Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kojima, Kunihiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Chimura, Motoki; Saha, P. K.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2025(1), p.013G01_1 - 013G01_19, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A comprehensive study on the random resonances was conducted to mitigate beam losses and ensure sufficient tunability of the operating point for further beam power ramp-up in the 3-GeV rapid cycling synchrotron of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. Low-intensity beam studies revealed considerable excitation of the half-integer random resonance. This half-integer random resonance was successfully compensated using trim quadrupole magnets without exciting other higher-order resonances. By implementing a conventional theoretical procedure based on resonance driving terms, we identified the leakage field from extraction magnets as the primary source of the error field driving the random resonance. High-intensity beam studies confirmed that our resonance compensation approach substantially mitigated beam loss in higher-tune regions, making it highly effective in improving operating point tunability.
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(8), p.1109 - 1116, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Harada, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Imai, Kenichi*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.04001_1 - 04001_7, 2022/11

 atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)
atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)Yamamoto, Takeshi; Fujita, Manami; Gogami, Toshiyuki*; Harada, Takeshi*; Hayakawa, Shuhei*; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ishikawa, Yuji*; Kamata, K.*; Kanauchi, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.03001_1 - 03001_5, 2022/11
Kitamura, Akihisa*; Okazaki, Sota*; Kondo, Mitsuru*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Hori, Rie*; Ikeda, Masayuki*; Ichimura, Koji*; Nakagawa, Yuki*; Mori, Hideki*
Shizuoka Daigaku Chikyu Kagaku Kenkyu Hokoku, (49), p.73 - 86, 2022/07
On July 3 2021, a debris flow caused by a landslide from a landfill occurred along the Aizome River in the Izusan area of Atami City, Shizuoka. In this study, debris flow deposits and soil samples were characterized in terms of their sedimentology and geochemically analyzed.
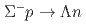 reaction in momentum range 470-650 MeV/
reaction in momentum range 470-650 MeV/
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai*; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 128(7), p.072501_1 - 072501_6, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:86.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary)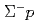 elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(4), p.045204_1 - 045204_20, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:89.84(Physics, Nuclear)Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:82.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
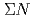 interaction from the
interaction from the 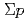 scattering experiment at J-PARC
scattering experiment at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1643, p.012174_1 - 012174_6, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.29(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Sato, Yuki; Ozawa, Shingo*; Terasaka, Yuta; Minemoto, Kojiro*; Tamura, Satoshi*; Shingu, Kazutoshi*; Nemoto, Makoto*; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.734 - 744, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:94.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tamura, Koji*; Toyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2020/05
, 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2020/05
The laser cutting technology is expected to be a promising candidate for the decommissioning measure of nuclear facilities, because it has a lot of advantage such as its high controllability and excellent suitability to remote handling by robot arm, etcetera. This report describes the recent result from laser cutting technology development for thick steel materials summarizing the cutting demonstration of 300 mm thick steels and dummy pressure vessel, the analysis of cutting condition of thick steel cutting, the observation of cutting process, remote controlled cutting system, the cutting in pile of steels by the system, and countermeasure for fume produce by cutting process.
Tamura, Koji*; Toyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 61(5), p.413 - 415, 2019/05
, 61(5), p.413 - 415, 2019/05
In decommissioning of nuclear reactors, it is necessary to disassemble the nuclear reactor structure. In addition to the conventional cutting method, the laser method has many advantages such as remote controllability and no need for replacement parts such as blades, which can be a powerful choice. Nuclear reactor structure such as a pressure vessel are made of steel materials with a thickness exceeding 100 mm, and the laser method has poor knowledge and experience in cutting such thick steel materials. Therefore, as a result of trial cutting of steel materials under various cutting conditions with the high power fiber laser which is progressively available nowadays, it has been demonstrated that laser cutting is also possible for thick plates such as those used in nuclear reactors, and cutting of thick steel plates. We also developed the cutting technology using remote control using a robot in order to apply it to the decommissioning of thick steel cutting on the spot.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
 Cs redistribution in the Oginosawa River catchment near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using integrated watershed modeling
Cs redistribution in the Oginosawa River catchment near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using integrated watershed modelingSakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.; Funaki, Hironori; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Mori, Koji*; Tada, Kazuhiro*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; Kitamura, Akihiro; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 182, p.44 - 51, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:34.81(Environmental Sciences)The Oginosawa River catchment lies 15 km south-west of the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear plant. The General-purpose Terrestrial Fluid-flow Simulator (GETFLOWS) code was used to study sediment and  Cs redistribution within the catchment. Cesium-137 input to watercourses came predominantly from land adjacent to river channels and forest gullies. Forested areas far from the channels only made a minor contribution to
Cs redistribution within the catchment. Cesium-137 input to watercourses came predominantly from land adjacent to river channels and forest gullies. Forested areas far from the channels only made a minor contribution to  Cs input to watercourses, total erosion of between 0.001-0.1 mm from May 2011 to December 2015. The 2.3-6.9% y
Cs input to watercourses, total erosion of between 0.001-0.1 mm from May 2011 to December 2015. The 2.3-6.9% y decrease in the amount of
decrease in the amount of  Cs in forest topsoil over the study period can be explained by radioactive decay (approximately 2.3% y
Cs in forest topsoil over the study period can be explained by radioactive decay (approximately 2.3% y ), along with a migration downwards into subsoil and a small amount of export. The amount of
), along with a migration downwards into subsoil and a small amount of export. The amount of  Cs available for release from land adjacent to rivers is expected to be lower in future than compared to this study period, as the simulations indicate a high depletion of inventory from these areas.
Cs available for release from land adjacent to rivers is expected to be lower in future than compared to this study period, as the simulations indicate a high depletion of inventory from these areas.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
 scattering experiment using high intensity pion beams at J-PARC
scattering experiment using high intensity pion beams at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Sugimura, Hitoshi; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 17, p.041002_1 - 041002_6, 2017/07
Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Malins, A.; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Machida, Masahiko; Mori, Koji*; Tada, Kazuhiro*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; Tawara, Yasuhiro*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 169-170, p.137 - 150, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:60.50(Environmental Sciences)This paper describes watershed modeling of catchments surrounding the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant to understand radio-cesium redistribution by water flows and sediment transport. We extended our previously developed three-dimensional hydrogeological model of the catchments to calculate the migration of radio-cesium in both sediment-sorbed and dissolved forms. The simulations cover the entirety of 2013, including nine heavy rainfall events, as well as Typhoon Roke in September 2011. Typhoons Man-yi and Wipha were the strongest typhoons in 2013 and had the largest bearing on radio-cesium redistribution. The simulated  Cs discharge quantities over the nine events in 2013 are in good agreement with field monitoring observations. Deposition mainly occurs on flood plains and points where the river beds broaden in the lower basins, and within dam reservoirs along the rivers. Differences in
Cs discharge quantities over the nine events in 2013 are in good agreement with field monitoring observations. Deposition mainly occurs on flood plains and points where the river beds broaden in the lower basins, and within dam reservoirs along the rivers. Differences in  Cs discharge ratios between the five basins are explained by differences in the initial fallout distribution within the basins, the presence of dam reservoirs, and the input supply to watercourses. It is possible to use these simulation results to evaluate future radioactive material distributions in order to support remediation planning.
Cs discharge ratios between the five basins are explained by differences in the initial fallout distribution within the basins, the presence of dam reservoirs, and the input supply to watercourses. It is possible to use these simulation results to evaluate future radioactive material distributions in order to support remediation planning.
 O
O /C hydrazine electrooxidation catalysts for anion exchange membrane fuel cells
/C hydrazine electrooxidation catalysts for anion exchange membrane fuel cellsSakamoto, Tomokazu*; Masuda, Teruyuki*; Yoshimoto, Koji*; Kishi, Hirofumi*; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Hori, Akihiro*; Horiuchi, Yosuke*; Serov, A.*; et al.
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 164(4), p.F229 - F234, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:38.72(Electrochemistry) studied by single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffraction
studied by single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractionKawasaki, Takuro; Kaneko, Koji; Nakamura, Ai*; Aso, Naofumi*; Hedo, Masato*; Nakama, Takao*; Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Tamura, Itaru; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 85(11), p.114711_1 - 114711_5, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:65.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)