Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Konoplev, A.*; Golosov, V.*; Laptev, G.*; Namba, Kenji*; Onda, Yuichi*; Takase, Tsugiko*; Wakiyama, Yoshifumi*; Yoshimura, Kazuya
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 151(Part 3), p.568 - 578, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:87 Percentile:91.41(Environmental Sciences)Wakatsuki, Takuma; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Shiraishi, Junya; Ide, Shunsuke; Takase, Yuichi*
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 39E, p.P5.144_1 - P5.144_4, 2015/06
Wakatsuki, Takuma; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Shiraishi, Junya; Ide, Shunsuke; Takase, Yuichi*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(6), p.065005_1 - 065005_12, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Uzawa, Akiko*; Takase, Nobuhiro*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Noguchi, Miho; Koda, Kana*; Ozaki, Masakuni*; Yamashita, Kei*; Li, H.*; Kase, Yuki*; et al.
Mutation Research; Genetic Toxicology And Environmental Mutagenesis, 756(1-2), p.146 - 151, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:63.98(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Tojo, Hiroshi; Ejiri, Akira*; Hiratsuka, Junichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Takase, Yuichi*; Itami, Kiyoshi; Hatae, Takaki
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 7(4), p.P04005_1 - P04005_11, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)Tojo, Hiroshi; Ejiri, Akira*; Hiratsuka, Junichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Takase, Yuichi*; Itami, Kiyoshi; Hatae, Takaki
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.023507_1 - 023507_4, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:45.01(Instruments & Instrumentation) /
/
 3; Experiments on the LATE device and JT-60U tokamak
3; Experiments on the LATE device and JT-60U tokamakUchida, Masaki*; Maekawa, Takashi*; Tanaka, Hitoshi*; Ide, Shunsuke; Takase, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Fumitake*; Nishi, Seiji*
Nuclear Fusion, 51(6), p.063031_1 - 063031_9, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Uzawa, Akiko*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Noguchi, Miho; Kase, Yuki*; Takase, Nobuhiro*; Ito, Atsushi*; Koike, Sachiko*; Ando, Koichi*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.508 - 512, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.66(Environmental Sciences)We studied double-strand breaks (DSB) induction and rejoining in clamped and non-clamped transplanted tumours in mice leg after exposure to 80 keV/ m carbon ions and X-rays. The yields of DSB in the tumours were analysed by a static-field gel electrophoresis. The OER of DSB after X-rays was 1.68, and this value was not changed after 1 h rejoining time (1.40). These damages in oxygenated conditions were rejoined 60-70% within 1 h in situ. No difference was found between the exposure to X-rays and carbon ions for the induction and rejoining of DSB. Thus, the values of OER and rejoined fraction after exposure to carbon ions were similar to those after X-rays, and the calculated relative biological effectivenesses of carbon ion were around 1 under both oxygen conditions. The yields of DSB in vivo depend on exposure doses, oxygen conditions and rejoining time, but not on the types of radiation quality.
m carbon ions and X-rays. The yields of DSB in the tumours were analysed by a static-field gel electrophoresis. The OER of DSB after X-rays was 1.68, and this value was not changed after 1 h rejoining time (1.40). These damages in oxygenated conditions were rejoined 60-70% within 1 h in situ. No difference was found between the exposure to X-rays and carbon ions for the induction and rejoining of DSB. Thus, the values of OER and rejoined fraction after exposure to carbon ions were similar to those after X-rays, and the calculated relative biological effectivenesses of carbon ion were around 1 under both oxygen conditions. The yields of DSB in vivo depend on exposure doses, oxygen conditions and rejoining time, but not on the types of radiation quality.
 3; Experiments on the LATE device and JT-60U tokamak
3; Experiments on the LATE device and JT-60U tokamakUchida, Masaki*; Maekawa, Takashi*; Tanaka, Hitoshi*; Ide, Shunsuke; Takase, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Fumitake*; Nishi, Seiji*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
Moreau, D.*; Mazon, D.*; Walker, M. L.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Flanagan, S. M.*; Gohil, P.*; Groebner, R. J.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Schuster, E.*; Ou, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.465 - 467, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Mase, Atsushi*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takase, Yuichi*; Nakamura, Yukio*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(5), p.297 - 298, 2008/05
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Bialek, J.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yutaka; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1512 - 1523, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:63.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design of modification of JT-60U, JT-60SA, has been optimized in viewpoint of plasma control, and operation regimes have been evaluated. Upper and lower divertors with different geometry are prepared for flexibility of plasma shape control. The beam lines of negative-ion NBI are shifted downward for off-axis current drive, in order to obtain a weak/reversed shear plasma. The feedback control coils along the port hole in the stabilizing plate are found effective to suppress the resistive wall mode (RWM) and sustain high 
 close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
 = 2.4 MA,
= 2.4 MA, 
 = 4.4,
= 4.4, 
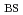 = 0.70,
= 0.70, 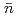
 /
/
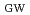 = 0.86, H
= 0.86, H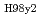 = 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration (
= 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration ( = 2.65). High
= 2.65). High 
 , high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
, high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kizu, Kaname; Kurita, Genichi; Masaki, Kei; Matsukawa, Makoto; Miura, Yukitoshi; Sakurai, Shinji; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.541 - 547, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)JT-60SA is positioned as the ITER satellite tokamak to conduct research elements to support and supplement ITER towards DEMO under the joint collaboration of Japan and EU. After the discussions in JA-EU Satellite Tokamak Working Group in 2005, the heating power is increased up to 41MW, 100s to ensure the ITER support research. With such increased heating power, the prospective plasma performances are analysed by the equilibrium and transport analysis codes. Operation window of a fully non-inductive current drive is extended to high density region. Simultaneous achievement of high equivalent Q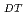 and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ito, Sanae*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Shinohara, Koji; Ejiri, Akira*; Takase, Yuichi*; Ido, Takeshi*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(10), p.1611 - 1625, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:80.61(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)It was found that the envelope of the ambient density fluctuation of the drift wave turbulence has spectral peaks aroound zonal flow frequencies. A method to detect the zonal flow using this characteristic was considered using the JFT-2M density fluctuation data. There is a possibility that the zonal flow will be able to be detected in the future burning plasmas by using the density fluctuations measured by some density fluctuation measurement by such as the microwave reflectometer and so on.
Sasao, Mamiko*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mase, Atsushi*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(9), p.779 - 782, 2007/09
This is a report of highlights from 2007 spring meetings of seven Topical Groups (TG) of International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA). In each meeting, high priority issues in physics of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and other burning plasma experiments have been discussed and investigated. Twenty-seven scientists from Japan have participated in those meetings. Dates and places of the meetings are shown below. (1) Diagnostics TG: 26-30 March, Princeton (USA), (2) Transport Physics TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (3) Confinement Database and Modeling TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (4) Edge Pedestal Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany) (5) Steady State Operation TG: 9-11 May, Daejeon (South Korea), (6)MHD TG: 21-24 May, San Diego (USA), (7) Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany).
 collapse after NBCD turn-off in JT-60U fully non-inductive reversed shear discharges
collapse after NBCD turn-off in JT-60U fully non-inductive reversed shear dischargesTakei, Nahoko; Nakamura, Yukiharu; Ushigome, Masahiro*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takechi, Manabu; Tobita, Kenji; Takase, Yuichi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Jardin, S. C.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(3), p.335 - 345, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.34(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Non-disruptive  -collapses with a regular intermittency have been observed after a forced turn-off of neutral beam current drive (NBCD) in JT-60U fully non-inductive, reversed shear (RS) discharges. Self-consistent transport simulations with improved core confinement and linear MHD stability analysis have first clarified that redistribution of return current induced after the NBCD turn-off lowers the safety factor of magnetic shear reversal, leading to the n =1 kink-ballooning instability with localized modes around internal transport barrier (ITB). It was also pointed out that an increase of the bootstrap current under continuous NB heating can lead to ITB reconstruction and thus causes subsequent beta-collapses.
-collapses with a regular intermittency have been observed after a forced turn-off of neutral beam current drive (NBCD) in JT-60U fully non-inductive, reversed shear (RS) discharges. Self-consistent transport simulations with improved core confinement and linear MHD stability analysis have first clarified that redistribution of return current induced after the NBCD turn-off lowers the safety factor of magnetic shear reversal, leading to the n =1 kink-ballooning instability with localized modes around internal transport barrier (ITB). It was also pointed out that an increase of the bootstrap current under continuous NB heating can lead to ITB reconstruction and thus causes subsequent beta-collapses.
Takase, Yuichi*; Ide, Shunsuke; Kamada, Yutaka; Kubo, Hirotaka; Mitarai, Osamu*; Nuga, Hideo*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takenaga, Hidenobu; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
A self-sustained state driven by the bootstrap current was achieved in JT-60U. Based on a high confinement reversed magnetic shear plasma, a plasma in which the bootstrap current frafciton of almost 100 percent (plasma current  0.55 MA) was successfully maintained for 2.5 s. The dynamic response of a completely self-driven system with negligible external current drive was studied. Repetition of beta collapses and recoveries were often observed. Furthermore, discharges in which the bootstrap current fraction can be expected to be larger than 100 percent were obtained.
0.55 MA) was successfully maintained for 2.5 s. The dynamic response of a completely self-driven system with negligible external current drive was studied. Repetition of beta collapses and recoveries were often observed. Furthermore, discharges in which the bootstrap current fraction can be expected to be larger than 100 percent were obtained.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Ido, Takeshi*; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Oasa, Kazumi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
We report on the potential/density fluctuations in the JFT-2M tokamak. We identified a geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) and its electric field structure. The GAM interacts with the background turbulence in consistent with a drift wave - zonal flow theory. The GAM modulates the turbulence, and the suppression depends on the direction and gradient of the flow velocity in consistent with a theory. During the H-mode, the GAM disappears presumably due to the suppression of the turbulence. We analysed the low frequency potential oscillation during the H-mode. A wavelet analysis showed a low frequency characteristic potential fluctuations (several handred kHz), which disappears in the L-mode and at the occurence of ELM. Observed poloidal flow is about 20 times as large as that of the GAM during the H-mode. If the potential has a spatial inhomogineity, there is a possibility that this low frequency fluctuation comes from the EXB flow or the zonal flow.