Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamai, Hiroshi; Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Dai-41-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/11
In light of recent delay of plutonium use in Japan and the increasing criticism of nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security in the nuclear fuel cycle, the validity of these criticisms will be examined for the sustainable development of the nuclear fuel cycle policy. Issues on the view point of nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security are examined.
Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Enerugi Rebyu, 40(8), p.56 - 57, 2020/07
Strict application of IAEA safeguards and nuclear security should be implemented for Japan's full-scale nuclear fuel cycle. Based on the knowledge and experience of research and development in the nuclear fuel cycle, nuclear material management, the effective and efficient promotion of new technologies should be promoted with scientific and demonstrative measures to strengthen the world's nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. Development or sophistication of new technologies, human resource development, and reinforcement of the international framework are future challenge in the international community.
Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Enerugi Rebyu, 40(7), p.58 - 59, 2020/06
Japan have promoted the peaceful use of plutonium with the nuclear non-proliferation commitment based on IAEA safeguards agreement and Japan-US nuclear cooperation agreement, as well as ensuring transparency of the policy that Japan has no plutonium without purpose of use. In promoting the nuclear fuel cycle, adherence to those measures and maintaining plutonium utilization by means of plutonium-thermal, and a fast reactor cycle to achieve large-scale and long-term energy supply and environmental improvement, therefore, further research and development is essential.
Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Enerugi Rebyu, 40(6), p.58 - 59, 2020/05
In order to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, it is important not only to ensure safety but also to ensure nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. Japan has contributed to the international community through strengthening nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security capabilities with technical and human resource development. However, in the wake of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011, Japan's nuclear power plants have not restarted or plutonium use has not progressed smoothly. Concerns have been shown. Towards appropriate steps of Japan's nuclear fuel cycle policy, such concerns are examined and future efforts are summarized.
Tazaki, Makiko; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Ryo; Kimura, Takashi; Kitade, Yuta; Nakanishi, Hiroaki; Suda, Kazunori
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-39-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 7 Pages, 2018/11
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Hiroaki; Kimura, Takashi; Shimizu, Ryo; Kitade, Yuta; Tazaki, Makiko; Tamai, Hiroshi; Suda, Kazunori
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-39-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/11
To extract the possible requirements for the Broader Conclusion (BC) drawn by the IAEA in the Member States, this study is to conduct the comparative analysis of the tendencies on the Member States from which the BC has been drawn and those from which the BC has not been drawn yet.
Kimura, Takashi; Tazaki, Makiko; Kitade, Yuta; Shimizu, Ryo; Tamai, Hiroshi; Nakanishi, Hiroaki; Suda, Kazunori
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-39-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2018/11
This is the summary of research result of State Level Concept (SLC) which has been developed and conducted by the IAEA and a major purpose of the research reported here is to promote the nuclear operator's understandings for the importance of Broder Conclusion drawn continuously by the IAEA under SLC.
Kitade, Yuta; Tamai, Hiroshi; Tazaki, Makiko; Shimizu, Ryo; Kimura, Takashi; Nakanishi, Hiroaki; Suda, Kazunori
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-39-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/11
Regional Safeguards is considered as one of the measures for strengthening IAEA safeguards and its concept is recognized at NPT Review Conference and also NSG Guidelines amended in 2011. This Study examines the elements for the proper establishment of Regional Safeguards.
Suda, Kazunori; Shimizu, Ryo; Tazaki, Makiko; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kitade, Yuta
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-38-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/04
Since India's nuclear explosion in 1974, there has been continued discussion on nuclear non-proliferation. At first, to prevent proliferation of nuclear weapons, the International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Evaluation (INFCE) was established to discuss reprocessing, plutonium handling, and so on. After that, to respond to the threat of proliferation posed by DPRK, the international community desired to further enhance nuclear non-proliferation by strengthening the IAEA safeguards system. In recent years, some researchers at universities and national laboratories are studying proliferation resistance from the standpoint of nuclear materials that may be inherently self-protecting. This paper discusses minimization of proliferation risk and future prospects based on alternative measures for reprocessing, plutonium handling, and recycling described in INFCE-WG4.
Tazaki, Makiko; Suda, Kazunori; Shimizu, Ryo; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kitade, Yuta
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-38-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
Tamai, Hiroshi; Tazaki, Makiko; Kitade, Yuta; Shimizu, Ryo; Suda, Kazunori
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-38-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/04
The United Kingdom, UK, in March 2017, notified the withdrawal from the European Union, EU. Since EURATOM is managed by the same organisation of EU, the withdrawal from EURATOM is considered to be unavoidable. UK has to define the regulation for the measures covered by EURATOM which include the implementing safeguards in the civil UK nuclear facilities and the nuclear cooperation agreements between EURATOM and third nations. UK experts recognise that such re-arrangements within 2-years are very tough hurdle, so that some alternative measures are proposed by industry side. For peaceful nuclear use in Japan, hindrances on the smooth transfers of nuclear materials and equipment between UK are concerned. This paper will discuss the UK withdrawal from EURATOM focused on the UK's correspondence and the potential influence on cooperation with Japan in view of nuclear non-proliferation.
Kuno, Yusuke; Oda, Takuji*; Tanaka, Satoru*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Tanabe, Tomoyuki*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Horio, Kenta*; Hamasaki, Manabu*; Shinohara, Nobuo*; Ikeda, Yuta*
Proceedings of INMM 52nd Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/07
The substance and implication of PR from the viewpoints of risk evaluation on nuclear proliferation was studied in this paper. As an example, ten next-generation reprocessing technology candidates were evaluated with GIF PR and PP methodology to find degree of relative difference in PR from the presently available technology - PUREX. PR effectiveness in proliferation risk was also assessed and it was found that the effectiveness of PR measures is subject to the status of each nation.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Suzuki, Yutaka; Kizu, Kaname; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Dolgetta, N.*; Portafaix, C.*; Zani, L.*; Pizzuto, A.*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.208 - 211, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Magnet system in JT-60SA consists of 18 toroidal field coils, 7 plasma equilibrium field (EF) coils, and central solenoid (CS) that has 4 modules of solenoids. Mechanical design of EF coils and CS is optimized in order to obtain the broad operational space of plasmas that are double-null plasma with high plasma current for high performance operation and ITER-like configuration with IP=3.5MA for ITER-relevant experiment. In the former design, called NCT, divertor coil (EF4) is made of Nb Sn conductor, as well as CS conductor. However, it is clear that 6.2T of Bmax is significant to operate ITER-like plasma. Therefore, material of cable for EF4 conductor is changed into NbTi, so that this contributes to cost reduction. Regarding CS design, material of conduit is changed into JK2LB in order to simplify the structure of pre-compression. Stress analysis for support structure and winding pack of EF coils and CS is currently carried out. In the case where the vertical unbalance force of CS is largest in the designed plasma operation, peak stress of conduit is less than fatigue limit in 18,000 cycles that is designed number of plasma shot in JT-60SA. This result shows the recent design of CS conductor has significant mechanical strength.
Sn conductor, as well as CS conductor. However, it is clear that 6.2T of Bmax is significant to operate ITER-like plasma. Therefore, material of cable for EF4 conductor is changed into NbTi, so that this contributes to cost reduction. Regarding CS design, material of conduit is changed into JK2LB in order to simplify the structure of pre-compression. Stress analysis for support structure and winding pack of EF coils and CS is currently carried out. In the case where the vertical unbalance force of CS is largest in the designed plasma operation, peak stress of conduit is less than fatigue limit in 18,000 cycles that is designed number of plasma shot in JT-60SA. This result shows the recent design of CS conductor has significant mechanical strength.
Fujita, Takaaki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Bialek, J.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yutaka; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1512 - 1523, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:63.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design of modification of JT-60U, JT-60SA, has been optimized in viewpoint of plasma control, and operation regimes have been evaluated. Upper and lower divertors with different geometry are prepared for flexibility of plasma shape control. The beam lines of negative-ion NBI are shifted downward for off-axis current drive, in order to obtain a weak/reversed shear plasma. The feedback control coils along the port hole in the stabilizing plate are found effective to suppress the resistive wall mode (RWM) and sustain high 
 close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
 = 2.4 MA,
= 2.4 MA, 
 = 4.4,
= 4.4, 
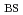 = 0.70,
= 0.70, 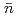
 /
/
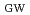 = 0.86, H
= 0.86, H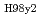 = 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration (
= 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration ( = 2.65). High
= 2.65). High 
 , high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
, high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kizu, Kaname; Kurita, Genichi; Masaki, Kei; Matsukawa, Makoto; Miura, Yukitoshi; Sakurai, Shinji; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.541 - 547, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)JT-60SA is positioned as the ITER satellite tokamak to conduct research elements to support and supplement ITER towards DEMO under the joint collaboration of Japan and EU. After the discussions in JA-EU Satellite Tokamak Working Group in 2005, the heating power is increased up to 41MW, 100s to ensure the ITER support research. With such increased heating power, the prospective plasma performances are analysed by the equilibrium and transport analysis codes. Operation window of a fully non-inductive current drive is extended to high density region. Simultaneous achievement of high equivalent Q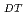 and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kamada, Masaki; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.791 - 797, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Modification of JT-60U to a superconducting device (so called JT-60SA) has been planned to contribute to ITER and DEMO. The NBI system is required to inject 34 MW for 100 s. The upgraded NBI system consists of twelve positive ion based NBI (P-NBI) units and one negative ion based NBI (N-NBI) unit. The injection power of the P-NBI units are 2 MW each at 85 keV, and the N-NBI unit will be 10 MW at 500 keV, respectively. On JT-60U, the long pulse operation of 30 s at 2 MW (85 keV) and 20 s at 3.2 MW (320 keV) have been achieved on P-NBI and N-NBI units, respectively. Since the temperature increase of the cooling water in both ion sources is saturated within 20 s, further pulse extension up to 100 s is expected to mainly modify the power supply systems in addition to modification of the N-NBI ion source for high acceleration voltage. The detailed technical design of the NBI system for JT-60SA is presented.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.76(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English