Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:74.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
 Fe
Fe GeO
GeO with andalusite structure
with andalusite structureKakimoto, Kazuo*; Takada, Saki*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Hatakeyama, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054704_1 - 054704_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Konomi, Taro*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011049_1 - 011049_6, 2021/03
Yee-Rendon, B.; Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011043_1 - 011043_5, 2021/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been working in the research and development of an Accelerator Driven Subcritical System (ADS) for the transmutation of nuclear waste. The ADS proposed by JAEA consists of a CW proton linac of 30 MW coupling with a subcritical core reactor. The accelerator will be operated with a beam current of 20 mA. Normal conducting Radio-Frequency Cavities (NRFC) and Superconducting Radio-Frequency Cavities (SRFC) will be used to achieve final energy of 1.5 GeV, and the SRFC will be employed for the main part of the acceleration: from 2 MeV to 1.5 GeV. In the first stage of the accelerator development, the focus was the design and optimization of the SRFC models and the beam optics. For the SRFC sections, the acceleration will be done by using Half Wave Resonators (HWR), Single Spokes (SS), and Elliptical cavities (Ellip) operating with a frequency of 162, 324, and 648 MHz, respectively. The beam optics were optimized satisfying the equipartitioning condition to control the emittance growth, which helped to reduce the beam halos and the beam loss.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.59(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Otani, Masashi*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Naito, Fujio*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Iinuma, Hiromi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012097_1 - 012097_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.48(Physics, Particles & Fields)A disk and washer (DAW) coupled cavity linac (CCL) has been developed for a middle velocity part in a muon linac to measure muon anomalous magnetic moment and search for electric dipole moment. I will accelerate muons from 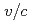 =
=  = 0.3 to 0.7 at an operational frequency of 1.3GHz. In this poster, the cavity design, beam dynamics design, and the cold-model measurements will be presented.
= 0.3 to 0.7 at an operational frequency of 1.3GHz. In this poster, the cavity design, beam dynamics design, and the cold-model measurements will be presented.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.48(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012054_1 - 012054_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Particles & Fields)An inter-digital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) is developed in a muon linac at the J-PARC E34 experiment. IH-DTL will accelerate muons from 0.34 MeV to 4.5 MeV at a drive frequency of 324 MHz. Since IH-DTL adopts an APF method, with which the beam is focused in the transverse direction using the rf field only, the proper beam matching of the phase-space distribution is required before the injection into the IH-DTL. Thus, an IH-DTL prototype was fabricated to evaluate the performance of the cavity and beam transmission. As a preparation of the high-power test, tuners and coupler are designed and fabricated. In this paper, the development of the tuner and the coupler and the result of the low-power measurement will be presented.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Konomi, Taro*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2019) (Internet), p.399 - 402, 2019/11
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 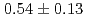 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yee-Rendon, B.; Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.107 - 111, 2019/07
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 407, 2019/07
An inter-digital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) is developed in a muon linac at the J-PARC E34 experiment. IH-DTL will accelerate muons from 0.34 MeV to 4.5 MeV at a drive frequency of 324 MHz. Since IH-DTL adopts an APF method, with which the beam is focused in the transverse direction using the rf field only, the proper beam matching of the phase-space distribution is required before the injection into the IH-DTL. Thus, an IH-DTL prototype was fabricated to evaluate the performance of the cavity and beam transmission. As a preparation of the high-power test, tuners and coupler are designed and fabricated. In the low power measurement, we decided the loop structure with witch the VSWR = 1.01 and field distortion of within 7%. In this paper, the development of the tuner and the coupler and the result of the low-power measurement will be presented.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Saito, Naohito; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2571 - 2574, 2019/06
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. Further improvement of the measurement system is needed to guarantee the required accuracy. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Otani, Masashi*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.37 - 40, 2019/06
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 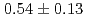 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo*; et al.
Proceedings of 29th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2018) (Internet), p.180 - 183, 2019/01
We have developed an Interdigital H-mode (IH) Drift-Tube Linac (DTL) design with an alternative phase focusing (APF) scheme for a muon linac, in order to measure the anomalous magnetic moment and electric dipole moment (EDM) of muons at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The IH-DTL accelerates muons from beta 0.08 to 0.28 at an operational frequency of 324 MHz. The output beam emittances are calculated as 0.315  and 0.195
and 0.195  mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.904 - 908, 2018/10
We have developed an Interdigital H-mode (IH) Drift-Tube Linac (DTL) design with an Alternative Phase Focusing (APF) scheme for a muon linac, in order to measure the anomalous magnetic moment and Electric Dipole Moment (EDM) of muons at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The IH-DTL accelerates muons from beta 0.08 to 0.28 at an operational frequency of 324 MHz. The output beam emittances are calculated as 0.315  and 0.195
and 0.195  mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
mm mrad in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, which satisfies the experimental requirement.
Otani, Masashi*; Sue, Yuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Iijima, Toru*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1067(5), p.052012_1 - 052012_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.76(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have measured the muon beam profile after acceleration using a radio frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). Positive muons are injected to an aluminum degrader and negative muoniums (Mu ) are generated. The generated Mu
) are generated. The generated Mu s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu
s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.