Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01033_1 - 01033_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:70.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Ni and
Ni and  Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV
Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeVTakeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.17 - 27, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.47(Instruments & Instrumentation)To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems and so on, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations, JENDL/HE-2007 and so on.
Nakano, Keita; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugawara, Takanori; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-018, 41 Pages, 2022/03
Neutronic analysis of beam window of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducted using PHITS and DCHAIN-PHITS codes. We investigate gas production of hydrogen and helium isotopes in the beam window, displacement per atom of beam window material, and heat generation in the beam window. In addition, distributions of produced nuclides, heat density, and activity are derived. It was found that at the maximum 12500 appm H production, 1800 appm He production, and damage of 62.1 DPA occurred in the beam window by the ADS operation. On the other hand, the maximum heat generation in the beam window was 374 W/cm . In the analysis of LBE,
. In the analysis of LBE,  Bi and
Bi and  Po were found to be the dominant nuclides in decay heat and radioactivity. Furthermore, the heat generation in the LBE by the proton beam was maximum around 5 cm downstream of the beam window, which was 945 W/cm
Po were found to be the dominant nuclides in decay heat and radioactivity. Furthermore, the heat generation in the LBE by the proton beam was maximum around 5 cm downstream of the beam window, which was 945 W/cm .
.
Nakano, Keita; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-014, 25 Pages, 2022/03
For the development of accelerator-driven transmutation system (ADS), measurement of nuclide production cross-sections in proton-induced reactions on  Be, C,
Be, C,  Al,
Al,  Sc, and V have been performed. The measured data are compared with the calculations by the latest nuclear reaction models and with the nuclear data library to investigate the reproducibilities.
Sc, and V have been performed. The measured data are compared with the calculations by the latest nuclear reaction models and with the nuclear data library to investigate the reproducibilities.
 Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protons
Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protonsTakeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.207 - 212, 2022/03
Prediction of nuclide production of spallation products by high-energy proton injection plays a fundamental and important role in shielding design of high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS). Since the prediction accuracy of the nuclear reaction models used in the production quantity prediction simulation is insufficient, it is necessary to improve the nuclear reaction models. We have measured nuclide production cross sections for various target materials with the aim of acquiring experimental data and improving nuclear reaction models. In this study, 1.3-, 2.2- and 3.0-GeV proton beams were irradiated to  Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.30 - 41, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:68.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nuclide production cross sections for proton-induced reactions on Mn and Co at incident energies of 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV were measured by the activation method at the J-PARC. In total, 143 production cross sections of reaction products were obtained. Among them, the cross sections of  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) S and
S and  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011045_1 - 011045_6, 2021/03
To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr, which were candidate materials to be used in ADS, were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations and JENDL/HE-2007.
 Fe for 0.4-3.0 GeV protons in J-PARC
Fe for 0.4-3.0 GeV protons in J-PARCMatsuda, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011047_1 - 011047_6, 2021/03
Accurate nuclide production cross-section data are required for the design of Accelerator-Driven nuclear transmutation System (ADS) such as the design of radioactive waste disposal, design of remote-handling procedure of highly activated components, and evaluation of exposure doses of rad-workers. Although much efforts have been devoted to nuclide production cross-section measurements so far, uncertainties of the measured data are sometimes large as several tens percentage, and there is no experimental data in the GeV energy region even for some of important nuclides. In this study, proton induced nuclide production cross-section of iron, which is the most important constituent element of steel, was measured. The present experiment was compared with calculations by the PHITS code with several physics models including Bertini and INCL4.6 and evaluated nuclear data JENDL-HE/2007. The most significant discrepancy found in this study was the production cross sections via the (p,xn) reaction. It was suggested that further improvements, such as the in-medium effect on the nucleon-nucleon scattering and the Pauli blocking, were required in the intra-nuclear cascade models used in this study.
 for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protons
for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protonsMatsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 483, p.33 - 40, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)A thick target neutron yield for a mercury target at an angle of 180 from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
 produced from thick mercury target irradiated with 3 GeV protons
produced from thick mercury target irradiated with 3 GeV protonsMatsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*
no journal, ,
Even though the neutron spectrum produced to most backward along the proton beam direction is essential for the shield design for Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) and high-intensity spallation neutron source, the experimental data are scarce. For the validation of source term of radiation, we have measured the energy spectrum of the neutron emitted to the most backward angle of 180 produced from mercury target irradiated with 3 GeV proton at the Material Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. In the experiment, the spectrum was measured by time-of-flight (TOF) method with the liquid scintillator (NE213) placed at the upstream of the bending magnet with flight-path of 126 m to the mercury target in order to obtain high energy resolution. In order to obtain low energy neutron around at 1 MeV, a small scintillator was employed. The neutron detection efficiency was calculated with the SCINFUL-R code with the correction of experimental result with
produced from mercury target irradiated with 3 GeV proton at the Material Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. In the experiment, the spectrum was measured by time-of-flight (TOF) method with the liquid scintillator (NE213) placed at the upstream of the bending magnet with flight-path of 126 m to the mercury target in order to obtain high energy resolution. In order to obtain low energy neutron around at 1 MeV, a small scintillator was employed. The neutron detection efficiency was calculated with the SCINFUL-R code with the correction of experimental result with  Cf source in low energy region less than 10 MeV. It was found that the PHITS calculation with INCL4.6 and GEM is in good agreement with the experiment in the energy reason less than 20 MeV.
Cf source in low energy region less than 10 MeV. It was found that the PHITS calculation with INCL4.6 and GEM is in good agreement with the experiment in the energy reason less than 20 MeV.
Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
Accelerator-driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS) is one of the promising options to solve the nuclear issue of the high-level radioactive waste disposal. Nuclide production cross sections of Pb and Bi, which play an important role as a spallation target and coolant, are necessary to evaluate the residual activity and to investigate the behavior of impurities. In this presentation, measured nuclide production cross sections of Bismuth by GeV proton irradiation will be presented together with theoretical calculations.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
For the purpose of improving nuclear design of high-energy and high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as the accelerator-driven transmutation system (ADS), proton-induced nuclide production cross section was measured, and the results were compared with nuclear reaction models and evaluated nuclear data. We will report the nuclide production cross section for Ni which is used as the proton beam window material for ADS.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
For the purpose of improving nuclear design of high-energy and high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as the accelerator-driven transmutation system (ADS), proton-induced nuclide production cross section was measured, and the results were compared with nuclear reaction models and evaluated nuclear data. We will report the nuclide production cross section for Zr and Ag.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki
no journal, ,
For the improvement of nuclear design for Accelerator-Driven System (ADS), a production cross-section with higher accuracy is required. For data acquisition around 1 GeV energy range at J-PARC, protons in the energy region from 0.4 to 3.0 GeV were irradiated on Ag and Ta. Experiment and analysis methods were employed that were presented in the AESJ2018 autumn meeting. They were compared with the calculated data by PHITS code, and the one by the latest intranuclear cascade model INCL++ and a statistical decay model ABLA07. It was found that calculations for the 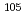 Ag,
Ag, 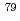 Kr, and
Kr, and 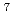 Be production cross-sections with INCL-4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, and INCL-6.0/ABLA07 could predict the experimental data within a factor 0.5 to 2. On the other hand, in the case of
Be production cross-sections with INCL-4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, and INCL-6.0/ABLA07 could predict the experimental data within a factor 0.5 to 2. On the other hand, in the case of 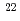 Na,
Na, 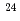 Na, and
Na, and 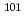 Rh cross sections, all calculations showed huge overestimation or underestimation. In order to increase lighter nuclides such as Be and Na, we adopted a statistical multifragmentation model in the calculation. Although the calulcation was slightly improved still it has a large discrepancy in the experiment. Thus, a modification of the intra-nuclear cascade model was required, which is to be performed.
Rh cross sections, all calculations showed huge overestimation or underestimation. In order to increase lighter nuclides such as Be and Na, we adopted a statistical multifragmentation model in the calculation. Although the calulcation was slightly improved still it has a large discrepancy in the experiment. Thus, a modification of the intra-nuclear cascade model was required, which is to be performed.
Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
Prediction of nuclide production of spallation products by high-energy proton injection plays a fundamental and important role in shielding design of high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS). Since the prediction accuracy of the nuclear reaction models used in the production quantity prediction simulation is insufficient, it is necessary to improve the nuclear reaction models. We have measured nuclide production cross sections for various target materials with the aim of acquiring experimental data and improving nuclear reaction models. In this study, 1.3-, 2.2- and 3.0-GeV proton beams were irradiated to two medium-heavy targets, i.e., Mn and Co, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes (INCL-4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JAM/GEM, INCL++/ABLA07) and the high energy nuclear data library JENDL/HE-2007 to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.