Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Aine*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Ishii, Koji*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Takeuchi, Yasunao*; Sato, Yoichi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.19 - 23, 2023/01
In the J-PARC main ring, density modulation due to longitudinal beam instability occurs during the debunching process of coasting beams. This leads to the generation of an electron cloud, which in turn causes transverse beam instabilities. The transverse beam instability causes beam loss and the electron cloud is assumed to cause vacuum degradation, both of which hinder the beam intensity enhancement, so it is essential to clarify the causes and countermeasures. In particular, the longitudinal impedance of several hundred MHz has been investigated as relevant, and measures to reduce the impedance of individual devices are underway. The Eddy-current type septum magnet, newly installed this year, was found to have a large impedance by simulation. Therefore, we are investigating a method to reduce the impedance by a flange loaded with SiC radio wave absorber, which can be applied to locations where there is no spatial margin to install a taper. In this report, we will discuss the characterization of SiC to be used in actual devices, impedance simulation reflecting the results of SiC evaluation, and evaluation of the effect of impedance countermeasures by impedance measurement using the wire method, and progress in evaluating the effect on the beam by beam simulation and beam study.
Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Takeuchi, Erina; Nishimura, Shusaku; Muto, Kotomi*; Matsunaga, Takeshi*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106725_1 - 106725_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.09(Environmental Sciences)To understand the spatial variation in soil  Cs inventory in complex mountainous topography, a whole-area investigation of
Cs inventory in complex mountainous topography, a whole-area investigation of  Cs deposition in a broad-leaved forest catchment of a mountain stream was conducted using grid sampling. Across the catchment, organic and surface mineral soil layers were collected at 42 locations in 2013 and 6 locations in 2015.
Cs deposition in a broad-leaved forest catchment of a mountain stream was conducted using grid sampling. Across the catchment, organic and surface mineral soil layers were collected at 42 locations in 2013 and 6 locations in 2015.  Cs deposition on the forest floor exhibited high spatial heterogeneity and altitude-dependent distribution over the catchment. The
Cs deposition on the forest floor exhibited high spatial heterogeneity and altitude-dependent distribution over the catchment. The  Cs retention ratio in the organic layer ranged from 6% to 82% in 2013. The
Cs retention ratio in the organic layer ranged from 6% to 82% in 2013. The  Cs retention ratios had positive correlations with the material inventory in the organic layer and the elevation. The
Cs retention ratios had positive correlations with the material inventory in the organic layer and the elevation. The  Cs retention ratios in the organic layer were less than 20% in 2015, even at the locations where the retention ratio was higher than 55% in 2013. Although there was spatial variation in the migration speed,
Cs retention ratios in the organic layer were less than 20% in 2015, even at the locations where the retention ratio was higher than 55% in 2013. Although there was spatial variation in the migration speed,  Cs migration from the organic layer to mineral soil was almost completed within 4 y of the deposition.
Cs migration from the organic layer to mineral soil was almost completed within 4 y of the deposition.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
 Cs fluvial export from a forest catchment evaluated by stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic characterization of organic matter
Cs fluvial export from a forest catchment evaluated by stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic characterization of organic matterMuto, Kotomi; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun; Takeuchi, Erina; Nishimura, Shusaku; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Matsunaga, Takeshi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 314(1), p.403 - 411, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:83.87(Chemistry, Analytical)Fluvial export of particulate and dissolved  Cs was investigated to reveal its sources and transfer mechanisms in a broadleaved forest catchment using a continuous collection system. The finest size fraction (
Cs was investigated to reveal its sources and transfer mechanisms in a broadleaved forest catchment using a continuous collection system. The finest size fraction ( 75
75 m), consisting of decomposed litter and surface mineral soil, was the dominant fraction in the particulate
m), consisting of decomposed litter and surface mineral soil, was the dominant fraction in the particulate  Cs load, although the contribution of coarser size fractions increased during high water discharge in 2014. The dissolved
Cs load, although the contribution of coarser size fractions increased during high water discharge in 2014. The dissolved  Cs originated from the decomposition of
Cs originated from the decomposition of  Cs-contaminated litter. Temporal changes in
Cs-contaminated litter. Temporal changes in  Cs distribution in the litter-mineral soil system indicated that the dissolved
Cs distribution in the litter-mineral soil system indicated that the dissolved  Cs load will be moderated in several years, while particulate
Cs load will be moderated in several years, while particulate  Cs load has the potential to continue for a long time.
Cs load has the potential to continue for a long time.
 Cs in a forested catchment affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
Cs in a forested catchment affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentMatsunaga, Takeshi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Takeuchi, Erina; Muto, Kotomi; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Nishimura, Shusaku; Koarashi, Jun; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Sato, Tsutomu*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 310(2), p.679 - 693, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.29(Chemistry, Analytical)Particulate  Cs in stream water was collected continuously for two years in order to assess the long-term trend of the
Cs in stream water was collected continuously for two years in order to assess the long-term trend of the  Cs discharge from the forest environment. Sampling was conducted from December 2011 to December 2013 in a mountainous stream, which received the
Cs discharge from the forest environment. Sampling was conducted from December 2011 to December 2013 in a mountainous stream, which received the  Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. A seasonal increase in fluvial transport load of particulate
Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. A seasonal increase in fluvial transport load of particulate  Cs associated with suspended solids (SS) was observed in August and September when rainfall was abundant. The particulate
Cs associated with suspended solids (SS) was observed in August and September when rainfall was abundant. The particulate  Cs concentration decreased at a faster rate than the rate due to radioactive decay. This decrease might be resulted from redistribution of the easily eroded and polluted soil surface due to heavy rain events such as typhoons. These findings indicate that the particulate
Cs concentration decreased at a faster rate than the rate due to radioactive decay. This decrease might be resulted from redistribution of the easily eroded and polluted soil surface due to heavy rain events such as typhoons. These findings indicate that the particulate  Cs load was subject to the inter-annual variations in rainfalls, and decreased gradually over a long period of time due to a decrease in
Cs load was subject to the inter-annual variations in rainfalls, and decreased gradually over a long period of time due to a decrease in  Cs concentration in SS.
Cs concentration in SS.
Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kakubo, Yuta*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Watanabe, Hideo*; Abe, Hiroaki*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Acta Materialia, 116, p.104 - 113, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:95.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Atom probe tomography (APT) and TEM were combined for identifying the stage at which solute clusters transform into compounds crystallographically distinct from the matrix, in the precipitation of the G-phase (Ni Si
Si Mn
Mn ) from ferrite solid solution subjected to isothermal annealing at 673 K. Based on a systematic analysis of solute clusters as a function of annealing time, the nucleation of the G-phase was found to occur via a two-step process. Moreover, the structural change was found to occur via another two-step process. There was a time lag between the end of cluster growth to become a critical size and the start of the structural change. During the incubation period solute enrichment occurred inside the clusters without further size growth, indicating that the nucleation of the G-phase occurs at the critical size with a critical composition. Judging from the results of APT, TEM and the simulation of electron diffraction patterns, the critical composition was estimated to be Ni
) from ferrite solid solution subjected to isothermal annealing at 673 K. Based on a systematic analysis of solute clusters as a function of annealing time, the nucleation of the G-phase was found to occur via a two-step process. Moreover, the structural change was found to occur via another two-step process. There was a time lag between the end of cluster growth to become a critical size and the start of the structural change. During the incubation period solute enrichment occurred inside the clusters without further size growth, indicating that the nucleation of the G-phase occurs at the critical size with a critical composition. Judging from the results of APT, TEM and the simulation of electron diffraction patterns, the critical composition was estimated to be Ni Si
Si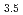 (Fe,Cr)
(Fe,Cr)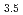 Mn
Mn .
.
Muto, Kotomi; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Takeuchi, Erina; Nishimura, Shusaku; Koarashi, Jun; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Matsunaga, Takeshi
KEK Proceedings 2015-4, p.252 - 257, 2015/11
As a result of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, a large amount of radiocesium released into the atmosphere was deposited in forests. This study estimated the monthly trend in the fluvial discharges of radiocesium from a forest. The study site was a forested catchment in Kitaibaraki City. Radiocesium in river water was collected with a filtration system as both particulate and dissolved components. Filters and columns including dissolved Cs absorbent were replaced every month. The collected suspended solids were sieved into 2000-3000  m, 500-2000
m, 500-2000  m, 75-500
m, 75-500  m, and
m, and  75
75  m fractions. The
m fractions. The  Cs concentrations in the samples were measured using
Cs concentrations in the samples were measured using  -ray spectrometry with Ge semiconductor detectors. The
-ray spectrometry with Ge semiconductor detectors. The  Cs discharge increased with the river water discharge. The particulate
Cs discharge increased with the river water discharge. The particulate  Cs discharge was dominant in both 2013 and 2014. The
Cs discharge was dominant in both 2013 and 2014. The  Cs discharge rate of the dissolved component increased in winter, when the river water discharge decreased.
Cs discharge rate of the dissolved component increased in winter, when the river water discharge decreased.
Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun; Takeuchi, Erina; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Nishimura, Shusaku; Matsunaga, Takeshi
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 147, p.1 - 7, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:61.81(Environmental Sciences)We collected a large amount of radiocesium air dose rate data by mountain-walking with a small  -ray survey system, KURAMA-II, to create an air dose rate map of a mountainous deciduous forest that received radiocesium from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Measurements were conducted in a small stream catchment 0.6 km
-ray survey system, KURAMA-II, to create an air dose rate map of a mountainous deciduous forest that received radiocesium from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Measurements were conducted in a small stream catchment 0.6 km in size in August and September 2013, and the relationship between air dose rates and the mountainous topography was examined. Air dose rates increased with elevation, suggesting that more radiocesium was deposited on ridges, and that it had remained there for 2.5 years with no significant migration due to soil erosion or water drainage. Slope aspect also strongly affected air dose rates. By the continuous measurement using KURAMA-II, we describe the variation in air dose rates in a mountainous area and suggest that it is important to consider topography when selecting sampling points to estimating dose rates or contaminant deposition.
in size in August and September 2013, and the relationship between air dose rates and the mountainous topography was examined. Air dose rates increased with elevation, suggesting that more radiocesium was deposited on ridges, and that it had remained there for 2.5 years with no significant migration due to soil erosion or water drainage. Slope aspect also strongly affected air dose rates. By the continuous measurement using KURAMA-II, we describe the variation in air dose rates in a mountainous area and suggest that it is important to consider topography when selecting sampling points to estimating dose rates or contaminant deposition.
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Takeuchi, Erina; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Nishimura, Shusaku; Koarashi, Jun; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Sato, Tsutomu*; Nagao, Seiya*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1291 - 1295, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Chemistry, Analytical)An innovative, yet simple method for the passive collection of radioactive materials in river water has been developed and validated. The method employes large filter vessels, containing multiple cartridge filters. River water is led to the system naturally using a drop of the riverbed by hose from upstream. This method makes long-term, unmanned monitoring possible. In addition to regular radioactivity analyses, this method provides an opportunity for the characterization of suspended materials based on its ample collection quantities (more than several tens of grams). This method may also be applicable to sediment-bound chemicals.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kakubo, Yuta*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Nozawa, Yasuko*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Onizawa, Kunio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 452(1-3), p.235 - 240, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:95.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructures and hardness of stainless steel weld overlay cladding of reactor pressure vessels subjected to the thermal aging at 400  C for 100-10,000 h were investigated using atom probe tomography and nanoindentation technique. The Cr concentration fluctuation in the
C for 100-10,000 h were investigated using atom probe tomography and nanoindentation technique. The Cr concentration fluctuation in the  -ferrite phase caused by spinodal decomposition rapidly progressed by the 100 h aging while NiSiMn clusters increased in number density at 2,000 h and coarsened at 10,000 h. The hardness of the
-ferrite phase caused by spinodal decomposition rapidly progressed by the 100 h aging while NiSiMn clusters increased in number density at 2,000 h and coarsened at 10,000 h. The hardness of the  -ferrite phase also rapidly increased at the short aging time. The Cr concentration fluctuation and the hardness were in good correlation with the degree of the Cr concentration fluctuation rather than the formation of the NiSiMn clusters. These results strongly suggested that the dominant factor of the hardening of the
-ferrite phase also rapidly increased at the short aging time. The Cr concentration fluctuation and the hardness were in good correlation with the degree of the Cr concentration fluctuation rather than the formation of the NiSiMn clusters. These results strongly suggested that the dominant factor of the hardening of the  -ferrite phase by the thermal aging was Cr spinodal decomposition.
-ferrite phase by the thermal aging was Cr spinodal decomposition.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kakubo, Yuta*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Nozawa, Yasuko*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 449(1-3), p.273 - 276, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:81.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructural changes and hardness of stainless steel weld overlay cladding of reactor pressure vessels subjected to the neutron irradiation with a dose of 7.2  10
10 n cm
n cm (E
(E  1 MeV) and a flux of 1.1
1 MeV) and a flux of 1.1  10
10 n cm
n cm s
s at 290
at 290 C were investigated by atom probe tomography and with nanoindentation technique. In order to isolate the effect of the irradiation, we compared the results of the measurements of the irradiated sample with that of the aged one at 300
C were investigated by atom probe tomography and with nanoindentation technique. In order to isolate the effect of the irradiation, we compared the results of the measurements of the irradiated sample with that of the aged one at 300 C for the time equivalent to the irradiation. The Cr concentration fluctuation was enhanced in the
C for the time equivalent to the irradiation. The Cr concentration fluctuation was enhanced in the  -ferrite phase of the irradiated sample. In addition, the enhancement of the concentration fluctuation of Si, which was not observed in the aged sample, was observed. The hardening at the
-ferrite phase of the irradiated sample. In addition, the enhancement of the concentration fluctuation of Si, which was not observed in the aged sample, was observed. The hardening at the  -ferrite phase was occurred by both the irradiation and the aging. However, the former was more than that expected from the Cr concentration fluctuation, which suggested that the Si concentration fluctuation and irradiation-induced defects were possible origins of the additional hardening.
-ferrite phase was occurred by both the irradiation and the aging. However, the former was more than that expected from the Cr concentration fluctuation, which suggested that the Si concentration fluctuation and irradiation-induced defects were possible origins of the additional hardening.
 -wave halos at the drip-line;
-wave halos at the drip-line; 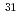 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(14), p.142501_1 - 142501_5, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:91.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Akira; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Saito, Takashi; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Technology 2013-043, 24 Pages, 2014/01
The big tsunami wave caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake triggered station black out of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The schedule until ending of the decommission is shown in the guidance from Japanese government. But the dose rate in the reactor vessel is quite high and it is not possible to specify the position of melted fuel debris by visual inspection. That is one of the most important issues in this process. This report describes the development of Self Powered Gamma Detector (SPGD) for the purpose to specify the position of melted fuel debris and situation in the reactor by measuring  rate in the reactor of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The
rate in the reactor of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The  irradiation examinations by changing the parameter of emitters figure were performed and the dependency of SPGD output on emitter shape was summarized.
irradiation examinations by changing the parameter of emitters figure were performed and the dependency of SPGD output on emitter shape was summarized.
Kitagaki, Toru; Hoshino, Takanori; Sambommatsu, Yuji; Yano, Kimihiko; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Igarashi, Takeshi*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 296(2), p.975 - 979, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.48(Chemistry, Analytical)Arai, Yoichi; Ogino, Hideki; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Kase, Takeshi; Nakajima, Yasuo
Proceedings in Radiochemistry, 1(1), p.71 - 74, 2011/09
Solvent cleanup method using activated alumina was discussed in this study. This method was one of candidate to remove TBP/ -dodecane degradation products. The degradation sample of 30% TBP/
-dodecane degradation products. The degradation sample of 30% TBP/ -dodecane was prepared by irradiation (1.6 MGy) using
-dodecane was prepared by irradiation (1.6 MGy) using  Co
Co  -source. The absorbed dose for sample was almost 1.6 MGy. The degradation products were qualitatively analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS). After the irradiation, solvent cleanup was performed by activated alumina and the cleanup using alumina was examined by phase separation test with 3M HNO
-source. The absorbed dose for sample was almost 1.6 MGy. The degradation products were qualitatively analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS). After the irradiation, solvent cleanup was performed by activated alumina and the cleanup using alumina was examined by phase separation test with 3M HNO . As the result, it was found that hexane and long-chain alcohols were mainly generated as the n-dodecane degradation products by irradiation, and almost 70% of the TBP/
. As the result, it was found that hexane and long-chain alcohols were mainly generated as the n-dodecane degradation products by irradiation, and almost 70% of the TBP/ -dodecane degradation products were removed and the phase separation performance were improved by the cleanup using activated alumina.
-dodecane degradation products were removed and the phase separation performance were improved by the cleanup using activated alumina.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kameda, Jun*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 415(2), p.198 - 204, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:92.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructural changes by thermal aging in stainless steel weld overlay cladding of nuclear reactor pressure vessels were investigated using atom probe tomography. The cladding material was composed of about 90% austenite phase and 10%  -ferrite phase and thermally aged at 400
-ferrite phase and thermally aged at 400 C for 10,000 h. In the ferrite phase, the thermal aging increased a fluctuation of Cr concentration due to spinodal decomposition and caused the precipitation of G phase with chemical composition of Ni:Si:Mn = 16:7:6. Moreover, significant hardening of the ferrite phase was induced by the thermal aging. On the other hand, the thermal aging did not affect on the microstructures and the hardness in the austenite phase, which indicates the microstructural changes were responsible for the hardening in the ferrite phase. The analyses of the magnitude of the spinodal decomposition and the hardness implied that the spinodal decomposition was the main cause of the hardening.
C for 10,000 h. In the ferrite phase, the thermal aging increased a fluctuation of Cr concentration due to spinodal decomposition and caused the precipitation of G phase with chemical composition of Ni:Si:Mn = 16:7:6. Moreover, significant hardening of the ferrite phase was induced by the thermal aging. On the other hand, the thermal aging did not affect on the microstructures and the hardness in the austenite phase, which indicates the microstructural changes were responsible for the hardening in the ferrite phase. The analyses of the magnitude of the spinodal decomposition and the hardness implied that the spinodal decomposition was the main cause of the hardening.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Takeuchi, Shinji; Maekawa, Keisuke; Osawa, Hideaki; Semba, Takeshi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.133 - 140, 2010/10
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kuramoto, Akira*; Kameda, Jun*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Hasegawa, Masayuki*; Okubo, Tadakatsu*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 402(2-3), p.93 - 101, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:96.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This study reports the effects of the composition and dose on microstructure evolution and hardening in high- and low-impurity A533B-1 steels neutron-irradiated in a wide range from 0.32 to 9.9  10
10 n cm
n cm (E
(E  1 MeV) under a constant high flux at JMTR. The early hardening was found to be caused by mainly matrix defects. The gradual hardening after middle stage of irradiation was found to be caused by the formation of Cu rich clusters (CRCs) and Mn-Ni-Si rich clusters (MNSCs), respectively, in the high- and low-impurity steels. By applying a RB model, it was found that the dislocation-pinning strength of the CRCs and MNSCs is almost the same. Moreover, the high-impurity steel subjected to the highest dose revealed the formation of MNSCs.
1 MeV) under a constant high flux at JMTR. The early hardening was found to be caused by mainly matrix defects. The gradual hardening after middle stage of irradiation was found to be caused by the formation of Cu rich clusters (CRCs) and Mn-Ni-Si rich clusters (MNSCs), respectively, in the high- and low-impurity steels. By applying a RB model, it was found that the dislocation-pinning strength of the CRCs and MNSCs is almost the same. Moreover, the high-impurity steel subjected to the highest dose revealed the formation of MNSCs.
Kawamura, Hideki*; Ando, Kenichi*; Noda, Masaru*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Matsuda, Takeshi*; Fujii, Haruhiko*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Ueda, Tadashi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Takeuchi, Shinji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-081, 182 Pages, 2010/03
Grouting has practical importance for the reduction of groundwater inflow into excavations during construction of underground facilities. Considering the performance assessment of a radioactive waste repository, the performance of the engineered barrier system could be adversely affected by a high pH plume generated from grout. Therefore, a quantitative estimation of the effectiveness of grouting and grout material is essential. This study has been performed in the Mizunami URL being excavated in crystalline rock as a part of the Project for Grouting Technology Development for the Radioactive Waste Repository funded by METI, Japan. The aims were to evaluate the applicability of existing grouting technology and to develop methodology to determine the distribution of grout and change in hydraulic properties of the grouted rock volume. The target rock is the volume of rock around a planned refuge niche where the pre-excavation grouting was performed at 200-m depth from ground surface. After excavation of the refuge niche, ten boreholes were drilled and different kinds of investigations were carried out during and after drilling. The results were integrated and groundwater flow analysis of pre and post excavation grouting conditions were carried out to estimate quantitatively the effect of pre-excavation grouting. The results suggest that current pre-excavation grouting technology is effective for reduction of groundwater inflow into excavations and that hydraulic conductivity of the surrounding rock can be reduced by more than one order of magnitude.