Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 transgenic
transgenic 
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sato, Ryohei*; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 86(2), p.125 - 131, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:79.71(Biology)In an effort to assess the characteristics of mutation induced by different LET radiation in higher plants, the mutational effects of carbon-ion beams and  -rays were investigated in
-rays were investigated in  . The
. The  transgenic
transgenic  (Arabidopsis/rpsL) mutation detection system was adopted. Dry seeds of Arabidopsis/rpsL were irradiated with
(Arabidopsis/rpsL) mutation detection system was adopted. Dry seeds of Arabidopsis/rpsL were irradiated with  -rays and 208-MeV carbon ions (208-MeV
-rays and 208-MeV carbon ions (208-MeV  C
C ), and the mutation frequency and mutation spectrum were examined. Our result suggested that 208-MeV
), and the mutation frequency and mutation spectrum were examined. Our result suggested that 208-MeV  C
C and
and  -rays induced different mutational effects in
-rays induced different mutational effects in  dry seed.
dry seed.
 hypersensitive and hypermutable in response to UV-B radiation
hypersensitive and hypermutable in response to UV-B radiationYoshihara, Ryohei; Nakane, Chiyoko*; Sato, Ryohei*; Yasuda, Ai*; Takimoto, Koichi*
Genes and Environment, 30(2), p.53 - 61, 2008/05
We generated a CPD photolyase knock-down in  by RNAi to investigate the role of CPD photorepair for protection of plants from solar UV. These knock-down lines exhibited hypersensitivity to UV-B and an increased occurrence of mutation induced by UV-B radiation compared with
by RNAi to investigate the role of CPD photorepair for protection of plants from solar UV. These knock-down lines exhibited hypersensitivity to UV-B and an increased occurrence of mutation induced by UV-B radiation compared with  proficient in CPD photolyase. These results indicate that CPD photoreactivation plays an important role for UV resistance of
proficient in CPD photolyase. These results indicate that CPD photoreactivation plays an important role for UV resistance of  and suppression of UV-induced mutagenesis.
and suppression of UV-induced mutagenesis.
 -rays in
-rays in 
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
Ionizing radiation induces DNA damages which cause mutation. Organisms have DNA repair systems to repair DNA damages. The relationship between types of mutation induced by ionizing radiation and DNA repair systems are well studied in bacteria and animal. In plant, however, little is known about it. In this study we will investigate ion-beam and  -rays induced mutations in plant by using
-rays induced mutations in plant by using  mutation detection system (Yoshihara et al. 2006). Ion-beam and
mutation detection system (Yoshihara et al. 2006). Ion-beam and  -rays are irradiated to
-rays are irradiated to  containing
containing  gene. Mutated
gene. Mutated  gene is collected as a plasmid by plasmid rescue from chromosomal DNA and analyze the types of mutations. We will report the results of ion-beam and
gene is collected as a plasmid by plasmid rescue from chromosomal DNA and analyze the types of mutations. We will report the results of ion-beam and  -rays induced mutations detected by this system.
-rays induced mutations detected by this system.
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
We analyzed mutation induced by 220 MeV C ,
,  -rays and carbon ions near the Bragg peak in
-rays and carbon ions near the Bragg peak in  seed. Mutations were detected by
seed. Mutations were detected by 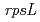 transgenic
transgenic  mutation detection system. Although mutant frequency was increase with 220 MeV C
mutation detection system. Although mutant frequency was increase with 220 MeV C or
or  -rays, that was background level in
-rays, that was background level in  irradiated carbon ion near the Bragg peak. The fluence of carbon ion near the Bragg peak was lower because it has higher cell killing effect. The fluence was too low to detect mutation by this method.
irradiated carbon ion near the Bragg peak. The fluence of carbon ion near the Bragg peak was lower because it has higher cell killing effect. The fluence was too low to detect mutation by this method.

Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
To analyze mutagenic effects of ionizing radiation in higher plant, seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis carrying 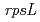 gene were irradiated with carbon ions and
gene were irradiated with carbon ions and  -rays. Mutation spectrum showed that the carbon ions and
-rays. Mutation spectrum showed that the carbon ions and  -rays frequently induced G
-rays frequently induced G A and deletions. In addition, the carbon ions induced complex-type mutations and the
A and deletions. In addition, the carbon ions induced complex-type mutations and the  -rays induced frameshift mutations with relatively higher frequency. The G
-rays induced frameshift mutations with relatively higher frequency. The G T and A
T and A C, which are caused by oxidized guanine, were hardly found in our experiment. Carbon ions near the Bragg peak had higher lethal effect pet unit dose than the carbon ions that penetrates the seeds. However, mutant frequency was remained at control level. The
C, which are caused by oxidized guanine, were hardly found in our experiment. Carbon ions near the Bragg peak had higher lethal effect pet unit dose than the carbon ions that penetrates the seeds. However, mutant frequency was remained at control level. The 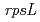 mutation analysis system only detects intragenic mutations, our result suggests that the carbon ions near the Bragg peak seldom induce intragenic mutations in the Arabidopsis dry seeds.
mutation analysis system only detects intragenic mutations, our result suggests that the carbon ions near the Bragg peak seldom induce intragenic mutations in the Arabidopsis dry seeds.
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Ayako; Nozawa, Shigeki; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Takimoto, Koichi*; Hidema, Jun*; Sakamoto, Ayako
no journal, ,
We analyzed  -ray-induced mutation spectrum in Arabidopsis seedling to investigate the effect of oxidative DNA damage on mutagenesis. Moreover, to evaluate the effect of nucleotide pool sanitization system on
-ray-induced mutation spectrum in Arabidopsis seedling to investigate the effect of oxidative DNA damage on mutagenesis. Moreover, to evaluate the effect of nucleotide pool sanitization system on  -ray-induced mutations, we analyzed a mutant deficient in the Arabidopsis
-ray-induced mutations, we analyzed a mutant deficient in the Arabidopsis 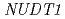 gene that is a homologue of
gene that is a homologue of 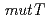 . The
. The  -ray sensitivity of the
-ray sensitivity of the 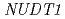 mutant was slightly higher, but not statistically significant, than that of wild type plant. However, the mutation spectra induced by
mutant was slightly higher, but not statistically significant, than that of wild type plant. However, the mutation spectra induced by  -rays were different between the wild type and
-rays were different between the wild type and 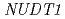 plants. From these results, it was suggested that the
plants. From these results, it was suggested that the 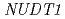 deficiency obviously affects on the mutagenesis but not the plant growth following
deficiency obviously affects on the mutagenesis but not the plant growth following  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Takimoto, Koichi*; Sakamoto, Ayako
no journal, ,
 -rays in higher plant
-rays in higher plantYoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
Mutation spectrum induced by 220 MeV Carbon ion beam (220 MeV C),  -rays and Carbon ion near the Bragg peak in
-rays and Carbon ion near the Bragg peak in  seed was determined. Mutant frequency was increased by 220 MeV C and
seed was determined. Mutant frequency was increased by 220 MeV C and  -rays irradiation. 220 MeV C and
-rays irradiation. 220 MeV C and  -rays induced G:C to A:T transition and deletion efficiently. 220 MeV C induced higher incidence of complex type of mutation. Frameshift mutation in
-rays induced G:C to A:T transition and deletion efficiently. 220 MeV C induced higher incidence of complex type of mutation. Frameshift mutation in  -rays irradiated seed was frequent, but it was background level in 220 MeV C irradiated seed. These difference of mutation spectrum might be caused by the difference of DNA damage formed by 220 MeV C and
-rays irradiated seed was frequent, but it was background level in 220 MeV C irradiated seed. These difference of mutation spectrum might be caused by the difference of DNA damage formed by 220 MeV C and  -rays irradiation. Mutant frequency in seed exposed to carbon ion near the Bragg peak was not increased. The fluence of carbon ion near the Bragg peak was lower because it has higher cell killing effect. The fluence of carbon ion might be too low to detect mutation in target gene.
-rays irradiation. Mutant frequency in seed exposed to carbon ion near the Bragg peak was not increased. The fluence of carbon ion near the Bragg peak was lower because it has higher cell killing effect. The fluence of carbon ion might be too low to detect mutation in target gene.

Yoshihara, Ryohei; Takimoto, Koichi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Sakamoto, Ayako; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
We constructed a mutation detection system by integrating a linearized plasmid DNA that has 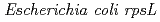 gene into the chromosomal DNA of
gene into the chromosomal DNA of  . We first analyzed the UV-induced mutation spectrum. The frequency of G to A transitions was increased after the exposure to UV light. To evaluate the effects of photorepair activity for CPDs in maintaining genomic integrity, we constructed RNAi plants in which the expression of CPD photolyase was suppressed. The mutation spectrum analysis in the RNAi plants showed that the frequency of frameshift mutations was increased together with that of G to A transitions. This suggests that the suppression of CPD photorepair not only increase the typical base substitutions but also other kinds of mutations. We next analyzed the mutation spectrum induced by
. We first analyzed the UV-induced mutation spectrum. The frequency of G to A transitions was increased after the exposure to UV light. To evaluate the effects of photorepair activity for CPDs in maintaining genomic integrity, we constructed RNAi plants in which the expression of CPD photolyase was suppressed. The mutation spectrum analysis in the RNAi plants showed that the frequency of frameshift mutations was increased together with that of G to A transitions. This suggests that the suppression of CPD photorepair not only increase the typical base substitutions but also other kinds of mutations. We next analyzed the mutation spectrum induced by  rays and carbon-ion beams (LET 121.5 keV/
rays and carbon-ion beams (LET 121.5 keV/ m). The results showed that
m). The results showed that  rays tended to induce shorter size of deletions than the carbon ions.
rays tended to induce shorter size of deletions than the carbon ions.
Takano, Masato; Ito, Yoshiyuki; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Takimoto, Mayumi*; Matsukura, Minoru*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Mori, Koichi*; Iwasaki, Mamoru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
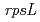 gene in plant
gene in plantYoshihara, Ryohei; Yasuda, Ai*; Sato, Ryohei*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Takimoto, Koichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshihara, Ryohei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Takimoto, Koichi*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
We irradiated carbon ion-beams (220-MeV C) and  -rays to
-rays to  carrying
carrying 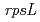 gene to analyze mutational effects of these radiations. Our results suggested that
gene to analyze mutational effects of these radiations. Our results suggested that  -rays might induce smaller size of deletion mutation compared to 220-MeV C. The induction of oxidized guanine by these radiations was low in dry seeds because of low incidence of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversion in irradiated group.
-rays might induce smaller size of deletion mutation compared to 220-MeV C. The induction of oxidized guanine by these radiations was low in dry seeds because of low incidence of G:C to T:A and A:T to C:G transversion in irradiated group.  -ray-induced mutation analysis in
-ray-induced mutation analysis in  seedling was similar to that in dry seed, suggesting the mutational effect of radiation used here in higher plant might be different from that in other organisms.
seedling was similar to that in dry seed, suggesting the mutational effect of radiation used here in higher plant might be different from that in other organisms.
Sato, Ryohei*; Yasuda, Ai*; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Takimoto, Koichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English