Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0Hydrogen(H) embrittlement in high-strength aluminum(Al) alloys is a crucial problem. H accumulation at the interface of precipitates in Al alloy is considered to cause embrittlement. However, there is no quantitative knowledge regarding the interaction between H distribution and stress field near cracks. In this study, using a multi-modal three-dimensional image-based simulation combining the crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis, we tried to capture the stress distribution near the crack, its influence on the H distribution, and the probability of crack initiation in the experimental condition. As a result, it was found that grain boundary cracks transition to quasi-cleavage cracks in the region where the cohesive energy of the semi-coherent interface of MgZn precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Higa, Ryota*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
Keikinzoku, 73(11), p.530 - 536, 2023/11
In Al-Zn-Mg alloys, suppression of hydrogen embrittlement is necessary to improve their strength. In this study, the distribution of stress, strain, and hydrogen concentration in the actual fracture region was investigated using the crystal plasticity finite element method and hydrogen diffusion analysis based on a model derived from three-dimensional polycrystalline microstructural data obtained by X-ray CT. In addition, the distributions of stress, strain, and hydrogen concentration were compared with the actual crack initiation behavior by combining in-situ observation of tensile tests using X-ray CT and simulation. The results show that stress loading perpendicular to the grain boundary due to crystal plasticity dominates grain boundary crack initiation. It was also found that internal hydrogen accumulation due to crystal plasticity has little effect on crack initiation.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Nishijima, Masahiko*; Kamada, Yasuhiro*
Corrosion, 79(8), p.818 - 830, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)7xxx aluminum alloys are representative high-strength aluminum alloys; however, mechanical property degradation due to hydrogen hinders further strengthening. We propose the dispersion of Mn-based second-phase particles as a novel technique for preventing 7xxx aluminum alloy hydrogen embrittlement. In this study, the deformation and fracture behaviors of high hydrogen 7xxx alloys containing 0.0% Mn and 0.6% Mn are observed in situ using synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography. The obtained macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement is quantitatively analyzed based on hydrogen partitioning in alloys. Adding 0.6% Mn, generating second-phase particles with high hydrogen trapping abilities, significantly suppresses hydrogen-induced quasicleavage fracture.
Miyagawa, Akihisa*; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 95(4), p.566 - 568, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.81(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We demonstrate that pKa of extractant impregnated in a polymer phase varies with the cross-linking degree and the coexistence of other extractants, which induces a change in the hydrophobicity of the polymer phase. The results presented herein will be beneficial for the development of novel solid-extraction adsorbents.
 hydrogen partitioning control
hydrogen partitioning controlToda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Su, H.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 105(2), p.240 - 253, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O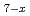 and its superconductive phase transition
and its superconductive phase transitionSuzuki, Takuya*; Takano, Hidekazu*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Kentaro*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Suzuki, Yoshio*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 36, p.249 - 257, 2005/03
no abstracts in English