Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Takahashi, Naoya; Niwa, Masakazu
JAEA-Testing 2017-001, 52 Pages, 2017/03
It is essential to understand the activity of faults in and around a target area to assess the long-term geosphere stability for geological isolation. Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) dating of fault gouge has been conducted in Tono Geoscience Center as one of the dating technique for faulting. This report includes methods for sample preparation, analyses, and age calculation on the K-Ar dating. This can contribute to an evaluation of calculated K-Ar ages.
 Ar resetting in an ultracataclasite by reactivation of a fossil seismogenic fault along the subducting plate interface in the Mugi M
Ar resetting in an ultracataclasite by reactivation of a fossil seismogenic fault along the subducting plate interface in the Mugi M lange of the Shimanto accretionary complex, southwest Japan
lange of the Shimanto accretionary complex, southwest JapanTonai, Satoshi*; Ito, Shun*; Hashimoto, Yoshitaka*; Tamura, Hajimu; Tomioka, Naotaka*
Journal of Structural Geology, 89, p.19 - 29, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:48.89(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We used the K-Ar ages of clay-sized mineral grains to investigate the timing of activity on the fossil seismogenic Minami-Awa Fault. The K-Ar ages from matrix shale of the m lange range from 85 to 48 Ma and decrease with decreasing amount of detrital mica. In contrast, the K-Ar ages of an ultracataclasite within the fault core are significantly younger, ranging from 29 to 23 Ma, and are unrelated to grain size. This indicates that
lange range from 85 to 48 Ma and decrease with decreasing amount of detrital mica. In contrast, the K-Ar ages of an ultracataclasite within the fault core are significantly younger, ranging from 29 to 23 Ma, and are unrelated to grain size. This indicates that  Ar diffused completely from the ultracataclasite between 29 and 23 Ma. The diffusion of
Ar diffused completely from the ultracataclasite between 29 and 23 Ma. The diffusion of  Ar in the ultracataclasite was probably caused by frictional heating or high-temperature fluid migration that occurred when the fault was reactivated. The results indicate that seismogenic faults that separate tectonic m
Ar in the ultracataclasite was probably caused by frictional heating or high-temperature fluid migration that occurred when the fault was reactivated. The results indicate that seismogenic faults that separate tectonic m lange from coherent strata in accretionary complex may slip, not only during accretion, but also long after accretion.
lange from coherent strata in accretionary complex may slip, not only during accretion, but also long after accretion.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yasue, Kenichi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.86 - 107, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:34.63(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-019, 42 Pages, 2015/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2015. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2015 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Shimada, Akiomi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-012, 43 Pages, 2015/08
The concept of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan is based on a multibarrier system which combines a stable geological environment with an engineered barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in tectonically active zone. This report is to outline 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) of research and development (R&D) for geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the HLW in JAEA. Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance, and the past progress in this report. The objectives, outline, contents and schedule during the next 7 years are described in detail. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and Systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Kokubu, Yoko; Kobori, Kazuo; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Matsubara, Akihiro; Shibata, Kenji; Tamura, Hajimu; Tanabe, Hiroaki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-033, 43 Pages, 2014/09
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2014. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2014 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Sueoka, Shigeru; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Ikuta, Masafumi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-047, 109 Pages, 2014/03
This annual report documents the progress of R&D in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 2nd Midterm Plan (FY 2010 - 2014) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) development and systematization of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application and verification of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Tamura, Hajimu; Sato, Keiko*
Chishitsu Gijutsu, (3), p.21 - 25, 2013/09
K-Ar age of fault is sometimes exclusive fact age of fault activity though the age of fault activity is determined on stratigraphy and ages by different dating methods. This note describes application of K-Ar dating to fault sample. Pseudotachylyte and Authigenic illite in fault gauge are major target material of dating. Sample preparation and determination of age are difficult for both of them and the geochronology is still in development stage. Dating examples of Pseudotachylyte says that sample separation is important to select part which was equilibrate to atomosphere in generation by spot analysis like laser fusion  Ar-
Ar-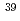 Ar dating, as illite examples that sample preparation to obtain fine - about 1 micrometer or less - grain and sample determination by inspection with electron microscope or XRD analysis are important.
Ar dating, as illite examples that sample preparation to obtain fine - about 1 micrometer or less - grain and sample determination by inspection with electron microscope or XRD analysis are important.
JRR-2 Control Office; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Kohayakawa, Toru; Morozumi, Minoru; Kambayashi, Yuichiro; Shitomi, Hajimu; Kokanezawa, Takashi; et al.
JAERI 1027, 57 Pages, 1962/09
no abstracts in English
Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Haginoya, Kinichi; Kohayakawa, Toru; Yamaki, Jikei; Yokota, Mitsuo; Horiki, Oichiro; Yuhara, Shunichi; et al.
JAERI 1023, 120 Pages, 1962/09
no abstracts in English
JRR-2 Operations Office; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Haginoya, Kinichi; Kohayakawa, Toru; Yamaki, Jikei; Yokota, Mitsuo; Horiki, Oichiro; et al.
JAERI 1024, 79 Pages, 1962/08
no abstracts in English
JRR-2 Critical Experiments Group; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Kohayakawa, Toru; Morozumi, Minoru; Kambayashi, Yuichiro; Shitomi, Hajimu; Kokanezawa, Takashi; et al.
JAERI 1025, 62 Pages, 1962/03
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Mayuko; Umeda, Koji; Asamori, Koichi; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Tamura, Hajimu
no journal, ,
In 1997, the Kagoshima earthquake doublet, consisting of two closely associated Mw 6 strike-slip events, five km and 48 days apart, has occurred in southwest Japan. The location is where an E-W trending discontinuity along 32N latitude on southern Kyushu Island is clearly defined in GPS velocities, indicating the presence of a highly active left-lateral shear zone. However, there have not been any obvious indications of active faulting at the surface prior to the earthquake doublet, which could be associated with this shear zone. Three-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric sounding data obtained in the source region of the earthquake doublet reveals a near-vertical conductive zone with a width of 20 km, extending down to the base of the crust and perhaps into the upper mantle toward the Okinawa trough. The prominent conductor corresponds to the western part of the active shear zone. Elevated  He/
He/ He ratios in groundwaters sampled from hot spring and drinking water wells suggest the emission of mantle-derived helium from the seismic source region. The geophysical and geochemical observations are significant indications that the invasion of mantle fluids into the crust, driven by upwelling asthenosphere from the Okinawa trough, triggers the notable left-lateral shearing in the zone in the present-day subduction system. In addition, the existence of aqueous fluids in and below the seismogenic layer could change the strength of the zones, and alter the local stress regime, resulting in the occurrence of the 1997 earthquake doublet.
He ratios in groundwaters sampled from hot spring and drinking water wells suggest the emission of mantle-derived helium from the seismic source region. The geophysical and geochemical observations are significant indications that the invasion of mantle fluids into the crust, driven by upwelling asthenosphere from the Okinawa trough, triggers the notable left-lateral shearing in the zone in the present-day subduction system. In addition, the existence of aqueous fluids in and below the seismogenic layer could change the strength of the zones, and alter the local stress regime, resulting in the occurrence of the 1997 earthquake doublet.
Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Tamura, Hajimu; Shibata, Kenji; Yokoyama, Tatsunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Tamura, Hajimu; Shibata, Kenji
no journal, ,
X-ray diffraction analysis and K-Ar dating were applied for fault gouges in the late Cretaceous Kojaku Granite, Tsuruga Peninsula. The fault gouge includes smectite, 1M type illite, and kaolinite, based on the X-ray diffraction analysis. The K-Ar dating shows approximately 39 to 45 Ma for the
type illite, and kaolinite, based on the X-ray diffraction analysis. The K-Ar dating shows approximately 39 to 45 Ma for the  0.1
0.1  m size fractions separated from the gouges. The K-Ar ages and the reconstructed cooling history of the granite suggest that the 1M
m size fractions separated from the gouges. The K-Ar ages and the reconstructed cooling history of the granite suggest that the 1M illite was formed at 60 to 110
illite was formed at 60 to 110  C (approximately 2 to 4 km in depth for 30
C (approximately 2 to 4 km in depth for 30  C/km of geothermal gradient).
C/km of geothermal gradient).
Tamura, Hajimu; Kokubu, Yoko; Umeda, Koji
no journal, ,
JAEA installed an IsotopX NGX noble gas mass spectrometer with an water sample oriented preparation system in Tono Geoscience Center to measure helium accumulation age and neon isotope ratio of ground water for estimation of ground water stability on long term geological stability survay on geological disposal of nuclear waste. High precision isotope analysis by multi-collector mass spectrometer is neccessary tool for neon isotope analysis of young ground water due to small isotopic variation of neon for nucleogenic reaction or mixing of volcanic fluids in ground water. NGX-004 was configured for simultanous measurement of neon isotopes with 2 faradays for  Ne and
Ne and  Ne, and 1 SEM for
Ne, and 1 SEM for  Ne spaced out 1 m/z each other. 10.084
Ne spaced out 1 m/z each other. 10.084  0.002 of
0.002 of  Ne/
Ne/ Ne and 0.02598
Ne and 0.02598  0.00004 of
0.00004 of  Ne/
Ne/ Ne were obtained by
Ne were obtained by 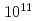 ohm faraday and
ohm faraday and 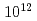 ohm faraday, and ion count and
ohm faraday, and ion count and 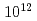 ohm faraday, which is able to resolve 0.2% difference.
ohm faraday, which is able to resolve 0.2% difference.
Niwa, Masakazu; Tamura, Hajimu*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Shimizu, Mayuko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Hajimu*; Kokubu, Yoko; Umeda, Koji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kokubu, Yoko; Tamura, Hajimu*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori
no journal, ,
High precision noble gas isotope analysis of groundwater is useful to estimate age and origin of groundwater. This study presents measurement of isotope ratio using a multi-collector noble gas mass spectrometer with six collectors and an auto noble gas purification instrument. The results of measurement of neon and helium in trial samples suggest that the mass spectrometer with high precision enable the noble gas isotope analysis of groundwater.