Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Masaru*; Muto, Marika*; Matsubara, Naohiro*; Uemura, Yohei*; Wakisaka, Yuki*; Yoneuchi, Tsubasa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Ishibara, Tomoko*; Tokushima, Takashi*; Noro, Shinichiro*; et al.
ACS Applied Energy Materials (Internet), 1(5), p.2358 - 2364, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:43.4(Chemistry, Physical)Uosaki, Kohei*; Morita, Jun*; Katsuzaki, Tomoko*; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Kondo, Toshihiro*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115(25), p.12471 - 12482, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.16(Chemistry, Physical)Ag/AgCl reaction at the Ag bilayer, which was underpotentially prepared on a Au(111) surface, was investigated using electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM), scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), surface X-ray scattering (SXS), and electrochemical techniques. When the potential was scanned positively from -200 mV, the Cl ion was adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode surface around 0 mV, and then the phase transition of the adsorbed Cl
ion was adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode surface around 0 mV, and then the phase transition of the adsorbed Cl ion layer from random orientation to (
ion layer from random orientation to (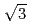

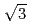 ) structure took place at around +130 mV. The Ag bilayer and Cl
) structure took place at around +130 mV. The Ag bilayer and Cl ions were oxidatively reacted to form the AgCl monolayer with (
ions were oxidatively reacted to form the AgCl monolayer with (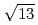

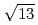 )
)  13.9
13.9 structure around +200 mV, accompanied with the formation of AgCl monocrystalline clusters on the AgCl monolayer surface. The structure of the AgCl monolayer on the Au(111) surface was changed from (
structure around +200 mV, accompanied with the formation of AgCl monocrystalline clusters on the AgCl monolayer surface. The structure of the AgCl monolayer on the Au(111) surface was changed from (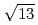

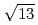 )R13.9
)R13.9 structure to (4
structure to (4 4) structure around +500 mV.
4) structure around +500 mV.
Kondo, Toshihiro*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Kitamura, Ken*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 13(7), p.1141 - 1145, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:14.88(Electrochemistry)The interfacial structures of Ag bilayer prepared by underpotential deposition on Au(111) were determined by STM and SXS before and after oxidative adsorption and after desorption of a SAM of C SH in alkaline ethanol solution. While no structural change was observed after oxidative formation of C
SH in alkaline ethanol solution. While no structural change was observed after oxidative formation of C SH SAM on the Ag/Au(111) in an ethanol solution containing 20 mM KOH and 0.1 mM C
SH SAM on the Ag/Au(111) in an ethanol solution containing 20 mM KOH and 0.1 mM C SH, some of the Ag atoms in the bilayer were stripped when the SAM was reductively desorbed.
SH, some of the Ag atoms in the bilayer were stripped when the SAM was reductively desorbed.
Kondo, Toshihiro*; Morita, Jun*; Hanaoka, Kazuya*; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(35), p.13197 - 13204, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:89.36(Chemistry, Physical)Potential-dependent surface structures of Au(111) and Au(100) single-crystal electrodes in a 50 mM H SO
SO solution were investigated at an atomic level using in situ surface X-ray scattering (SXS) techniques. It was confirmed that both the Au(111) and Au(100) surfaces were reconstructed with an attached submonolayer of an oxygen species, most probably water, at 0 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Results at +0.95 V supported a previously suggested model for both the Au(111) and the Au(100) electrodes that, based on infrared and scanning tunneling microscopy measurements, the surfaces were a (1
solution were investigated at an atomic level using in situ surface X-ray scattering (SXS) techniques. It was confirmed that both the Au(111) and Au(100) surfaces were reconstructed with an attached submonolayer of an oxygen species, most probably water, at 0 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Results at +0.95 V supported a previously suggested model for both the Au(111) and the Au(100) electrodes that, based on infrared and scanning tunneling microscopy measurements, the surfaces were a (1 1) structure with the coadsorbed sulfate anion and hydronium cation (H
1) structure with the coadsorbed sulfate anion and hydronium cation (H O
O ). At +1.05 V, where a small amount of an anodic current flowed, adsorption of a monolayer of oxygen species was observed on both surfaces.
). At +1.05 V, where a small amount of an anodic current flowed, adsorption of a monolayer of oxygen species was observed on both surfaces.