Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.937 - 941, 2023/11
In the J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), the 400MeV H beam is changed to H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced atKEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
beam is changed to H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3GeV. So far, RCS had used two types of charge exchange foil. One is the HBC (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon) foil and the other is the Kaneka GTF (Graphene Thin Film). HBC foil is a patented deposition method developed at KEK for the stable production of thick carbon foil. Initially, the RCS used HBC foil produced atKEK. However, in 2017, JAEA had started HBC foil production and has been using it since then. Recently, we have succeeded in depositing thick pure carbon foil, which had been considered difficult to produce by the arc deposition method. As a new challenge, this pure carbon foil was used in the user operation from March 2023. As a result, Pure carbon foils showed less deformation and more stable charge exchange performance than HBC and GTF.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Takeda, Osamu*; Saeki, Riuji*; Muto, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.629 - 633, 2023/01
In the J-PARC 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), a 400 MeV H- beam injected from the linac is exchange to an H+ beam by a charge exchange foil and accelerated to 3 GeV. The charge exchange foils mainly used in the RCS are HBC foil (Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil), which are made by adding a small amount of boron to carbon rods and using them as electrodes by the arc deposition method. Since 2018, foils produced by JAEA have been used for user operation. So far, no major problems have occurred due to the foils. Meanwhile, the beam power of the RCS has been gradually increased from 500 kW to 830 kW since 2018. As beam power increases, the foil issues were identified to achieve the RCS design power of 1 MW. In this paper, we will report on the recent foil usage status and issue in the user operation.
 Te
Te
Wang, Y.*; Kajihara, Shun*; Matsuoka, Hideki*; Saika, B. K.*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Ishizaka, Kyoko*; Iwasa, Yoshihiro*; Nakano, Masaki*
Nano Letters, 22(24), p.9964 - 9971, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:84.45(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Matsuoka, Hideki*; Barnes, S. E.*; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Bahramy, M. S.*; Saika, B. K.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Wang, Y.*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(4), p.1807 - 1814, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:76.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) V
V Te
Te
Sumida, Kazuki*; Kakoki, Masaaki*; Reimann, J.*; Nurmamat, M.*; Goto, Shinichi*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Kokh, K. A.*; Tereshchenko, O. E.*; G dde, J.*; et al.
dde, J.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 21(9), p.093006_1 - 093006_8, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary) ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studiesSakamoto, Shoya*; Tu, N. T.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; Wakabayashi, Yuki K.*; Shibata, Goro*; Horio, Masafumi*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
Shikin, A. M.*; Estyunin, D. A.*; Surnin, Yu. I.*; Koroleva, A. V.*; Shevchenko, E. V.*; Kokh, K. A.*; Tereshchenko, O. E.*; Kumar, S.*; Schwier, E. F.*; Shimada, Kenya*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.4813_1 - 4813_17, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:70.89(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamakawa, Emi*; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Miki, Nobuharu*; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Horino, Koki*; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; et al.
ANS RPSD 2018; 20th Topical Meeting of the Radiation Protection and Shielding Division of ANS (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2018/08
The existing beam power of the J-PARC Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500 kW, and higher radiation doses are concentrated in the injection area. These activations are caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce dose exposure to workers near the injection point, we study a new design of the injection scheme. Experience has shown that eddy currents are generated in the metal flange near the magnet owing to the pulsed magnetic field, and the temperature exceeds 100 degrees C. The shield installed in the new injection system needs to have a layer structure, in which an insulator is inserted between iron shields to reduce the eddy current. From the results of the shielding calculation, even if 1 mm of polyethylene was inserted between two 9-mm-thick SUS 316 plates, which serve as shielding material, the shielding performance was reduced only about 5%, and we confirmed that it would function well.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takeda, Osamu*; Miki, Nobuharu*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.374 - 378, 2017/12
The 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) aims to deliver 1-MW proton beam to the neutron target and Main Ring synchrotron. Present beam power of the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500-kW and the higher radiation doses were concentrated in the injection area. These activations were caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce the worker dose near the injection point, we have studied a new design of the injection scheme to secure enough space for radiation shielding and bellows. In the new system, two of four injection pulse bump magnets are replaced and we are able to ensure the additional space around the injection foil chamber. So far, new injection system seems not impossible. However, preliminary study result indicated that temperature of the duct and shielding metals would be slightly higher. The eddy current due to the shift bump magnet field generates heat. Thus we have to study details of above effect.
 -decaying millisecond isomeric state in
-decaying millisecond isomeric state in 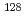 Cd
Cd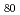
Jungclaus, A.*; Grawe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lorusso, G.*; Simpson, G. S.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Taprogge, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Taprogge, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 772, p.483 - 488, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:54.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takeda, Osamu*; Miki, Nobuharu*
Proceedings of 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '17) (Internet), p.579 - 581, 2017/05
The 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex aims to deliver 1-MW proton beam to the neutron target and Main Ring synchrotron. Present beam power of the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron is up to 500-kW and the higher radiation doses were concentrated in the injection area. These activations were caused by the interaction between the foil and the beam. To reduce the worker dose near the injection point, we have studied a new design of the injection scheme to secure enough space for radiation shielding and bellows. In the new system, two of four injection pulse bump magnets are replaced and we are able to ensure the additional space around the injection foil chamber. So far, new injection system seems not impossible. However, preliminary study result indicated that temperature of the duct and shielding metals would be slightly higher. The eddy current due to the shift bump magnet field generates heat. Thus we have to study details of above effect.
Sekine, Yurina; Endo, Hitoshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Takeda, Shigeo*; Mukai, Sadaatsu*; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Littrell, K. C.*; Sasaki, Yoshihiro*; Akiyoshi, Kazunari*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 120(46), p.11996 - 12002, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:29.31(Chemistry, Physical)The detailed structure of a nanogel formed by self-association of cholesterol-bearing pullulans (CHP) was determined by contrast variation small-angle neutron scattering. The decomposition of scattering intensities into partial scattering functions of each CHP nanogel component, i.e., pullulan, cholesterol, and the cross-term between the pullulan and the cholesterol allows us to investigate the internal structure of the nanogel. The effective spherical radius of the skeleton formed by pullulan chains was found to be about 8.1 nm. In the CHP nanogel, there are about 19 cross-linking points where a cross-linking point is formed by aggregation of trimer cholesterol molecules with the spatially inhomogeneous distribution of the mass fractal dimension of 2.6. The average radius of the partial chains can also be determined to be 1.7 nm. As the result, the complex structure of the nanogels is coherently revealed at the nanoscopical level.
 decay of semi-magic
decay of semi-magic 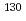 Cd; Revision and extension of the level scheme of
Cd; Revision and extension of the level scheme of 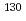 In
InJungclaus, A.*; Grawe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lorusso, G.*; Simpson, G. S.*; S derstr
derstr m, P. A.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Taprogge, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; et al.
m, P. A.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Taprogge, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(2), p.024303_1 - 024303_8, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:77.17(Physics, Nuclear) rays emitted from excited states south-east of
rays emitted from excited states south-east of  Sn; The
Sn; The  g
g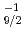
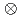
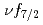 multiplet of
multiplet of  In
In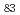
Jungclaus, A.*; Gargano, A.*; Grawe, H.*; Taprogge, J.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lorusso, G.*; Shimizu, Y.*; Simpson, G. S.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(4), p.041301_1 - 041301_6, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:77.17(Physics, Nuclear)Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yamakawa, Emi*; Takeda, Osamu; Yamamoto, Kazami; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.938 - 943, 2015/09
In the 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), we adopted the multi-turn charge exchange injection scheme using the stripper foils to achieve the high power proton beam. Therefore it is difficult to suppress the interaction between the stripper foils and the beam theoretically. And then, there are high residual dose around the stripper foil. From the measurements of the residual dose distribution and simulations using the PHITS, it is identified that secondary particles produced in the nuclear reactions with the foil had caused the high residual activity around there. And then, it was clear that the beam loss caused by the H particles which were converted from the injected H
particles which were converted from the injected H particles by the residual-gas stripping generates the localized high peak residual dose. In this presentation, we report the current status and the cause of the residual dose at the injection area in the RCS.
particles by the residual-gas stripping generates the localized high peak residual dose. In this presentation, we report the current status and the cause of the residual dose at the injection area in the RCS.
 thin films
thin filmsIshigami, Keisuke*; Yoshimatsu, Kohei*; Toyota, Daisuke*; Takizawa, Masaru*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Shibata, Goro*; Harano, Takayuki*; Takahashi, Yukio*; Kadono, Toshiharu*; Verma, V. K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 92(6), p.064402_1 - 064402_5, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:84.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)