Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Md produced in the
Md produced in the  He +
He +  Es reaction
Es reactionNishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Kean, K. R.*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Chiera, N. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(4), p.044609_1 - 044609_12, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Rapp, L.*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Firestein, K. L.*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Habara, Hideaki*; Mukai, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Kazuo*; Gamaly, E. G.*; Kodama, Ryosuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023101_1 - 023101_18, 2024/04
It is generally known that irradiating a solid surface with a laser pulse of ultra-relativistic intensity generates a plasma on the surface, which in turn creates an ultrahigh pressure inside. In this study, the crystal structure analysis of high-pressure phases generated inside silicon single-crystals irradiated by this laser was performed using the diffraction system at the Stress and Imaging apparatus of BL22XU, which is a JAEA-BL. The results obtained confirm the existence of high-pressure phases that silicon is said to possess: body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal, and tetragonal phases in the interior. We can get the results that the crystal structure of silicon polymorphs of being include body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal-diamond, tetragonal exists. In the future, we will accumulate data and apply them to control the internal structure, strength, and functionality of materials.
Watabe, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yamaya, Taiga*; Kawachi, Naoki*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(2), p.130 - 142, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Environmental Sciences)Previously, we have developed DynamicMC for modelling relative movement of ORNL phantom in a radiation field for MCNP. Using this software, 3-dimensional dose distributions in a phantom irradiated by a certain mono-energetic source can be deduced through its graphical user interface (GUI). In this study, we extended DynamicMC to be used in combination with the PHITS by providing it with a higher flexibility for dynamic movement for a less sophisticated anthropomorphic phantom. We anticipate that the present work and the developed open-source tools will be in the interest of nuclear radiation physics community for research and teaching purposes.
 Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(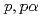 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The cluster structure of the neutron-rich isotope  Be has been probed via the (
Be has been probed via the (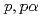 ) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the
pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the  Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Song, K.*; Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Gas entrainment (GE) phenomena caused by a free surface vortex may cause the disturbance in core power of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). For this reason, the entrained gas flow rate by the GE should be evaluated accurately for the practical safety design of SFRs. In this study, for the purpose of examining the applicability of CFD for the accurate evaluation of GE phenomena, a CFD is applied to the simulation of the free surface vortex and accompanied GE phenomena in a cylindrical vessel with a suction pipe, and the CFD results and the experimental data of the GE are compared. As a result, the CFD and experiments show similar two-phase flow pattern inside the suction pipe, and the shape of the gas core at the free surface is also very similar. Therefore, it is confirmed that the CFD can predict the GE phenomena triggered by a free surface vortex properly and accurately within the acceptable error range.
Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.*; Shariful, I. M.*; Eljamal, R.*; Bensaida, K.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tokunaga, Kohei; Eljamal, O.*
Advanced Materials Letters (Internet), 14(2), p.23021721_1 - 23021721_10, 2023/04
Maamoun, I.; Bensaida, K.*; Eljamal, R.*; Falyouna, O.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tosco, T.*; Sugihara, Yuji*; Eljamal, O.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 358, p.119216_1 - 119216_13, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:98.15(Chemistry, Physical)Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, R.*; Bensaida, K.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tosco, T.*; Sugihara, Yuji*; Eljamal, O.*
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3), p.107431_1 - 107431_17, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:93.04(Engineering, Environmental) K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) /MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions
/MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutionsFalyouna, O.*; Bensaida, K.*; Maamoun, I.; Ashik, U. P. M.*; Tahara, Atsushi*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Aoyagi, Noboru; Sugihara, Yuji*; Eljamal, O.*
Journal of Cleaner Production, 342, p.130949_1 - 130949_15, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:98.03(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)Zhao, Y.*; Suzuki, T.*; Iimori, T.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J. R.*; Horio, Masafumi*; Sato, Yusuke*; Fukaya, Yuki; Kanai, T.*; Okazaki, K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115304_1 - 115304_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 O +
O +  Np
NpTanaka, Shoya*; Hirose, Kentaro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Kean, K. R.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Aritomo, Yoshihiro*
Physical Review C, 105(2), p.L021602_1 - L021602_5, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.00(Physics, Nuclear) O+
O+ Np reaction
Np reactionVermeulen, M. J.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Kean, K. R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Tsekhanovich, I.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ishizaki, Shoma*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_11, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear)Yano, Midori; Ito, Takayuki*; Tanaka, Yusuke*; Matsuoka, Daisuke*; Araki, Fumiaki*; Czauderna, T.*; Stephens, K.*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.201 - 208, 2020/10
Visual analysis plays an important role in understanding and evaluating the climate models, their variables, and their outputs because complex processes are required for the tuning of the climate models. Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are effective for 3D visualization and have been recently employed for visual analysis of more various scientific data. However, researchers may have some problematic situations while using VR space depending on user operations and target geometries. Here, we propose an image-based view selection method to solve these situations and understand differences in ocean states between simulations and observations based on shapes of mode water regions. This view selection takes evaluation criteria for shape comparison of mode water regions generated from simulations and observations into account. This paper introduces two example cases applying this view selection and discusses on a degree of shape matching of mode water regions of each case.
Cappia, F.*; Tanaka, Kosuke; Kato, Masato; McClellan, K.*; Harp, J.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 533, p.152076_1 - 152076_14, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Taiki*; Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Boll, R. A.*; Brewer, N. T.*; Van Cleve, S.*; Dean, D. J.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(5), p.052502_1 - 052502_6, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:85.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Kishi, Hirofumi*; Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Asazawa, Koichiro*; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Kato, Takeshi*; Zulevi, B.*; Serov, A.*; Artyushkova, K.*; Atanassov, P.*; Matsumura, Daiju; et al.
Nanomaterials (Internet), 8(12), p.965_1 - 965_13, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.03(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)