Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kajita, Shin*; Hatae, Takaki; Sakuma, Takeshi; Takamura, Shuichi*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Itami, Kiyoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2405121_1 - 2405121_4, 2012/09
Tanaka, Hirohiko*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kawashima, Hisato; Takamura, Shuichi*; Uesugi, Yoshihiko*; JT-60U Team
Nuclear Fusion, 49(6), p.065017_1 - 065017_7, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:78.77(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Comparison between fluctuation characteristics at high-field-side (HFS) and low-field-side (LFS) scrape off layers (SOLs) has been made, for the first time, in the L mode plasma of the JT-60U tokamak using reciprocating Langumuir probes. Statistical analysis based on probability distribution function (PDF) was employed to describe intermittent (non-diffusion) transport in SOL plasma fluctuations. The positive bursty events appeared most frequently at LFS midplane associated with blobby plasma transport, then the PDF is strongly skewed positively, while the PDF in HFS SOL is close to Gaussian distribution. Conditional averaging analysis of the positive bursty events at LFS midplane indicates the intermittent feature with a rapid increase and a slow decay is similar to that of plasma blobs theoretically predicted. Statistical self-similarity was also investigated with Fourier power spectrum and statistics of waiting-time and duration-time of the fluctuation.
Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Mase, Atsushi*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takase, Yuichi*; Nakamura, Yukio*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(5), p.297 - 298, 2008/05
no abstracts in English
Kajita, Shin; Ono, Noriyasu*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Sakaguchi, Wataru*; Nishijima, Dai*
Applied Physics Letters, 91(26), p.261501_1 - 261501_3, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:78.80(Physics, Applied)Nanosecond laser ablation of tungsten (W) that was exposed to helium plasmas was investigated using optical emission spectroscopy. Sub-micrometor holes/bubbles are formed on the surface of W specimen when it was exposed to the helium plasma at sufficient higher temperature (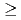 1500-1600 K). The onset pulse energy to detect W I becomes
1500-1600 K). The onset pulse energy to detect W I becomes  0.2 J/cm
0.2 J/cm after the W specimen was exposed to high-density helium plasmas, though the emission from a pure virgin W (before helium plasma irradiation) cannot be detected when the pulse energy was lower than 1 J/cm
after the W specimen was exposed to high-density helium plasmas, though the emission from a pure virgin W (before helium plasma irradiation) cannot be detected when the pulse energy was lower than 1 J/cm . Laser-induced bursting of the holes/bubbles is suggested to be the physical mechanism leading to the significant reduction in the ablation power threshold.
. Laser-induced bursting of the holes/bubbles is suggested to be the physical mechanism leading to the significant reduction in the ablation power threshold.
Sasao, Mamiko*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mase, Atsushi*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(9), p.779 - 782, 2007/09
This is a report of highlights from 2007 spring meetings of seven Topical Groups (TG) of International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA). In each meeting, high priority issues in physics of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and other burning plasma experiments have been discussed and investigated. Twenty-seven scientists from Japan have participated in those meetings. Dates and places of the meetings are shown below. (1) Diagnostics TG: 26-30 March, Princeton (USA), (2) Transport Physics TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (3) Confinement Database and Modeling TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (4) Edge Pedestal Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany) (5) Steady State Operation TG: 9-11 May, Daejeon (South Korea), (6)MHD TG: 21-24 May, San Diego (USA), (7) Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany).
Loarte, A.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Matthews, G. F.*; Stangeby, P. C.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Counsell, G. F.*; Federici, G.*; Kallenbach, A.*; Krieger, K.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S203 - S263, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:932 Percentile:96.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress, since the ITER Physics Basis publication (1999), in understanding the processes that will determine the properties of the plasma edge and its interaction with material elements in ITER is described. Significant progress in experiment area: energy and particle transport, the interaction of plasmas with the main chamber material elements, ELM energy deposition on material elements and the transport mechanism, the physics of plasma detachment and neutral dynamics, the erosion of low and high Z materials, their transport to the core plasma and their migration at the plasma edge, retention of tritium in fusion devices and removal methods. This progress has been accompanied by the development of modelling tools for the physical processes at the edge plasma and plasma-materials interaction. The implications for the expected performance in ITER and the lifetime of the plasma facing materials are discussed.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Fujii, Takashi*; Fujiyama, Hiroshi*; Takabe, Hideaki*; Adachi, Kazuo*; Morimiya, Osamu*; Fujimori, Naoji*; Watanabe, Takayuki*; Hayashi, Yasuaki*; et al.
Kara Zukai, Purazuma Enerugi No Subete, P. 164, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Lipschultz, B.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Bonnin, X.*; Coster, D. P.*; Counsell, G.*; Doerner, R.*; Dux, R.*; Federici, G.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Fundamenski, W.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
The work of the ITPA SOL/divertor group is reviewed. The high-n nature of ELMs has been elucidated and new measurements have determined that they carry 10-20% of the ELM energy to the far SOL with implications for ITER limiters and the upper divertor. Analysis of ELM measurements imply that the ELM continuously loses energy as it travels across the SOL. The prediction of ITER divertor disruption power loads have been reduced as a result of finding that the divertor footprint broadens during the thermal quench and that the plasma can lose up to 80% of its thermal energy before the thermal quench (not for VDEs or ITBs). Disruption mitigation through massive gas puffing has been successful at reducing divertor heat loads but estimates of the effect on the main chamber walls indicate 10s of kG of Be would be melted/mitigation. Long-pulse studies have shown that the fraction of injected gas that can be recovered after a discharge decreases with discharge length. The use of mixed materials gives rise to a number of potential processes.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Ono, Noriyasu*; Kawashima, Hisato; Miyoshi, Hideaki*; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takamura, Shuichi*; Uesugi, Yoshihiko*; Takechi, Manabu; Nakano, Tomohide; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Radial transport of the SOL plasma was recently studied in order to understand heat and particle loading to the first wall and the SOL formation mechanism. Fast propagation of the ELM plasma and fluctuation properties in H- and L-modes were determined at low-field-side (LFS) SOL using reciprocating Mach probes in JT-60U. Large and short peaks were found in ELM plasma flux, which was regularly enhanced after each ELM event. Transport dynamics of the first large 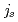 peak was determined, i.e. it propagated to near the first wall with the fast velocity of 1.3-2.5 km/s. Statistical analysis of a probability distribution function was applied to describe intermittent (non-diffusion) transport in SOL plasma fluctuations. It was found that the positive bursty events appeared in a wide SOL region, where the flow reversal of the SOL plasma was observed. Influences of the radial transport of the convective blobby plasma on the SOL formation and the flow reversal were investigated.
peak was determined, i.e. it propagated to near the first wall with the fast velocity of 1.3-2.5 km/s. Statistical analysis of a probability distribution function was applied to describe intermittent (non-diffusion) transport in SOL plasma fluctuations. It was found that the positive bursty events appeared in a wide SOL region, where the flow reversal of the SOL plasma was observed. Influences of the radial transport of the convective blobby plasma on the SOL formation and the flow reversal were investigated.
Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Mase, Atsushi*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(2), p.195 - 198, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Masaaki*; Hiraishi, Takehiro*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Nakano, Tomohide; Kawano, Yasunori; Ozeki, Takahisa; Sugihara, Masayoshi
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 31F, 4 Pages, 2007/00
It is of importance to evaluate the decay time of the plasma current for estimation of the electromagnetic force acting on the vacuum vessel during plasma disruptions in tokamak devices. The L/R model predicts that the decay time is proportional to three-haves power of the electron temperature, indicating the importance of the electron temperature for the estimation. However, it is difficult to measure the electron temperature of the disruptive plasma with the Langmuir probe due to the heat flux and due to the significant electromagnetic force. We propose a measurement technique of the electron temperature by using temperature-sensitive He I lines with high time resolution. In this method, the incident light to a spectrometer is divided into three, each of which transmits a bandpass filter, and then is measured with an absolutely calibrated photo-multiplier. The measured intensity ratios are analyzed with a collisional-radiative model. It is confirmed that the electron temperature determined by this technique is in agreement with that measured by a Langmuir probe in some devices. In the present work, the temporal evolution of the electron temperature during the disruptive plasma of JT-60U is measured with this technique.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Nakano, Tomohide; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Iio, Shunji*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Ono, Yasushi*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 82(7), p.448 - 450, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Kajita, Shin*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Nakano, Tomohide
Physics of Plasmas, 13(1), p.013301_1 - 013301_9, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:85.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Nakano, Tomohide; Iio, Shunji*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Ono, Yasushi*; Sugihara, Masayoshi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(11), p.960 - 961, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Mase, Atsushi*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(2), p.128 - 130, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Iio, Shunji*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Ono, Yasushi*; Kato, Takako*; Kawano, Yasunori; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(7), P. 642, 2004/07
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Higashijima, Satoru; Iio, Shunji*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Ono, Yasushi*; Kawano, Yasunori; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(11), p.1194 - 1196, 2003/11
The ITPA (International Tokamak Physics Activity) meeting was held at Scientific Educational Center of Ioffe Institute (St. Petersburg) in Russia. In the meeting, topical physics group meetings of "Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics", "MHD, Disruptions and Control", "Energetic Particles, Heating and Steady State Operation", and "Diagnostics" were carried out. The joint meeting for plasma control was also held. In getting many participants from Japan, Europe, Russia, ITER international team, U.S.A. and China (observer), the active discussions were carried out. The outline of discussions in each topical group and in the plasma control joint meeting is reported here.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Wakatani, Masahiro*; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Kamada, Yutaka; Yatsu, Kiyoshi*; Hatae, Takaki; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Iio, Shunji*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Kawano, Yasunori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(1), P. 70, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Takamura, Shuichi*; Wakatani, Masahiro*; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi; Toi, Kazuo*; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Hatae, Takaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(7), p.692 - 694, 2002/07
The second ITPA (International Tokamak Physics Activity) meeting was held at General Atomics (San Diego) and Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (Princeton) in U.S.A. In the meeting, topical physics group meetings of "Coordinating Committee", "Transport and Internal Barrier Physics", "Confinement Database and Modeling", "Edge and Pedestal Physics", "Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics", and "Diagnostics" were carried out. In getting many participants from Japan, Europe, Russia, ITER international team and U.S.A., the active discussions were carried out. On the other hand, the topical group members concerned that the contribution from Japan will be decreased if the experimental period of JT-60U is reduced. Here, the outline of discussions in each topical group is reported.
Wakatani, Masahiro*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Ninomiya, Hiromasa
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(1), p.72 - 73, 2002/01
no abstracts in English