Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Taguchi, Katsuya; Makino, Risa; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Suzuki, Kazuyuki; Takano, Masato; Koshino, Katsuhiko; Ishida, Michihiko; Nakano, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Toshiya
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-17-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.499 - 502, 2021/07
In 2018, Tokai Reprocessing Plan (TRP) shifted to the decommissioning stage. In order to proceed with steady decommissioning work, TRP effort to enhance project management function. This paper describes the establishment and role of the Decommissioning Project Management Office, effectiveness of applying the project management tool and its utilization concept, and the method of materialize the equipment dismantling plan.
Aiko, Kazuma*; Toki, Atsushi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Sato, Takahiro; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Koka, Masashi; Saito, Yuichi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Okochi, Takuo*; et al.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 19(2), p.223 - 226, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.7(Instruments & Instrumentation)Miura, Kenta*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; Uehara, Masato*; Kiryu, Hiromu*; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Okubo, Takeru; Yamazaki, Akiyoshi; Kada, Wataru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 126, 2012/01
 m band using focused proton beam
m band using focused proton beamMiura, Kenta*; Machida, Yuki*; Uehara, Masato*; Kiryu, Hiromu*; Ozawa, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Tomoyuki*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; et al.
Key Engineering Materials, 497, p.147 - 150, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:95.12(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) m band using focused proton beam
m band using focused proton beamMiura, Kenta*; Machida, Yuki*; Uehara, Masato*; Kiryu, Hiromu*; Ozawa, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Tomoyuki*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; et al.
Key Engineering Materials, 497, p.147 - 150, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:2.48Sudo, Katsuo; Takano, Tatsuo; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Kato, Masato
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been contracted to advance the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development project. As one part of the project, a simplified MOX pellet fabrication method has been developed for fast reactor fuels. In previous reports, feasibility of a simplified MOX pellet fabrication method was confirmed through hot and cold laboratory-scale experiments. The die wall lubrication pressing technology was one of the important technologies included in the development of the simplified MOX pellet fabrication method. In the work described here, a pressing machine with a die wall lubrication system was developed, and MOX pellet fabrication experiments were carried out on the kilogram MOX scale.
Takano, Tatsuo; Sudo, Katsuo; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Kato, Masato
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/12
Development of high burn-up fuels is essential to improve economy of the fast reactor fuel cycle. Increase of fuel burn-up is known to cause fuel-cladding chemical interaction (FCCI) and it mainly determines a lifetime of fuel pin. In order to extend a lifetime of fuel pin by mitigating FCCI, development of low oxygen-to-metal (O/M) MOX fuel has been carried out in plutonium fuel development center of JAEA. MOX fuel needs adjustment of the O/M ratio to less than 1.97 for high burn-up of 150 GWd/t. Therefore, O/M adjustment technology is one of the main subjects in development of a simplified MOX pellet fabrication method which has been advanced in the FaCT (Fast reactor Cycle Technology development) project. In previous work, changes in O/M ratio of MOX pellet during heat treatment were calculated from measurement results of oxygen potentials. On the basis of above calculation, heating tests were carried out to prepare low O/M ratio MOX pellets on a laboratory scale. The O/M ratios obtained in the heating tests were well consistent with calculation results. In the present study, a kilogram MOX scale furnace to adjust O/M ratio of MOX pellets for targeted value has been developed as next step.
Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Takano, Tatsuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/12
In this work, the shrinkage behavior and O/M change of MOX pellet during sintering process were investigated with dilatometer and thermo-gravimeter, and equations to analyze the sintering behavior were derived. The derived equations represented the change of density and O/M ratio of MOX pellet during heat treatment as functions of heat treatment conditions such as heating rate, holding temperature and 
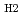 /
/
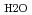 ratio in an atmosphere. They contribute the development of advanced pellet production process and would accurately control density and O/M ratio of MOX pellets.
ratio in an atmosphere. They contribute the development of advanced pellet production process and would accurately control density and O/M ratio of MOX pellets.
 Sn superconducting conductors in ITER
Sn superconducting conductors in ITERNabara, Yoshihiro; Isono, Takaaki; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Hamada, Kazuya; Matsui, Kunihiro; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Kawano, Katsumi; Uno, Yasuhiro*; Seki, Shuichi*; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.270 - 275, 2010/08
Saito, Yasuo; Takano, Masato; Tanaka, Kenji; Kobayashi, Kentaro; Otani, Yoshikuni
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radiation Safety Management 2007 (ISRSM 2007), p.275 - 280, 2007/11
The Low-radioactive Waste Treatment Facility (LWTF), which aims to provide the safe, efficient and economic treatment and disposal of Low-level Liquid Waste (LLW) generated from LWR spent fuel reprocessing, was constructed at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), and a cold test is now being carried out. New treatment processes such as a removal process for radio-nuclides and the ROBE (BORSAURE EINENGUNG ANLAGE) solidification process are being implemented in the LWTF. In order to treat the large amount of sodium nitrate contained in the concentrated LLW with higher safety and economy, R&D work on nitrate-ion decomposition technology using a catalytic reduction method and on the solidification process by cementation is being undertaken. The results of this R&D will be adopted in the LWTF in the near future. This report describes an outline of liquid waste treatment in the LWTF and new treatment technologies for LLW to achieve safe, efficient and economic treatment and disposal.
Kato, Masato; Nakamichi, Shinya; Takano, Tatsuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.916 - 920, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Sasa, Toshinobu; Kikuchi, Kenji; Nishihara, Kenji; Kurata, Yuji; Umeno, Makoto*; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Mizumoto, Motoharu; et al.
Proceedings of 4th International Workshop on the Utilisation and Reliability of High Power Proton Accelerators, p.507 - 517, 2005/11
Under the framework of J-PARC, the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) plans to construct the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF). The TEF consists of two facilities: the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) and the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T). The TEF-P is a critical facility which can accept a 600 MeV - 10 W proton beam. The TEF-T is a material irradiation facility using a 600 MeV - 200 kW proton beam, where a Pb-Bi target is installed, but neutron multiplication by nuclear fuel will not be attempted. This report describes the purposes of the facility, the present status of the conceptual design, and the expected experiments to be performed.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Umeno, Makoto*; Mizubayashi, Hiroshi*; Mori, Keijiro*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Saito, Shigeru; Kai, Tetsuya; Nakai, Kimikazu*; Zako, Akira*; Kasahara, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2005-021, 114 Pages, 2005/03
To perform the research and development for accelerator-driven system (ADS), Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) plans to build a Transmutation Experimental Facility under the JAERI-KEK joint J-PARC program. Transmutation Experimental Facility consists of two buildings, Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility to make reactor physics experiment with subcritical core, and ADS Target Test Facility for the preparation of irradiation database for various structural materials. In this report, purpose to build, experimental schedule, and design study of the ADS target test facility with drawer type spallation target are summarized.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Nishihara, Kenji; Kikuchi, Kenji; Kurata, Yuji; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Umeno, Makoto*; Ouchi, Nobuo; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 230(1-3), p.209 - 222, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAERI carries out research and development on accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides and long-lived fission products. The system is composed of high intensity proton accelerator, lead-bismuth spallation target and lead-bismuth cooled subcritical core with nitride fuel. About 2,500 kg of minor actinide is loaded into the subcritical core. Annual transmutation amount using this system is 250 kg with 800MW of thermal output. A superconducting linear accelerator with the beam power of 30MW is connected to drive the subcritical core. Many research and development activities are under way and planned in the fields of subcritical core design, spallation target technology, lead-bismuth handling technology, accelerator development, and minor actinide fuel development. Especially, to study and evaluate the feasibility of the ADS from physics and engineering aspects, the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is proposed under a framework of the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator Project.
Kikuchi, Kenji; Saito, Shigeru; Kurata, Yuji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Umeno, Makoto*; Mori, Keijiro*; Takano, Hideki; Wakai, Eiichi
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2003/04
In order to construct ADS Target Test facility in J-PARC project the research and development on Pb-Bi technology have been carried, which cover target design with computer simulation, flowing loop test, stagnant corrosion test, oxygen sensor and cleaning techniques. Obtained results are as follows: Corrosion rate of SUS316 under flowing Pb-Bi at 1m/s at 450 C is 0.1 mm / 3000 hrs. Fe and Cr were melted into lead bismuth from SS316 in the high temperature part and deposited in the low-temperature part according to the difference of solubility. The corrosion thickness decreases with increasing Cr content in the stagnant corrosion test at saturated oxygen concentration. Reliable oxygen sensors are to be developed by using suitable reference electrodes. As a result of cleaning tests, blushing process was needed to remove Pb-Bi effectively after immersion in the silicon oil. The mixed acid easily dissolved Pb-Bi and removed almost perfectly. But specimens themselves were affected by coloring.
C is 0.1 mm / 3000 hrs. Fe and Cr were melted into lead bismuth from SS316 in the high temperature part and deposited in the low-temperature part according to the difference of solubility. The corrosion thickness decreases with increasing Cr content in the stagnant corrosion test at saturated oxygen concentration. Reliable oxygen sensors are to be developed by using suitable reference electrodes. As a result of cleaning tests, blushing process was needed to remove Pb-Bi effectively after immersion in the silicon oil. The mixed acid easily dissolved Pb-Bi and removed almost perfectly. But specimens themselves were affected by coloring.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Nishihara, Kenji; Kikuchi, Kenji; Kurata, Yuji; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Umeno, Makoto*; Ouchi, Nobuo; et al.
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2003/04
JAERI carries out research and development on accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides and long-lived fission products in high-level radioactive waste. The system is composed of high intensity proton accelerator, lead-bismuth spallation target and lead-bismuth cooled subcritical core with nitride fuel. About 2500 kg of minor actinide is loaded into the subcritical core. Annual transmutation amount using this system is 250 kg with 800MW of thermal output. A superconducting linear accelerator with the beam power of 20 - 30MW is connected to drive the subcritical core. The nitride fuel without uranium, such as (Np, Am, Pu)N, is selected. The fuel irradiated in the ADS is reprocessed by pyrochemical process followed by the re-fabrication of the fuel. Many research and development activities are under way. Especially, to study and evaluate the feasibility of the ADS from physics and engineering aspects, the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is proposed under a framework of the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator Project.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Ouchi, Nobuo; Kikuchi, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Kurata, Yuji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Takano, Hideki; Nishihara, Kenji; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; et al.
Proceedings of GLOBAL2003 Atoms for Prosperity; Updating Eisenhower's Global Vision for Nuclear Energy (CD-ROM), p.1374 - 1379, 2003/00
JAERI is developing an Accelerator Driven System (ADS) for transmutation of nuclear waste such as minor actinide and long-lived fission product. To acquire the knowledge and the elemental technology that are necessary for the validation of engineering feasibility of ADS, JAERI has started a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program since 2002. The first stage of the program will be continued for three years. The program is conducted by JAERI with many institutes, universities and private companies. Items of R&D are concentrated on three technical areas peculiar to ADS: (1) a superconducting linear accelerator, (2) lead-bismuth eutectic as spallation target and core coolant, and (3) subcritical core design and physics. The outline and the preliminary results of the program are summarized in the present report.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Sasa, Toshinobu; Takano, Hideki; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Nishihara, Kenji; Kikuchi, Kenji; Kurata, Yuji; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Umeno, Makoto*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC 2002) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2002/10
To reduce the burden on the final disposal of the nuclear waste, the Acclelerator-Driven System (ADS) which can transmute minor actinides efficiently has been studied in JAERI. The proposed ADS design is an 800MWth subcritical core with lead-bismuth coolant and minor-actinide nitride fuel driven by a neutron source of a superconductivity linear accelerator with 30MW and a lead-bismuth spallation target. To realize the ADS, many research and development are under way in the fields of the accelerator, the spallation target and the nitride fuel. Moreover, a new experimental facility, the Transmutation Experimental Facility, is proposed under a framework of the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator Project to study the feasibility of the ADS from physics and engineering aspects.
 thin films prepared by ion beam assisted reactive deposition method
thin films prepared by ion beam assisted reactive deposition methodSasase, Masato*; Takano, Ichiro*; *; *
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, A, 116A(9), p.804 - 809, 1996/09
no abstracts in English