Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationAono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2017-025, 32 Pages, 2017/11
We have developed analytical methods for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for
Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Hoken Butsuri, 51(4), p.209 - 217, 2016/12
A large amount of contaminated rubbles were generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS). For safe decommissioning of F1NPS, it is important to evaluate the composition and concentration of radionuclides in the rubbles. In this paper, to characterize the rubbles collected at F1NPS in Unit-1, Unit-2 and Unit-3, radiochemical analysis was operated. As a result of radiochemical analysis,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  Co,
Co,  Cs and
Cs and 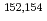 Eu,
Eu,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  H,
H,  C,
C,  Sr and
Sr and  Tc, and
Tc, and  -particle-emitting nuclides
-particle-emitting nuclides 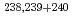 Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm were detected. In contrast,
Cm were detected. In contrast,  Nb and
Nb and  Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that
Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co and
Co and  Sr concentrations depended on
Sr concentrations depended on  Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Seki, Kotaro; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akimoto, Yuji*; Tokunaga, Takahito; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Haraga, Tomoko; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2016-013, 37 Pages, 2016/07
In this study, based on the simple and rapid analytical method established from the wastes from research facilities, we created analytical schemes which is applicable to rubble and plants collected at Fukushima Daiichi, then transported to Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. We examined the applicability, and confirmed quantifiability of radioactivity concentration with high recovery rate without being affected by fission products such as  Sr and
Sr and  Cs.
Cs.
Omori, Hiroyuki; Nebashi, Koji; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-029, 31 Pages, 2015/03
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required for the radioactive waste generated from research facilities in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to dispose of in a near-surface repository. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid waste generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid waste generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In this report, we reported the analytical data determined in fiscal 2014 ( Cs and
Cs and  Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.301 - 307, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:80.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the severe accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant, large amounts of contaminated stagnant water have accumulated in turbine buildings and their surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of the radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. This evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011. The release ratios of tritium, iodine, and cesium were several tens of percent, whereas those of strontium and barium were smaller by one or two orders of magnitude. The release ratios in the Fukushima accident were equivalent to those in the TMI-2 accident.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:94.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nisawa, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Go*; Murakami, Hironori*; Okajima, Yuka*; Yamamoto, Kenichiro*; Semba, Yasunori*; Uesugi, Kentaro*; Tanaka, Yoshihito*; Yamamoto, Masaki*; et al.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(2), p.219 - 225, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:53.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)A Si(111) winged crystal has been designed to minimize anticlastic bending and improve sagittal focusing efficiency. The crystal was thin with wide stiffening wings. The length-to-width ratio of the crystal was optimized by finite element analysis, and the optimal value was larger than the "golden value". The analysis showed that the slope error owing to anticlastic bending is less than the Darwin width. The X-rays were focused two-dimensionally using the crystal and a tangentially bent mirror. The observed profiles of the focal spot agreed well with the results of a ray-tracing calculation in the energy range from 8 to 17.5 keV. X-ray diffraction measurements with a high signal-to-noise ratio using this focusing system were demonstrated for a small protein crystal.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(1), p.13 - 19, 2012/03
After the severe accident in the Fukushima-1 Nuclear Power Plant, large amount of contaminated stagnant water has been produced in turbine buildings and those surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. The present evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011.
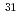 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Deguchi, Shigeki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; Inabe, Naoto*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_4, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:198 Percentile:97.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kizaki, Hiroyuki*; Wada, Shinichi*; Sako, Erika*; Sumii, Ryohei*; Waki, Satoshi*; Isari, Koji*; Sekitani, Tetsuji*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 144-147, p.447 - 451, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.30(Spectroscopy)no abstracts in English
 -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in arabidopsis root
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in arabidopsis rootOno, Yutaka; Oura, Chiharu*; Rahman, A.; Aspuria, E. T.; Hayashi, Kenichiro*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*
Plant Physiology, 133(3), p.1135 - 1147, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:132 Percentile:92.47(Plant Sciences)PCIB ( -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid) is known as a putative antiauxin and is widely used to inhibit auxin action, although the mechanism of PCIB-mediated inhibition of auxin action is not characterized very well at molecular level. In the present work, we showed that PCIB inhibited BA::GUS expression induced by IAA, 2,4-D and NAA. PCIB also inhibited auxin dependent DR5::GUS expression. RNA hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analyses suggested that PCIB reduced auxin-induced accumulation of transcripts of
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid) is known as a putative antiauxin and is widely used to inhibit auxin action, although the mechanism of PCIB-mediated inhibition of auxin action is not characterized very well at molecular level. In the present work, we showed that PCIB inhibited BA::GUS expression induced by IAA, 2,4-D and NAA. PCIB also inhibited auxin dependent DR5::GUS expression. RNA hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analyses suggested that PCIB reduced auxin-induced accumulation of transcripts of 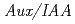 genes. In addition, PCIB relieved the reduction of GUS activity in
genes. In addition, PCIB relieved the reduction of GUS activity in 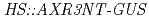 transgenic line in which auxin inhibits GUS activity by promoting degradation of the AXR3NT-GUS fusion protein. Physiological analysis revealed that PCIB inhibited lateral root production, gravitropic response of roots and growth of primary roots. These results suggest that PCIB impairs auxin signaling pathway by regulating Aux/IAA protein stability, and thereby affects the auxin-regulated Arabidopsis root physiology.
transgenic line in which auxin inhibits GUS activity by promoting degradation of the AXR3NT-GUS fusion protein. Physiological analysis revealed that PCIB inhibited lateral root production, gravitropic response of roots and growth of primary roots. These results suggest that PCIB impairs auxin signaling pathway by regulating Aux/IAA protein stability, and thereby affects the auxin-regulated Arabidopsis root physiology.
Wada, Shinichi*; Sumii, Ryohei*; Isari, Koji*; Waki, Satoshi*; Sako, Erika*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekitani, Tetsuji*; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
Surface Science, 528(1-3), p.242 - 248, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:84.35(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Wada, Shinichi*; Sako, Erika*; Sumii, Ryohei*; Waki, Satoshi*; Isari, Koji*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekitani, Tetsuji*; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 199, p.361 - 365, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.22(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
Atomic Collision Research in Japan, (23), p.84 - 85, 1997/00
no abstracts in English

 (C-D) states in NEXAFS spectra of condensed formic acid layers
(C-D) states in NEXAFS spectra of condensed formic acid layersSekiguchi, Hiromi*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
J. Phys., IV, 7, p.499 - 500, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*; Obi, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
J. Phys., IV, 7, p.505 - 506, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Sekiguchi, Hiromi*; Tanaka, Kenichiro*
Surface Science, 390(1-3), p.199 - 203, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.00(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English