Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshimoto, Masataka*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Watanabe, Kenta*; Shimizu, Keisuke*; Horisawa, Yuhei*; Kobayashi, Takeshi*; Tsurita, Hanae*; Suzuki, Kota*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Hirayama, Masaaki*
Sustainable Energy & Fuels (Internet), 8(6), p.1236 - 1244, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0Photo-rechargeable systems, which can efficiently convert and store solar energy into chemical energy within single devices, are essential to harness sunlight effectively. Photo-(de)intercalation plays a pivotal role in the functionality of photorechargeable systems. Nevertheless, the photo-(de)intercalation process has not been conclusively confirmed owing to potential interference from side reactions, such as the decomposition of liquid electrolytes and the elution of electrode materials. In this study, we successfully demonstrated photo-responsive Li -deintercalation using an all-solid-state thin-film battery comprised of epitaxially-grown anatase TiO
-deintercalation using an all-solid-state thin-film battery comprised of epitaxially-grown anatase TiO doped with Nb (a-TiO
doped with Nb (a-TiO :Nb) as the cathode. Under light irradiation, Li
:Nb) as the cathode. Under light irradiation, Li -deintercalation occurred and was subsequently reversibly intercalated into a-TiO
-deintercalation occurred and was subsequently reversibly intercalated into a-TiO :Nb during discharge.
:Nb during discharge.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Horisawa, Yuhei*; Yoshimoto, Masataka*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Suzuki, Kota*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Hirayama, Masaaki*
Nano Letters, 24(6), p.1916 - 1922, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Electrochemistry has extended from reactions at solid/liquid interfaces to those at solid/solid interfaces. In this study, we achieve the stable photoelectrochemical reaction at the semiconductor-electrode/solid-electrolyte interface in Nb-doped anatase-TiO (a-TiO
(a-TiO :Nb)/Li
:Nb)/Li PO
PO (LPO)/Li all-solid-state cell. The oxidative currents of a-TiO
(LPO)/Li all-solid-state cell. The oxidative currents of a-TiO :Nb/LPO/Li increase upon light irradiation when a-TiO
:Nb/LPO/Li increase upon light irradiation when a-TiO :Nb is located at a potential that is more positive than its flat-band potential. The photoelectrochemical reaction at the semiconductor/solid-electrolyte interface is driven by the same principle as that at semiconductor/liquid-electrolyte interfaces. Thus, we extend photoelectrochemistry to all-solid-state systems composed of solid/solid interfaces.
:Nb is located at a potential that is more positive than its flat-band potential. The photoelectrochemical reaction at the semiconductor/solid-electrolyte interface is driven by the same principle as that at semiconductor/liquid-electrolyte interfaces. Thus, we extend photoelectrochemistry to all-solid-state systems composed of solid/solid interfaces.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Hotchi, Hideaki*; Saha, P. K.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.64 - 68, 2023/11
The J-PARC 3GeV synchrotron (RCS) provides high intensity proton beams to the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) and the Main Ring (MR). The harmonic number (h) of the RCS is 2 and the RCS normally accelerates two bunches. For some experiments at the MLF, a single bunch is preferred. In this case, one of the rf bucket is filled with protons and the other is empty. Therefore the beam intensity is halved. If the RCS can accelerate with h=1, the intensity per bunch can be doubled, enabling to provide single bunch beams to the MLF with the maximum intensity. This possibly increases the MR beam power by injecting high intensity single bunches eight times. In this presentation, we report mainly on the consideration of h=1 acceleration in the RCS by longitudinal simulations.
Arai, Sora; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Kitamura, Ryo
JAEA-Technology 2023-009, 18 Pages, 2023/05
The linac located at the head of the J-PARC accelerators and required to provide the stable and high-quality beam. One of the accelerating cavities in the linac is the Separated-type Drift Tube Linac (SDTL). It is important to appropriately apply the RF power into the cavity for the stable operation. However, after the recovery from the Great East Japan Earthquake, the RF power could not be applied into the cavities for several SDTL cavities because the voltage standing wave ratio increased around the designed operating power. The investigation revealed that the inner surface of the cavity was exposed to high humidity and the backflow of oil from the rotary pump for a long period of time after the earthquake. It was suggested that the residue on the inner surface caused the multipactor resulted in the failure when the power was applied. The residue was wiped out with organic solvents and acids, resulted in solving the failure. This report describes the method and results of the cleaning for the cavity in 2021.
Kosaka, Satoshi*; Arai, Sora; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Kitamura, Ryo
JAEA-Technology 2023-003, 34 Pages, 2023/05
The negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam is accelerated with a peak current of 50 mA in the J-PARC linac. The linac consists of the H- ion source and four kinds of accelerating cavities; a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ), a drift-tube linac (DTL), a separated-DTL (SDTL), and an annular-ring coupled structure linac (ACS). The accelerating electric field exists between the drift-tubes in the tank of the DTL. The quadrupole magnet for the beam focusing (DTQ) is installed in the drift-tube. The DTQ at J-PARC employs electromagnets to generate the magnetic field. It is important to set correctly the polarity of the magnetic field of the DTQ for tuning the beam. In this paper, we report the method of confirming the magnetic field polarity of DTQ, that is, the current wiring polarity by measuring DC current using a clamp meter on the power supply side and visually confirming the cable wiring connection on the electromagnet side.
) ion beam is accelerated with a peak current of 50 mA in the J-PARC linac. The linac consists of the H- ion source and four kinds of accelerating cavities; a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ), a drift-tube linac (DTL), a separated-DTL (SDTL), and an annular-ring coupled structure linac (ACS). The accelerating electric field exists between the drift-tubes in the tank of the DTL. The quadrupole magnet for the beam focusing (DTQ) is installed in the drift-tube. The DTQ at J-PARC employs electromagnets to generate the magnetic field. It is important to set correctly the polarity of the magnetic field of the DTQ for tuning the beam. In this paper, we report the method of confirming the magnetic field polarity of DTQ, that is, the current wiring polarity by measuring DC current using a clamp meter on the power supply side and visually confirming the cable wiring connection on the electromagnet side.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(3), p.032802_1 - 032802_12, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is a useful device for performing longitudinal beam tuning using the pointwise longitudinal phase distribution measured at selected points in the beam transportation. To measure the longitudinal phase distribution of a low-energy negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H
) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
determined by single-crystal neutron diffractionTanaka, Seiya*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Maruyama, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Shigenori*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014403_1 - 014403_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) beam
beamKitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.330 - 332, 2023/01
In the J-PARC linac, a new bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is developed to stably measure the high-intensity and low-energy H beam by improving the strength of the target probe for the heat loading. The new target probe is made of the graphite. The first measurement of the longitudinal beam profile has been realized with the BSM at the core region of the high-intensity beam. Since the beam profile can be measured with the new BSM at any transverse position thanks to the new target probe, we propose the advanced application of the beam diagnostics with the BSM. In this presentation, some new approaches of the beam diagnostics with the BSM; the transverse profile measurement using the secondary electrons and the beam current evaluation from the transverse profile measurement, are discussed beyond the original usage of the BSM.
beam by improving the strength of the target probe for the heat loading. The new target probe is made of the graphite. The first measurement of the longitudinal beam profile has been realized with the BSM at the core region of the high-intensity beam. Since the beam profile can be measured with the new BSM at any transverse position thanks to the new target probe, we propose the advanced application of the beam diagnostics with the BSM. In this presentation, some new approaches of the beam diagnostics with the BSM; the transverse profile measurement using the secondary electrons and the beam current evaluation from the transverse profile measurement, are discussed beyond the original usage of the BSM.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Miura, Akihiko; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.212 - 214, 2023/01
In the J-PARC linac, the bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is developed to precisely and rapidly measure the longitudinal beam profile at the front-end, towards the improvement of the beam matching. The graphite target having the good strength to the high-power beam, has been introduced in order to resist the heat loading of the high-intensity beam. The resolution and other uncertainties were evaluated for the BSM. The longitudinal Twiss parameters and emittance were measured using the BSM and the IMPACT, which was the 3D particle-in-cell simulation code. The precision of the longitudinal emittance measurement was improved, by implementing uncertainties related to the BSM into the calculation. In this presentation, we will report a series of the measurement result, the method of the beam diagnostics with the BSM at the front-end, and the comparison between the measurement and the beam simulation.
 beam by using bunch shape monitor with graphite target
beam by using bunch shape monitor with graphite targetKitamura, Ryo
Proceedings of International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2022) (Internet), p.532 - 535, 2022/12
At J-PARC Linac, bunch shape monitors (BSMs) have been used to measure a longitudinal profile of high power H beam. Operational principle of the monitor is similar to that of the streak-camera. The BSM inserts a biased-solid target into H
beam. Operational principle of the monitor is similar to that of the streak-camera. The BSM inserts a biased-solid target into H beam to extract and accelerate secondary electrons. These electrons are then modulated with synchronized RF. After passing through dipole B field, a longitudinal profile is converted to a transverse one. For the BSM, a choice of target material is essential to reduce beam loss and to have sufficient tolerance for breakage by the interaction with high power beams. The BSM with graphite target realized the measurement of high-power 3 MeV beam for the first time.
beam to extract and accelerate secondary electrons. These electrons are then modulated with synchronized RF. After passing through dipole B field, a longitudinal profile is converted to a transverse one. For the BSM, a choice of target material is essential to reduce beam loss and to have sufficient tolerance for breakage by the interaction with high power beams. The BSM with graphite target realized the measurement of high-power 3 MeV beam for the first time.
 Sr
Sr CoO
CoO at initial electrochemical process in an alkaline solution
at initial electrochemical process in an alkaline solutionMatsuzaki, Akira*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Oguchi, Shoya*; Komo, Mamoru*; Ikezawa, Atsunori*; Suzuki, Kota*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Arai, Hajime*; Kanno, Ryoji*
Electrochemistry (Internet), 90(10), p.107001_1 - 107001_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Electrochemistry)Oxygen reduction and evolution reactions (ORR and OER) of perovskite-type La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO were characterized using two-dimensional model electrodes with different reaction planes. Synthesized by pulsed laser deposition, these thin and flat electrodes can reveal the reaction plane dependence of the ORR activity. From steady-state polarization measurements in KOH (aq.), the ORR activity was the highest on the (001) film during the first ORR/OER cycle, and it decreased significantly during the second cycle. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction clarified crystal structure changes in the bulk and surface regions of La
were characterized using two-dimensional model electrodes with different reaction planes. Synthesized by pulsed laser deposition, these thin and flat electrodes can reveal the reaction plane dependence of the ORR activity. From steady-state polarization measurements in KOH (aq.), the ORR activity was the highest on the (001) film during the first ORR/OER cycle, and it decreased significantly during the second cycle. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction clarified crystal structure changes in the bulk and surface regions of La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO , and these changes are associated with forming oxygen defects during the initial electrochemical process. Furthermore, the La
, and these changes are associated with forming oxygen defects during the initial electrochemical process. Furthermore, the La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO surface partially decomposed upon reacting. Therefore, the interfacial structures formed in the electrochemical reaction field is important for enhancing ORR and OER activities.
surface partially decomposed upon reacting. Therefore, the interfacial structures formed in the electrochemical reaction field is important for enhancing ORR and OER activities.
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O (0
(0  x
x  0.2) hexagonal ferrite
0.2) hexagonal ferriteMaruyama, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Seiya*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nakao, Akiko*; Moriyama, Kentaro*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Utsumi, Shigenori*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 892, p.162125_1 - 162125_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.86(Chemistry, Physical)Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
 beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitor
beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitorKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011012_1 - 011012_6, 2021/03
The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) is required to measure the bunch size of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
Kitamura, Ryo; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kim, B.*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Mibe, Tsutomu*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(3), p.033403_1 - 033403_9, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.91(Physics, Nuclear)A negative muonium ion (Mu ) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu
) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu
ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu ion source. The measured event rate of Mu
ion source. The measured event rate of Mu ions was
ions was 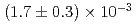 Mu
Mu /s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was
/s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was 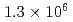 /s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu
/s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was
ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was 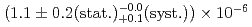 . This Mu
. This Mu ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
 MnO
MnO cathode in an all-solid-state thin-film battery during cycling
cathode in an all-solid-state thin-film battery during cyclingHikima, Kazuhiro*; Hinuma, Yoyo*; Shimizu, Keisuke*; Suzuki, Kota*; Taminato, So*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Masuda, Takuya*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Kanno, Ryoji*
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13(6), p.7650 - 7663, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:67.96(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We evaluated the structural change of the cathode material Li MnO
MnO that was deposited as an epitaxial film with an (001) orientation in an all-solid-state battery. In case of the electrode with LiPO
that was deposited as an epitaxial film with an (001) orientation in an all-solid-state battery. In case of the electrode with LiPO coating. Experiments revealed a structural change to a high-capacity (activated) phase that proceeded gradually and continuously with cycling. The activated phase barely showed any capacity fading. We propose a mechanism of structural change with cycling: charging to a high voltage at a sufficiently low Li concentration typically induces irreversible transition to a phase detrimental to cycling that could, but not necessarily, be accompanied by the dissolution of Mn and/or the release of O into the electrolyte, while a gradual irreversible transition to an activated phase happens at a similar Li concentration under a lower voltage.
coating. Experiments revealed a structural change to a high-capacity (activated) phase that proceeded gradually and continuously with cycling. The activated phase barely showed any capacity fading. We propose a mechanism of structural change with cycling: charging to a high voltage at a sufficiently low Li concentration typically induces irreversible transition to a phase detrimental to cycling that could, but not necessarily, be accompanied by the dissolution of Mn and/or the release of O into the electrolyte, while a gradual irreversible transition to an activated phase happens at a similar Li concentration under a lower voltage.
 molecule adsorption on polar and
molecule adsorption on polar and  -plane surfaces of GaN
-plane surfaces of GaNSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Asai, Yuya*; Tamura, Ryo*; Uedono, Akira*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(46), p.25282 - 25290, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.15(Chemistry, Physical)The initial oxidation of different GaN surfaces [the polar Ga-face (+c) and N-face (-c) and the nonpolar (10 0) (
0) ( )plane] under O
)plane] under O molecular beam irradiation was studied by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT molecular dynamics calculation. The results predict that triplet O
molecular beam irradiation was studied by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT molecular dynamics calculation. The results predict that triplet O either dissociates or chemisorbs at the bridge position on the +c-surface, while on N-terminated -c-surface the O
either dissociates or chemisorbs at the bridge position on the +c-surface, while on N-terminated -c-surface the O 2 molecule only undergoes dissociative chemisorption. On the
2 molecule only undergoes dissociative chemisorption. On the  -GaN surface, although the dissociation of O
-GaN surface, although the dissociation of O is dominant, the bond length and angle were found to fluctuate from those of O
is dominant, the bond length and angle were found to fluctuate from those of O molecules adsorbed on the polar surfaces. The computational model including both the surface spin and polarity of GaN is useful for understanding the interface between GaN and oxide layers in metal-oxide electronic.
molecules adsorbed on the polar surfaces. The computational model including both the surface spin and polarity of GaN is useful for understanding the interface between GaN and oxide layers in metal-oxide electronic.
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi
JAEA-Review 2020-015, 66 Pages, 2020/09
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculated from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2019 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.251 - 253, 2020/09
A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) in the low-energy region is being developed in the J-PARC linac to accelerate the high-intensity proton beam with the low emittance. A highly-oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was introduced as the target of the BSM to mitigate the thermal loading. The stable measurement of the BSM was realized thanks to the HOPG target, while the tungsten target was broken by the thermal loading from the high-intensity beam. However, since the longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM using the HOPG target was wider than the expected one, the improvement of tuning parameters is necessary for the BSM. The BSM consists of an electron multiplier, a bending magnet, and a radio-frequency deflector, which should be tuned appropriately. Behavior of these components were investigated and tuned. The longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM after the tuning was consistent with the expected one.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.