless steel (SS) kinetics and B
C-stainless steel (SS) kinetics and B C-SS eutectic material relocation (freezing), and B
C-SS eutectic material relocation (freezing), and B C-SS eutectic and kinetics models for severe accident code systems,
C-SS eutectic and kinetics models for severe accident code systems,
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2022. A specific result in this paper is to obtain first experimental data of B C-SS eutectic freezing.
C-SS eutectic freezing.
Emura, Yuki; Takai, Toshihide; Kikuchi, Shin; Kamiyama, Kenji; Yamano, Hidemasa; Yokoyama, Hiroki*; Sakamoto, Kan*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.911 - 920, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Pellegrini, M.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2023-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/09
A research project has been conducting thermophysical property measurement of a eutectic melt, eutectic melting reaction and relocation experiments, eutectic reaction mechanism investigation, and physical model development on the eutectic melting reaction for reactor application analysis in order to simulate the eutectic melting reaction and relocation behavior of boron carbide as a control rod material and stainless steel during a core disruptive accident in an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor designed in Japan. This paper describes the project overview and progress until JFY2022.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Fukai, Hirofumi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/09
This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2020. Specific results in this paper are the measurement of the eutectic reaction rates and the validation of physical model describing the eutectic reaction in the analysis code through the numerical analysis of the B C-SS eutectic reaction rate experiments in which a B
C-SS eutectic reaction rate experiments in which a B C pellet was placed in a SS crucible.
C pellet was placed in a SS crucible.
Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Shigeki*; Ishioka, Noriko*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 9(4), p.21-00397_1 - 21-00397_11, 2022/08
For the mass production of astatine-211, a promising radiopharmaceutical for cancer treatment, the National Institute for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology has proposed the innovative "Liquid Bismuth Target System." The target window in this system must be made from a material that resists the highly corrosive liquid bismuth environment. To meet this requirement, a promising target window material was selected in corrosion experiments performed in stagnant liquid bismuth. Based on knowledge of corrosion in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic gained during the development of fast reactors and accelerator-driven subcritical systems, experiments were carried out under saturated dissolved oxygen and low oxygen conditions, and the corrosion behaviors of the specimens were evaluated. The FeCrAl-alloy exhibited the most excellent corrosion resistance, followed by FeCrMo-alloy. Both materials are suitable candidates for the target window.
Quaini, A.*; Goss , S.*; Payot, F.*; Suteau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Saas, L.*; Gubernatis, P.*; Martin-Lopez, E.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; et al.
, S.*; Payot, F.*; Suteau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Saas, L.*; Gubernatis, P.*; Martin-Lopez, E.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/04
CEA and JAEA defined new sub-tasks under the current implementing arrangement: Kinetics of interaction in core material mixtures- Physical properties of core material mixtures, High temperature thermodynamic data for the UO -Fe-B
-Fe-B C system, Experimental studies on B
C system, Experimental studies on B C-SS kinetics and B
C-SS kinetics and B C-SS eutectic material relocation (freezing), B
C-SS eutectic material relocation (freezing), B C/SS eutectic and kinetics models for SIMMER code systems, Methodology for the modelling of mixtures liquefaction kinetics. The paper describes major R&D results obtained in the France-Japan collaboration under the previous implementing arrangement as well as experimental and analytical roadmaps under the current arrangement.
C/SS eutectic and kinetics models for SIMMER code systems, Methodology for the modelling of mixtures liquefaction kinetics. The paper describes major R&D results obtained in the France-Japan collaboration under the previous implementing arrangement as well as experimental and analytical roadmaps under the current arrangement.
Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yamano, Hidemasa
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(4), p.20-00540_1 - 20-00540_11, 2021/08
In a core disruptive accident scenario, boron carbide, which is used as a control rod material, may melt below the melting temperature of stainless steel owing to the eutectic reaction with them. The eutectic mixture produced is assumed to extensively relocate in the degraded core, and this behavior plays an important role in significantly reducing the neutronic reactivity. However, these behaviors have never been simulated in previous severe accident analysis. To contribute to the improvement of the core disruptive accident analysis code, the thermophysical properties of the eutectic mixture in the solid state were measured, and regression equations that show the temperature (and boron carbide concentration) dependence are created.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2021/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a CDA computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2019. Specific results in this paper are the validation of physical model describing B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a CDA computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2019. Specific results in this paper are the validation of physical model describing B C-SS eutectic reaction in the CDA analysis code, SIMMER-III, through the numerical analysis of the B
C-SS eutectic reaction in the CDA analysis code, SIMMER-III, through the numerical analysis of the B C-SS eutectic melting experiments in which a B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments in which a B C block was placed in a SS pool.
C block was placed in a SS pool.
Kikuchi, Shin; Takai, Toshihide; Yamano, Hidemasa; Sakamoto, Kan*
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) may occur. Thus, behavior of B
C) and stainless steel (SS) may occur. Thus, behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, the reaction experiments using SS crucibles and the pellets of SS with low B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, the reaction experiments using SS crucibles and the pellets of SS with low B C concentration as samples were performed to simulate the state of the reaction interface in which the eutectic reaction and interdiffusion of B
C concentration as samples were performed to simulate the state of the reaction interface in which the eutectic reaction and interdiffusion of B C-SS have progressed to a certain extent. It was revealed that the rate constants of eutectic reaction between SS and SS with low B
C-SS have progressed to a certain extent. It was revealed that the rate constants of eutectic reaction between SS and SS with low B C concentration are smaller than that of B
C concentration are smaller than that of B C-SS eutectic reaction at high temperatures.
C-SS eutectic reaction at high temperatures.
Kikuchi, Shin; Sakamoto, Kan*; Takai, Toshihide; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2020-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/09
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B
C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B
C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B C or SS with low B
C or SS with low B C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B
C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B
C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B C concentration were smaller than that of B
C concentration were smaller than that of B C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B
C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B C containing SS became small when decreasing the B
C containing SS became small when decreasing the B C concentration against SS.
C concentration against SS.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 86(883), p.19-00360_1 - 19-00360_13, 2020/03
It is necessary to simulate a eutectic melting reaction and relocation behavior of boron carbide (B C) as a control rod material and stainless steel (SS) during a core disruptive accident in an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor designed in Japan because the B
C) as a control rod material and stainless steel (SS) during a core disruptive accident in an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor designed in Japan because the B C-SS eutectic relocation behavior has a large uncertainty in the reactivity history based on a simple calculation. A physical model simulating the eutectic melting reaction and relocation was developed and implemented into a severe accident simulation code. The developed model must be validated by using test data. To validate the physical model, therefore, the visualization tests of SS-B
C-SS eutectic relocation behavior has a large uncertainty in the reactivity history based on a simple calculation. A physical model simulating the eutectic melting reaction and relocation was developed and implemented into a severe accident simulation code. The developed model must be validated by using test data. To validate the physical model, therefore, the visualization tests of SS-B C eutectic melting reaction was carried out by contacting SS melts of several kg with a B
C eutectic melting reaction was carried out by contacting SS melts of several kg with a B C pellet heated up to about 1500
C pellet heated up to about 1500  C. The tests have shown the eutectic reaction visualization as well as freezing and relocation of the B
C. The tests have shown the eutectic reaction visualization as well as freezing and relocation of the B C-SS eutectic in upper part of the solidified test piece due to the density separation. Post-test material analyses by using X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscope techniques have indicated that FeB appeared at the B
C-SS eutectic in upper part of the solidified test piece due to the density separation. Post-test material analyses by using X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscope techniques have indicated that FeB appeared at the B C-SS contact interface and (Fe,Cr)
C-SS contact interface and (Fe,Cr) B at the top surface of the test piece. Glow discharge optical emission spectrometry has been applied to quantitative analysis of boron concentration distributions. The boron concentration was high at the upper surface and near the original position of the B
B at the top surface of the test piece. Glow discharge optical emission spectrometry has been applied to quantitative analysis of boron concentration distributions. The boron concentration was high at the upper surface and near the original position of the B C pellet.
C pellet.
 C in the solid phase
C in the solid phaseTakai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nuclear Technology, 205(9), p.1164 - 1174, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:72.77(Nuclear Science & Technology) C addition on thermophysical properties of austenitic stainless steel in a solid state
C addition on thermophysical properties of austenitic stainless steel in a solid stateTakai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.847 - 852, 2019/09
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.418 - 427, 2019/09
Eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
 C in the solid phase
C in the solid phaseTakai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 2018 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2018) (CD-ROM), p.1007 - 1013, 2018/04
 by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry
by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometryNakajima, Kunihisa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 491, p.183 - 189, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One of the main chemical forms of cesium in the gas phase during severe accidents of light water reactor is expected to be cesium metaborate, CsBO , by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO
, by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO (g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO
(g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO
was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO (g),
(g), 
 H
H
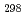 (CsBO
(CsBO ,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7
,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7 10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0
10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0 10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
Takai, Toshihide; Sato, Isamu*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Furukawa, Tomohiro
JAEA-Technology 2015-043, 56 Pages, 2016/02
Fundamental research on FP-chemistry for fission product release behaviors under severe accident was carried out for reinforcement of source term evaluation, and implementation of the 1F decommissioning R&D project. There were subjects to clarified (1) FP chemistry behavior between vapor species release and aerosol formation and (2) physical parameters which would be affect subsequent aerosol's chemical behavior, for improvement of FP transport model. Applicability of measuring/analyzing techniques presently used was studied for evaluating foregoing properties. And the validity was verified by trial measurements. In conclusion, Raman spectrometry and high temperature X-ray diffraction were hopeful to determine FP-chemical form against vapor/aerosol species and aerosol species, respectively. Combination use of cascade impactor and scanning type electron microscope with energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry was hopeful to determine physical parameters of aerosol.