Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Takashi; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Ando, Toshinari; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nakajima, Hideo; Sugimoto, Makoto; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 56-57, p.59 - 70, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:75.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi*; Thome, R.*; Salpietro, E.*; Egorov, S. A.*; Martovetsky, N.*; Ricci, M.*; Zanino, R.*; Zahn, G.*; Martinez, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 41(5), p.645 - 651, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:82.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ishigaki, Toru; Harjo, S.; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mori, Kazuhiro*; Mochiku, Takashi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Ebata, Kazuhiro*; Takano, Yoshiki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Hosoya, Takaaki; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishigaki, Toru; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Sakuma, Takashi*; Tomota, Yo*; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; Hayashi, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki prefecture, the local government of the area for J-PARC site, was decided to build a versatile neutron diffractometer (IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer) to promote an industrial application for neutron beam in J-PARC. This diffractometer is planned to be a high throughput diffractometer so that materials engineers and scientists can use it like the chemical analytical instruments in their materials development process. It covers in d range 0.18  d (
d ( )
)  5 with
5 with  d/d = 0.16 % at high resolution bank, and covers
d/d = 0.16 % at high resolution bank, and covers  d (
d ( )
)  800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already beginning and will be completed in the beginning of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC. The current status for this instrument also will be reported.
800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already beginning and will be completed in the beginning of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC. The current status for this instrument also will be reported.
Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Hosoya, Takaaki; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki prefecture has started to construct IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer for industrial use at MLF, J-PARC. It is designed to achieve the efficiency which is more than 50 times larger than the present high performance diffractometer BIX-4. To realize this performance, the diffractometer will be installed on a coupled moderator has more intense peak but wider pulse shape than a decoupled one. It is expected that some neighbor Bragg spots will overlap partially each other along the time axis. We should develop the data reduction software system for the diffractometer including the program of peak de-convolution with fast algorism. The detector configuration should be also important to realize high performance for measurement speed and data accuracy. The strategy of data collection, the strategy of de-convoluting overlapped Bragg spots and its validity will be reported based on the results of the simulations with the original programs.
Tanaka, Ichiro*; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer is a new single-crystal neutron diffractometer for biological and chemical crystallography, and is now being constructed at J-PARC by Ibaraki Prefectural Government in Japan. This diffractometer is designed for the protein crystals with the cell dimension up to 135  . The measurement efficiency is more than 50 times larger than the present neutron diffractometer, BIX-3/BIX-4 in JRR-3 reactor at JAEA. To achieve this performance, we have selected a coupled moderator, and worked out the optimisation of the neutron guide tube. For the detector, a new wavelength-shifting-fiber type scintillation area detector system with high spatial (0.5-1.0 mm) and time (1ms-) resolution are in development.
. The measurement efficiency is more than 50 times larger than the present neutron diffractometer, BIX-3/BIX-4 in JRR-3 reactor at JAEA. To achieve this performance, we have selected a coupled moderator, and worked out the optimisation of the neutron guide tube. For the detector, a new wavelength-shifting-fiber type scintillation area detector system with high spatial (0.5-1.0 mm) and time (1ms-) resolution are in development.
Shobu, Takahisa; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Ariki, Katsuyoshi*; Choe, H.*; Takano, Yoshiki*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; Ebata, Kazuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
The TOF neutron biological diffractometer in J-PARC proposed by Ibaraki prefectural government is designed to cover the samples have their cell edges up to 135A, and to realize the efficiency is more than 50 times larger than the present high performance diffractometer, BIX-4. To achieve this performance, the diffractometer will be installed on a coupled moderator has more intense peak but wider pulse shape. The overlapping of Bragg spots along the time-axis expected should be considered for the determination of optic parameters and it is necessary to de-convolute the overlapped spots with higher accuracy. The original simulation programs of TOF diffraction data were developed to obtain information of spot-overlapping, completeness of Bragg spots and spot profiles along time-axis. In this paper, the consideration of important designed parameters focused on biological macromolecular and the strategy of de-convoluting overlapped spots will be reported based on the simulation results.
Ishigaki, Toru; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Sakuma, Takashi*; Tomota, Yo*; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki prefecture, the local goverment of the area for J-PARC site, was decided to build a versatile neutron diffractometer (IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer) to promote a industrial application for neutron beam in J-PARC. This diffractometer is planned to be a high throughput diffractometer so that materials engineers and scientists can use it like the chemical analytical instruments in their materials development process. It covers in d range 0.18  d (
d ( )
)  5 with
5 with 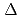
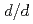 = 0.16% at high resolution bank, and covers 5
= 0.16% at high resolution bank, and covers 5  d (
d ( )
)  800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already begun and will be compleated in the beggining of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC.
800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already begun and will be compleated in the beggining of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC.
Ishigaki, Toru; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mori, Kazuhiro*; Mochiku, Takashi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Ebata, Kazuhiro*; Takano, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Hosoya, Takaaki; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki prefecture has started to construct IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer for industrial use at MLF, J-PARC. It is designed to achieve the efficiency which is more than 50 times larger than the present high performance diffractometer BIX-4. To realize this performance, the diffractometer will be installed on a coupled moderator has more intense peak but wider pulse shape than a decoupled one. It is expected that some neighbor Bragg spots will overlap partially each other along the time axis. The overlapping of Bragg spots should be considered for optimization of design parameters and it is necessary to de-convolute the overlapped spots. The three original simulation programs of TOF diffraction data with designed parameters of the diffractometer were developed to obtain information of spot-overlapping, completeness of Bragg spots and spot profiles along the time axis. The consideration of important designed parameters will be reported based on the simulation results.
Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Hosoya, Takaaki; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Hosoya, Takaaki; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki Prefectural Government in Japan has started to construct a TOF single crystal neutron diffractometer for biological macromolecules for industrial use at J-PARC. For this diffractometer, design of an efficient neutron transportation system is important because this diffractometer has 40m source-sample distance. Recently, we designed a supermirror neutron guide which can transport 0.7-3.8 Angstrom neutron efficiently. The total length of the mirror section is 25m. At the first 17m, the mirror has curvature (R=4300m) for horizontal direction in order to remove high-energy neutron and  ray. Simultaneously, all of the mirror section has tapered angle for vertical direction in order to reduce the frequency of neutron reflection at the surface of the supermirror. The neutron flux and profile at the sample position was calculated by Monte Carlo simulation softwares, McStas and IDEAS and compared with a curved, non-tapered guide we had designed previously. In result, the new supermirror system has 2 times gain for 0.7 Angstrom neutron and 1.5 times for 1.5 Angstrom neutron, and the beam profile at the sample position has a rectangular shape.
ray. Simultaneously, all of the mirror section has tapered angle for vertical direction in order to reduce the frequency of neutron reflection at the surface of the supermirror. The neutron flux and profile at the sample position was calculated by Monte Carlo simulation softwares, McStas and IDEAS and compared with a curved, non-tapered guide we had designed previously. In result, the new supermirror system has 2 times gain for 0.7 Angstrom neutron and 1.5 times for 1.5 Angstrom neutron, and the beam profile at the sample position has a rectangular shape.
Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Ariki, Katsuyoshi*; Choe, H.*; Takano, Yoshiki*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Choe, H.*; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Shobu, Takahisa; Ariki, Katsuyoshi*; Kinugasa, Hideyuki*; Takano, Yoshiki*; Sakashita, Masanobu*; Nakamura, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shobu, Takahisa; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Choe, H.*; Takano, Yoshiki*; Sakashita, Masanobu*; Nakamura, Akihiro*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kurita, Keisuke; Harayama, Isao; Iikura, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Post-installed anchors are a common technology used in seismic retrofitting work, and it is expected that their range of application will expand to include renovation work such as expansions and reconstructions. In this study, neutrons, which have an extremely high penetrating power for materials, were used to evaluate the long-term adhesion characteristics of post-installed anchors from the results of measuring the strain distribution of rebar under load, etc.