Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Beerwerth, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(44), p.14609 - 14613, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:69.40(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
 at the single-atom level
at the single-atom levelSteinegger, P.*; Asai, Masato; Dressler, R.*; Eichler, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Piguet, D.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(13), p.7122 - 7132, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:63.01(Chemistry, Physical)A new experimental method "vacuum chromatography" has been developed to measure adsorption enthalpy of superheavy elements, and its feasibility has been examined using short-lived thallium isotopes. The short-lived thallium isotopes were produced at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The thallium ion beam prepared with an on-line isotope separator which ionized and mass-separated the thallium isotopes was injected into an isothermal vacuum chromatography apparatus. A temperature-dependent adsorption property of thallium atom on SiO surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
 = 102)
= 102)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Vascon, A.; Takeda, Shinsaku; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the IP of the heavy elements, we have developed a novel measurement method based on a surface ionization technique by using a surface ionization ion source coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system for an Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. In this work, we have determined IP value of No by using the method. In a surface ionization process, an ionization efficiency of an atom depends on its IP. To obtain a relationship between IP and ionization efficiency in present system, we measured ionization efficiencies of various short-lived isotopes. Ionization efficiency of
gas-jet transport system for an Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. In this work, we have determined IP value of No by using the method. In a surface ionization process, an ionization efficiency of an atom depends on its IP. To obtain a relationship between IP and ionization efficiency in present system, we measured ionization efficiencies of various short-lived isotopes. Ionization efficiency of  No produced in the
No produced in the  Cm(
Cm( C, 4n) reaction was also measured. Measured ionization efficiency of
C, 4n) reaction was also measured. Measured ionization efficiency of  No was 0.8%, which yields IP value of No to be 6.6 eV. This value is in a good agreement with the value which has been evaluated by extrapolation from those of the lighter actinide elements, 6.65 eV.
No was 0.8%, which yields IP value of No to be 6.6 eV. This value is in a good agreement with the value which has been evaluated by extrapolation from those of the lighter actinide elements, 6.65 eV.
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Nagai, Yasuki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Takeda, Shinsaku*
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of  Y (T
Y (T = 64 h), which has been used for the nuclear medicine. Enriched
= 64 h), which has been used for the nuclear medicine. Enriched  Zr nitrate samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the
Zr nitrate samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron.
C(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron.  Y was successfully produced via the (n, p) reaction, and separated from the Zr nitrate target by three columns method with a hydrochloric acid. After the purification, a labelling of DTPA with
Y was successfully produced via the (n, p) reaction, and separated from the Zr nitrate target by three columns method with a hydrochloric acid. After the purification, a labelling of DTPA with  Y had been performed. In this result, the yield was about 90% under
Y had been performed. In this result, the yield was about 90% under  2.5
2.5  M of DTPA, although the yields were decreased at the DTPA concentration below 2.5
M of DTPA, although the yields were decreased at the DTPA concentration below 2.5  M.
M.
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kin, Tadahiro*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Kawabata, Masako; Saeki, Hideya; et al.
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64. Enriched Mo-100, Zr-90, Zn-68 and Zn-64 oxide samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the
C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the  -rays. Particularly, yields of impurity radionuclides were much smaller than that of Mo-99 and Cu-67, and therefore radioactive waste produced during chemical processing would be reduced compared with other proposed reaction systems. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
-rays. Particularly, yields of impurity radionuclides were much smaller than that of Mo-99 and Cu-67, and therefore radioactive waste produced during chemical processing would be reduced compared with other proposed reaction systems. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
 Y with fast neutrons by the Be(p,n) reaction
Y with fast neutrons by the Be(p,n) reactionTakeda, Shinsaku; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Nagai, Yasuki; Sakama, Minoru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 = 102)
= 102)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Takeda, Shinsaku; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Makii, Hiroyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
We successfully determined the first ionization energy (IE) of nobelium (No,  = 102) using a short-lived No isotope,
= 102) using a short-lived No isotope,  No produced in the
No produced in the Cm(
Cm( C, 4n) reaction, based on the IE dependence of the ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process. The IE value of No was evaluated to be 6.6 eV. This value is in a good agreement with the value which has been estimated by an extrapolation from those of the lighter actinide elements, 6.65 eV.
C, 4n) reaction, based on the IE dependence of the ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process. The IE value of No was evaluated to be 6.6 eV. This value is in a good agreement with the value which has been estimated by an extrapolation from those of the lighter actinide elements, 6.65 eV.
 SO
SO with Aliquat336 as homologues of seaborgium (Sg)
with Aliquat336 as homologues of seaborgium (Sg)Mitsukai, Akina; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Kaneya, Yusuke; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have started studying sulphate-complex formation of a transactinide element, seaborgium (Sg). In this study, we report on the extraction behavior of carrier-free radioisotopes  Mo and
Mo and  W which are lighter homologs of Sg, from aqueous H
W which are lighter homologs of Sg, from aqueous H SO
SO solution with amine extractant, Aliquat336, dissolved in toluene by a batch method. These radioisotopes were produced in the
solution with amine extractant, Aliquat336, dissolved in toluene by a batch method. These radioisotopes were produced in the  Zr(
Zr( ,
,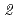 )
) Mo and
Mo and  Ta(
Ta(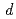 ,x
,x )
) W reactions at the RIKEN K70 AVF cyclotron. Results of the extraction experiments showed that the distribution ratios of Mo and W increase sharply above ~3.0 M H
W reactions at the RIKEN K70 AVF cyclotron. Results of the extraction experiments showed that the distribution ratios of Mo and W increase sharply above ~3.0 M H SO
SO . Based on the slope analysis, it was indicated that anionic sulphate-complex of [MO
. Based on the slope analysis, it was indicated that anionic sulphate-complex of [MO (SO
(SO )
) ]
] (M = Mo, W) are formed in
(M = Mo, W) are formed in  5 M H
5 M H SO
SO . These results suggest that the present system is applicable to the extraction of Sg.
. These results suggest that the present system is applicable to the extraction of Sg.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Vascon, A.*; Sakama, Minoru*; Sato, Daisuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
Nagame, Yuichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
del, M.*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Vascon, A.*; Sakama, Minoru*; Sato, Daisuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.