Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 n eigenmodes in reversed shear plasmas in JT-60U negative-ion-based neutral beam injection discharges
n eigenmodes in reversed shear plasmas in JT-60U negative-ion-based neutral beam injection dischargesTakechi, Manabu; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Ishikawa, Masao; Cheng, C. Z.*; Shinohara, Koji; Ozeki, Takahisa; Kusama, Yoshinori; Takeji, Satoru*; Fujita, Takaaki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 12(8), p.082509_1 - 082509_7, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:71.2(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Rapid frequency sweeping modes observed in reversed magnetic shear (RS) plasmas on the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute Tokamak 60 Upgrade (JT-60U) have been identified as Reversed-Shear-induced Alfv n Eigenmodes (RSAEs), which are ideal MHD Alfv
n Eigenmodes (RSAEs), which are ideal MHD Alfv n eigenmodes (AEs) localized to the region of minimum safety factor,
n eigenmodes (AEs) localized to the region of minimum safety factor,  , and are excited by negative-ion-based neutral beam injection. The chirping and subsequent saturation of the mode frequency are consistent with theoretical predictions for the transition from RSAEs to Toroidal Alfv
, and are excited by negative-ion-based neutral beam injection. The chirping and subsequent saturation of the mode frequency are consistent with theoretical predictions for the transition from RSAEs to Toroidal Alfv n eigenmodes (TAEs). The previously observed rapid frequency sweeping modes in ion cyclotron wave heated plasmas in JT-60U can also be similarly explained. The observed AE amplitude is largest during the transition from RSAEs to TAEs, and fast ion loss is observed when the AE amplitude is largest at this transition. It is preferable to operate outside the transition range of
n eigenmodes (TAEs). The previously observed rapid frequency sweeping modes in ion cyclotron wave heated plasmas in JT-60U can also be similarly explained. The observed AE amplitude is largest during the transition from RSAEs to TAEs, and fast ion loss is observed when the AE amplitude is largest at this transition. It is preferable to operate outside the transition range of 
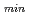 , e.g., 2.4
, e.g., 2.4 

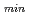
 2.7 for the n = 1 AE to avoid substantial fast ion loss in RS plasmas.
2.7 for the n = 1 AE to avoid substantial fast ion loss in RS plasmas.
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Oyama, Naoyuki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Chankin, A. V.; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Shinohara, Koji; Takeji, Satoru
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1250 - 1257, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:46.47(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kurita, Genichi; Tsuda, Takashi; Azumi, Masafumi; Ishida, Shinichi; Takeji, Satoru*; Sakasai, Akira; Matsukawa, Makoto; Ozeki, Takahisa; Kikuchi, Mitsuru
Nuclear Fusion, 43(9), p.949 - 954, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:67.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to improve economic and environmental suitability of tokamak fusion reactors, both the accomplishment of high beta plasmas and the practical use of low activation materials to reduce the amount of radioactive waste are crucially important. Low radio-activation ferritic steel is considered as a most promising candidate for structural material in DEMO reactors, and there is the possibility of reduction of critical beta value by the deterioration of MHD stability due to ferromagnetism of ferritic steel. This paper investigates the effect of ferromagnetism with plasma flow on the beta limit of tokamak plasma by carrying out MHD stability analyses including ferromagnetic and plasma flow effects.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.14(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Chankin, A. V.; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Fukuda, Takeshi; Isayama, Akihiko; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kamada, Yutaka; Kubo, Hirotaka; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nakano, Tomohide; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316, p.828 - 833, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:78.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In JT-60U, extensive plasma-neutral exchange during a typical type I ELM leads to a transient increase in the total number of charged particles in the plasma. The density rise is especially large at the edge, with the increase in the inner vertical interferometer signal (FIR1) of up to 40%, in the case of a giant ELM. Fast measurements of edge plasma density, electron temperature, magnetic fluctuations and Bremsstrahlung emission have been conducted to study the dynamics of the ELM evolution. In order to pinpoint the exact location of the density rise, a dedicated set of experiments with the horizontal plasma sweep to scan the separatrix position at the inner midplane with respect to the FIR1 chord, has been carried out at different wall conditions.
Tobita, Kenji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Shinohara, Koji; Nishitani, Takeo; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kramer, G. J.*; Nemoto, Masahiro*; Kondoh, Takashi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.315 - 326, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)Energetic particle experiments in JT-60U are summarized, mainly covering ripple loss and Alfven eigenmodes (AE modes). Significant loss was observed for 85 keV NBI ions and fusion-produced tritons increased when toroidal field ripple at the plasma surface, especially in reversed shear plasma. Measurement of hot spots on the first wall due to ripple loss confirmed agreement with code predictions, validating the modeling incorporated in an orbit-following Monte Carlo code. A variety of AE modes were destabilized in ICRF minority heating and negative-ion-based NBI (N-NBI) heating. Most of the observed modes are gap modes identified to be TAE, EAE and NAE. Interesting finding is pulsating modes accompanying frequency sweep, which were destabilized by N-NBI and sometimes induced a beam ion loss of up to 25%. Also presented are energetic particle issues in auxiliary heating with ICRF and N-NBI.
Fukuda, Takeshi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Takeji, Satoru; Isayama, Akihiko; Kawano, Yasunori; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Nagashima, Akira; Nishitani, Takeo; Konoshima, Shigeru; Tamai, Hiroshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.357 - 367, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takeji, Satoru; Isayama, Akihiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tokuda, Shinji; Ishii, Yasutomo; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Ishida, Shinichi; Kamada, Yutaka; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Yoshino, Ryuji; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.278 - 297, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:6.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Ishida, Shinichi; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirai, Hiroshi; Koide, Yoshihiko; Fukuda, Takeshi; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.185 - 254, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:48.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)With the main aim of providing physics basis for ITER and the steady-state tokamak reactors, JT-60/JT-60U has been developing and optimizing the operational concepts, and extending the discharge regimes toward sustainment of high integrated performance in the reactor relevant parameter regime. In addition to achievement of the equivalent break-even condition (QDTeq up to 1.25) and a high fusion triple product = 1.5E21 m-3skeV, JT-60U has demonstrated the integrated performance of high confinement, high beta-N, full non-inductive current drive with a large fraction of bootstrap current in the reversed magnetic shear and in the high-beta-p ELMy H mode plasmas characterized by both internal and edge transport barriers. The key factors in optimizing these plasmas are profile and shape controls. As represented by discovery of various Internal Transport Barriers, JT-60/JT-60U has been emphasizing freedom and restriction of profiles in various confinement modes. JT-60U has demonstrated applicability of these high confinement modes to ITER and also clarified remaining issues.
Chankin, A. V.; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Fukuda, Takeshi; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Miura, Yukitoshi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takeji, Satoru; Takenaga, Hidenobu
Nuclear Fusion, 42(6), p.733 - 742, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:55.84(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Iio, Shunji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Ozeki, Takahisa; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Takase, Yuichi*; Takeji, Satoru*; Tobita, Kenji; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Miyamoto, Kenro*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(6), P. 601, 2002/06
no abstracts in English
Neudatchin, S. V.; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takeji, Satoru
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 44(5A), p.A383 - A389, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Takeji, Satoru; Tokuda, Shinji; Kurita, Genichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Takechi, Manabu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(5), p.447 - 454, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Takeji, Satoru; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Fukuda, Takeshi; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 42(2), p.180 - 186, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:68.29(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Takeji, Satoru; Tokuda, Shinji; Fujita, Takaaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishii, Yasutomo; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Matsumoto, Taro; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 42(1), p.5 - 13, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:89.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ichige, Hisashi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kato, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of 19th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering (SOFE), p.221 - 225, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Ozeki, Takahisa; Takeji, Satoru; Iio, Shunji*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 77(11), P. 1165, 2001/11
The 13th ITER physics R&D expert meeting on MHD, Disruption and Control was held on Funchal of Madeira island, Portugal, in June 25-26 after 28th European Physical Society meeting. The eighteen members of the physics R&D experts and of Joint Central team of ITER were attened the meeting. They reconsidered the disruption data base and discussed recent progresses of the stability of long pulse discharges and the influence on the plasma confinement. They also give some suggestions to the ITER design. The report describes the summary of discussions.