Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Miura, Hikaru*; Yamada, Shinya*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi*; Yomogida, Takumi; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okada, Shinji*; Itai, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 495, p.139031_1 - 139031_19, 2025/09
In this presentation, we analyzed the chemical state of cesium in radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs) released during the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident using high-resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XANES) and micro X-ray fluorescence ( -XRF). The results identified two forms of cesium: one dissolved in glass and the other enriched on the surfaces of internal voids. The latter is considered to have originally existed as a gas and became concentrated during the cooling and solidification of the molten glass. These findings are crucial for understanding the formation process of CsMPs during the accident, as well as for future decommissioning and safety assessments.
-XRF). The results identified two forms of cesium: one dissolved in glass and the other enriched on the surfaces of internal voids. The latter is considered to have originally existed as a gas and became concentrated during the cooling and solidification of the molten glass. These findings are crucial for understanding the formation process of CsMPs during the accident, as well as for future decommissioning and safety assessments.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Igawa, Kenichi*; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/03
To investigate possibility of the insertion of the reactivity by the deflection of the upper core support plate, structural mechanics analyses of the domain consisting of the fuel assemblies and core support plates and evaluation of the reactivity due to the inclination of the fuel assemblies in EBR-II were carried out. As a result, it was indicated that the upper core support plate deflected downward larger at the low flowrate condition than that at the high flowrate condition and positive reactivity was inserted due to the inclination of the fuel assemblies at the low flowrate condition.
Chiba, Kaori*; Matsui, Takuro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Yutani, Katsuhide*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Protein Science, 32(10), p.e4765_1 - e4765_13, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ohgama, Kazuya; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Dai-29-Ki Sokai, Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/03
An evaluation method for reactivity feedback due to core deformation during reactor power increase in sodium-cooled fast reactors is being developed for realistic core design evaluation. In this evaluation method, fuel assembly bowing was modeled with a beam element of the finite element method, and the assembly's pad contact between adjacent assemblies was modeled with a dedicated element which could consider the wrapper tube cross-sectional distortion and the pad stiffness depending on pad contact conditions. This fuel assembly bowing analysis model was verified for thermal bowing of a single assembly and assembly pad contact between adjacent assemblies in a core as past benchmark problems. The calculation results by this model showed good agreement with those of reference solutions of theoretical solutions or results by participating institutions in the benchmark. This study confirmed that the analysis model was able to calculate thermal assembly bowing appropriately.
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Yokoyama, Kenji; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2022/03
In sodium-cooled fast reactors, reactivity feedback is generated by thermal deformation of the core fuel assembly during core temperature rise. To utilize the core deformation reactivity as an inherent safety characteristic and to eliminate excessive conservativeness of core design in the safety evaluation, an evaluation method by coupling analyses of neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structural deformation has been developed. An experiment of unprotected loss-of-flow event in the experimental fast breeder reactor EBR-II was analyzed. The analysis results show that the core deformation reactivity has a negative feedback effect, and that the deformation reactivity is affected not only by the fuel movement but also by the movement of reflectors around the fuel. As a result, the availability of the evaluation method for core deformation reactivity feedback by coupled analysis approach is confirmed.
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
For design optimization of fast reactors, in order to consider the feedback reactivity due to thermal deformation of the core when the core temperature rises, which could not be considered in the conventional design analysis, a neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structure mechanics coupled analysis method has been developed. Neutronics code, plant dynamics code, and structural mechanics code are coupled by a control module in python script. This paper outlines the coupling method of analysis codes and the results of its application to an experiment in an actual plant.
Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Nishikawa, Shiro*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Usui, Norihisa*; Kamachi, Masafumi*; Aso, Noriko*; Tanaka, Yusuke*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 18(1), p.81 - 96, 2014/09
A drift simulation of tsunami debris flushed out from the Tohoku district, Japan, into the North Pacific due to the tsunami on March 11, 2011, has been conducted to monitor and forecast the drift path over the North Pacific. Results showed that tsunami debris was first transported eastward by the intense Kuroshio Extension and westerly, spreading in the north and south directions by both an energetic ocean eddy and a storm track over the ocean. Tsunami debris with larger windage was transported over the North Pacific by ocean surface wind rather than ocean current and arrived at the west coast of the North American Continent in the fall of 2011. Tsunami debris located near the North American Continent migrated, associated with the basin-scale seasonal change in the atmospheric pressure pattern. Our forecast run suggested that the tsunami debris belt will be formed from the North American Continent in the east to the Philippines in the west.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:110 Percentile:94.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Asazawa, Koichiro*; Martinez, U.*; Halevi, B.*; Suzuki, Toshiyuki*; Arai, Shigeo*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Atanassov, P.*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
Journal of Power Sources, 234, p.252 - 259, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:72 Percentile:86.16(Chemistry, Physical)Tanaka, Toshiyuki*; Miyajima, Rikio*; Asai, Hideaki*; Horiuchi, Yasuharu; Kumada, Koji; Asai, Yasuhiro*; Ishii, Hiroshi*
Earth Planets and Space, 65(2), p.59 - 66, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:23.52(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, S.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Skobelev, I.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.236 - 240, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:61.70(Physics, Applied)We irradiated the focusing soft X-ray laser pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm and the duration of 7 ps to aluminum surface. After the irradiation process, the irradiated surface was observed with a scanning electron microscope. The surface modifications caused by soft X-ray laser single pulse exposure were clearly seen. In addition, it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed in the shallow features. The nano-meter size modified surface structures on aluminum induced by the soft X-ray laser pulse is interesting as the newly surface structure. Hence, the soft X-ray laser beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining. We also provide a thermomechanical modeling of the soft X-ray laser interaction with aluminum briefly to explain the surface modification.
Norman, G.*; Starikov, S.*; Stegailov, V.*; Fortov, V.*; Skobelev, I.*; Pikuz, T. A.; Faenov, A.*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Kato, Yoshiaki*; Ishino, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 112(1), p.013104_1 - 013104_8, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:82.06(Physics, Applied)Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A. Y.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, T. A.; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Kaihori, Takeshi; Kawachi, Tetsuya
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 7(2), p.147 - 151, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.59(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We irradiated the soft X-ray laser (SXRL) pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm, the duration time of 7 ps to aluminum (Al), copper (Cu) and gold (Au) surfaces. After the irradiation processes of SXRL beam with laser flux of  14 mJ/cm
14 mJ/cm for Al case and of
for Al case and of  21 mJ/cm
21 mJ/cm for Cu and Au cases, the modified surfaces were observed with the visible microscope, the scanning electron microscope, and the atomic force microscope. The surface modifications caused by the SXRL irradiations were clearly seen on the surfaces, and it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed on the Al surface under a single pulse shot. The conical structures were formed in the features with the average depth of about 40 nm, and this value was in accordance with the attenuation length of the SXRL beam for Al. The modified structure on Al surface induced by SXRL pulse irradiations is different from those of Cu and Au surfaces. The modified structure formed on Al surface induced by the SXRL pulse exposure is interesting as the newly structure. Hence, the SXRL beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining, which enable to fabricate of three dimensional structures with nano-meter size on Al surface.
for Cu and Au cases, the modified surfaces were observed with the visible microscope, the scanning electron microscope, and the atomic force microscope. The surface modifications caused by the SXRL irradiations were clearly seen on the surfaces, and it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed on the Al surface under a single pulse shot. The conical structures were formed in the features with the average depth of about 40 nm, and this value was in accordance with the attenuation length of the SXRL beam for Al. The modified structure on Al surface induced by SXRL pulse irradiations is different from those of Cu and Au surfaces. The modified structure formed on Al surface induced by the SXRL pulse exposure is interesting as the newly structure. Hence, the SXRL beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining, which enable to fabricate of three dimensional structures with nano-meter size on Al surface.
Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Tanaka, Kosuke; Hirosawa, Takashi; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Onose, Shoji
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/12
A new fast reactor (FR) cycle concept was previously proposed that incorporates MgO-based inert matrix fuels (IMFs) containing minor actinides harmonious with the existing FR cycle technologies. A basic study of MgO-based IMFs was made regarding their fabrication, characterization and reprocessing in terms of applicability to existing FR cycle technology. It was concluded from these basic investigations of MgO-based IMFs that the existing FR cycle technologies can be applied to those for MgO-based IMFs, and the basic technologies of MgO-based IMFs containing minor actinides harmonious with the existing FR cycle technologies were established.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Terakawa, Kota*; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Imazono, Takashi; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.353 - 358, 2011/12
The understanding of the dynamics of the initial process is important for the micro processing and welding by the ultra-short laser pulse. The X-ray laser is suitable for probing this initial process because it has short wavelength (Ni-like Ag, 13.9 nm) and short duration (7 ps). For this investigation, the origin of time of the pumping pulse is quite important. In this study, we used the scintillation plate and the plasma gate technique to realize the spatial and temporal synchronization of the pump and probe pulses. For the spatial alignment, a CsI scintillation plate that was set at the sample position was illuminated by both the X-ray laser pulse, and the fluorescence light were detected by the CCD camera. For the temporal synchronization, we set a thin foil at the sample position. We measured the transmission of the X-ray laser while changing a temporal delay of the pumping laser with respect to the time of X-ray laser pulse to obtain the origin of the irradiation time.
Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Kishimoto, Maki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Momoko; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.15 - 24, 2011/12
This paper reviews recent improvement in the source development of laser-driven X-ray lasers and the applications in the research fields of material science, laser processing, X-ray imaging, and radiation damage in biological cells. In the application for material science, we have firstly observed temporal correlation between the domain structures of ferro-electric substance under the Curie temperature. In the laser processing, new X-ray laser interferometer reveals us the nano-scale surface distortion of substance pumped by a femto-second optical pulse. In the X-ray diffraction image, we have taken several static images of micro-structure of samples: now we are trying to extend the objective to nano-scale dynamics using pump and probe method. In the radiation damage of biological cells, we observed double strand break in DNA using X-ray laser exposure; this results are compared with the case using incoherent several KeV X-ray exposure.
Osaka, Masahiko; Miwa, Shuhei; Tanaka, Kosuke; Akutsu, Yoko; Ikeda, Kaoru*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Usuki, Toshiyuki; Yano, Toyohiko*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 38(12), p.2661 - 2666, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)Novel concepts for effective utilization of molybdenum (Mo) from nuclear waste and magnesium silicates from hazardous asbestos wastes are proposed. A fast reactor cycle scheme that incorporates each material is described in the present paper. Basic studies on some fundamental technologies for the present cycle are given. Basic separation aspects for Mo by using LIX63 micro capsules and tertiary pyridine resin were investigated. A simple chemical synthesis route for Mo precursor powder from Mo containing HNO solution was tested. Effects of impurities in recovered Mo on sintering behavior were experimentally investigated.
solution was tested. Effects of impurities in recovered Mo on sintering behavior were experimentally investigated.
Tanaka, Teruya*; Sato, Satoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Ochiai, Kentaro; Murata, Isao*; Takakura, Kosuke; Sato, Fuminobu*; Kada, Wataru*; Iida, Toshiyuki*; Konno, Chikara; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(2), p.681 - 686, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)Irradiation experiments of 14 MeV neutrons have been performed on a Li block assembly of 46  51
51  51 cm
51 cm with a 5 cm thick V-alloy layer inside to examine the accuracy of neutronics calculations for the Li/V-alloy blanket design. Foils of Nb, Ni, In and Au for reaction rate measurements of
with a 5 cm thick V-alloy layer inside to examine the accuracy of neutronics calculations for the Li/V-alloy blanket design. Foils of Nb, Ni, In and Au for reaction rate measurements of  Nb(n,2n)
Nb(n,2n)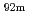 Nb,
Nb,  Ni(n,p)
Ni(n,p) Co,
Co,  In(n,n')
In(n,n')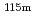 In,
In,  Au(n,
Au(n, )
)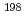 Au reactions and
Au reactions and  Li enriched (
Li enriched ( Li: 95.5%) and
Li: 95.5%) and  Li enriched (
Li enriched ( Li: 99.9%) Li
Li: 99.9%) Li CO
CO pellets for tritium production rate measurements were installed in the assembly. Results of the measurements were compared with those of calculations with MCNP5, JENDL-3.3 and JENDL/D-99. The comparisons for the reaction rates in the Nb, Ni and In foils indicate that measurements and calculations of the fast neutron transport are consistent almost within 10%. In the comparison for the reaction rates in the Au foils, the underestimation of 15% was found at a surface of the V-alloy layer. There is a possibility that this is due to the elastic scattering cross section of V around 4 keV as previously reported. The comparisons for tritium production rates in the
pellets for tritium production rate measurements were installed in the assembly. Results of the measurements were compared with those of calculations with MCNP5, JENDL-3.3 and JENDL/D-99. The comparisons for the reaction rates in the Nb, Ni and In foils indicate that measurements and calculations of the fast neutron transport are consistent almost within 10%. In the comparison for the reaction rates in the Au foils, the underestimation of 15% was found at a surface of the V-alloy layer. There is a possibility that this is due to the elastic scattering cross section of V around 4 keV as previously reported. The comparisons for tritium production rates in the  Li enriched and
Li enriched and  Li enriched Li
Li enriched Li CO
CO pellets indicate that calculated rates were larger than results of the measurements by 2-8% and 1-4%, respectively.
pellets indicate that calculated rates were larger than results of the measurements by 2-8% and 1-4%, respectively.
Kanamori, Masashi; Suto, Toshiyuki; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Takada, Jun*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.42 - 45, 2011/07
It has been ten years since the Tokai-mura JCO criticality accident. Verification of dose control method and dose estimation for the termination of the accident was performed. At the time of the termination work, personal dose estimation and control was performed based on measurements of neutron and  ray doses taken before the termination work. But the personal dose for workers as a result of termination work was found to be at least 50 times higher than the estimation made beforehand. We reevaluated doses based on the results of close range measurement from 40 m to 100 m, and based on theoretical reduction by distance. The results were found to match personal doses with a precision between 60-80%. Therefore, work can likely be done safely by taking into account three factors, (1) annual dose limits for workers, (2) dose to workers from sources other than the pertinent work, (3) measurement error, and adopting 10 mSv as a dose guideline for tasks such as dose evaluation.
ray doses taken before the termination work. But the personal dose for workers as a result of termination work was found to be at least 50 times higher than the estimation made beforehand. We reevaluated doses based on the results of close range measurement from 40 m to 100 m, and based on theoretical reduction by distance. The results were found to match personal doses with a precision between 60-80%. Therefore, work can likely be done safely by taking into account three factors, (1) annual dose limits for workers, (2) dose to workers from sources other than the pertinent work, (3) measurement error, and adopting 10 mSv as a dose guideline for tasks such as dose evaluation.