Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tian, Q.*; Feng, L.*; Wu, C.*; Wen, J.*; Qiu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Yu, Q.*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 669, p.1006 - 1014, 2024/09
Kato, Tomoaki; Kozai, Naofumi; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kaplan, D. I.*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.580 - 589, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study reports the effect of fulvic acids, which is a natural organic substance generally contained in groundwater, on the oxidation states of radioactive iodine anions (iodide and iodate). Iodide and iodate are contained in the contaminated water of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and supposed to be removed by activated carbon (AC) via adsorption. When fulvic acids does not exist in the experimental system, the adsorption of iodide on AC was less than that of iodate and their oxidation states after the adsorption were not changed. When fulvic acids existed, a fraction of the adsorbed iodate was reduced to iodide. This result indicates that the reduction of the adsorbed iodate progresses during the storage of the spent AC.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Tani, Yukinori*; Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(2), p.1109 - 1114, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)We investigated the sorption of Pu(IV) on biogenic Mn oxide produced by Mn(II)-oxidizing fungus. The sorption of Pu(IV) on biogenic Mn oxide was similar to that of U(VI) and different from that of Th(IV), possibly due to oxidation of Pu(IV) to Pu(VI). When Pu(IV) was sorbed on hyphae only, it was desorbed into the solution phase over time. Pu(IV) could be solubilized by complexation with organic ligands secreted by fungal cells. In particular, Pu(IV) desorption was observed under circumneutral pH conditions.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:96.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Deng, G.*; Ma, T.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Qiu, X.*; Yu, Q.*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 286, p.143 - 158, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.51(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In this study, Ce(III) adsorption on Mn(IV) oxide was investigated in the presence of dextran, one of polysaccharides. As a result, Ce(IV) on Mn(IV) oxide was solubilized by the complexation with dextran.

 on Ni-Zn layered hydroxide salt and its application to removal of ReO
on Ni-Zn layered hydroxide salt and its application to removal of ReO
 as a surrogate of TcO
as a surrogate of TcO

Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kaplan, D. I.*; Grambow, B.
Applied Clay Science, 182, p.105282_1 - 105282_8, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.92(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, Ni-Zn layered hydroxide salt (LHS) was used for adsorption experiments of ReO
 , as a surrogate of TcO
, as a surrogate of TcO
 , in aqueous solutions with various initial Re and sodium salt concentrations. The maximum adsorption amount of Re was estimated at 127.7 mg/g (6.86
, in aqueous solutions with various initial Re and sodium salt concentrations. The maximum adsorption amount of Re was estimated at 127.7 mg/g (6.86  10
10 eq/g) by fitting adsorption isotherm of ReO
eq/g) by fitting adsorption isotherm of ReO
 to Langmuir plot. The adsorption of ReO
to Langmuir plot. The adsorption of ReO
 at neutral pH was a reversible process by anion exchange, and decreased with increasing Cl
at neutral pH was a reversible process by anion exchange, and decreased with increasing Cl , NO
, NO
 and SO
and SO
 in solution. EXAFS analysis indicated that ReO
in solution. EXAFS analysis indicated that ReO
 was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on Ni-Zn LHS. The Ni-Zn LHS is a more robust adsorbent for ReO
was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on Ni-Zn LHS. The Ni-Zn LHS is a more robust adsorbent for ReO
 than the Mg-Al LDH in terms of solution pH and tolerance to competing anions, and may be an effective alternative to the traditional and more limited method of removing aqueous TcO
than the Mg-Al LDH in terms of solution pH and tolerance to competing anions, and may be an effective alternative to the traditional and more limited method of removing aqueous TcO
 by reductive precipitation.
by reductive precipitation.
 , Zn
, Zn +, and Co
+, and Co
Kato, Tomoaki*; Yu, Q.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Saito, Takumi*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Environmental Sciences, 86, p.78 - 86, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.12(Environmental Sciences)This paper investigated the fate of the dissolved permanganate in aqueous solution after contact with bacterial cells and metal accumulation during precipitation of Mn oxides. When Mn(VII) was contacted with bacterial cells, cells were damaged and Mn(VII) was reduced by cells to lower valence and precipitated as Mn oxides (biomass Mn oxides). When Co ions were present, Co was incorporated into Mn oxides as Co
ions were present, Co was incorporated into Mn oxides as Co . These results suggest that Mn(VII) can be used to remove metal ions when introduced to wastewater as disinfectant.
. These results suggest that Mn(VII) can be used to remove metal ions when introduced to wastewater as disinfectant.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Grambow, B.
Journal of Porous Materials, 26(2), p.505 - 511, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.75(Chemistry, Applied)In this study, we utilized X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy to clarify the coordination structure of Re in Mg-Al LDH as a surrogate of Tc. Adsorption experiments of ReO
 on calcined and uncalcined Mg-Al LDHs were conducted in aqueous solutions with different concentrations of NaCl, NaNO
on calcined and uncalcined Mg-Al LDHs were conducted in aqueous solutions with different concentrations of NaCl, NaNO , and Na
, and Na SO
SO . Calcined Mg-Al LDH showed much higher adsorption than uncalcined one. The adsorption of ReO
. Calcined Mg-Al LDH showed much higher adsorption than uncalcined one. The adsorption of ReO
 was reversible, and decreased with increasing concentration of competing anions like Cl
was reversible, and decreased with increasing concentration of competing anions like Cl , NO
, NO
 , or SO
, or SO
 . Analysis of Re L
. Analysis of Re L -edge extended X-ray absorption fine structure indicated that ReO
-edge extended X-ray absorption fine structure indicated that ReO
 was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on Mg-Al LDH. The observed Re adsorption-desorption behavior, which was sensitive to the presence of competing anions, was consistent with the formation of outer sphere-complex.
was adsorbed as an outer-sphere complex on Mg-Al LDH. The observed Re adsorption-desorption behavior, which was sensitive to the presence of competing anions, was consistent with the formation of outer sphere-complex.
Yu, Q.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tani, Yukinori*; Onuki, Toshihiko
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 2(8), p.797 - 810, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:57.45(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Most of Mn oxides are biogenic and known to adsorb cesium (Cs) on the surface. This study investigated structural transformation of biogenic birnessite by accommodating commonly occurring natural heavy metals (Zn, Ni) during the formation of Mn oxides and the influence of those metals on the adsorption behavior of Cs on Mn oxides. It was found that the presence of heavy metals during bio-oxidation of Mn(II), followed by exposure to a low pH aqueous solution, increased the number of available layer vacancies, which consequently increased the adsorption capacity of Cs in the final product birnessite.
Cui, Y.-T.*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Hatanaka, Tatsuya*; Nakamura, Naoki*; Ando, Masaki*; Yoshida, Toshihiko*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju
NanotechJapan Bulletin (Internet), 11(4), 6 Pages, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
 glycoprotein; Microbial transformation of heavy elements in the aquatic environment
glycoprotein; Microbial transformation of heavy elements in the aquatic environmentKozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko; Sato, Takahiro*; Kamiya, Tomihiro*; Grambow, B.
Chemosphere, 196, p.135 - 144, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.18(Environmental Sciences)Transformation of heavy elements by microbes such as bacteria and fungi has been an intense research subject; however, little is known about that of protozoa. This study investigated interaction of a representative protozoa,  , with heavy elements (Eu(III), Pb(II), U(VI)). Non-destructive elemental analysis by micro-PIXE hardly detected those elements on living cells after sorption experiments but clearly detected on the cells that were killed with a fixative beforehand. Chromatographic analysis of aquatic species of those heavy elements after the sorption experiments revealed a fraction of those elements bound to a glycoprotein dissolved from the cell surface of living
, with heavy elements (Eu(III), Pb(II), U(VI)). Non-destructive elemental analysis by micro-PIXE hardly detected those elements on living cells after sorption experiments but clearly detected on the cells that were killed with a fixative beforehand. Chromatographic analysis of aquatic species of those heavy elements after the sorption experiments revealed a fraction of those elements bound to a glycoprotein dissolved from the cell surface of living  cells to form soluble pseudocolloid. These findings suggest that complexation of heavy elements with the dissolved surface glycoprotein reduced the sorption of those heavy elements on living cells.
cells to form soluble pseudocolloid. These findings suggest that complexation of heavy elements with the dissolved surface glycoprotein reduced the sorption of those heavy elements on living cells.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Kaplan, D. I.*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Applied Geochemistry, 85(Part B), p.119 - 120, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.30(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We have prepared a special issue for Applied Geochemistry entitled "Transformation and Fate of Natural and Anthropogenic Radionuclides in the Environments". Here, we present 13 peer-reviewed articles on the general theme of natural and anthropogenic radionuclides in different environments. At the same time, these articles cover various topics of field research on the distribution of radionuclides, as well as laboratory experiments on adsorption and redox chemistry of these. The articles have been written by the attendees of the session at the Goldschmidt 2016 held in Yokohama, Japan, and by other authors who submitted their manuscripts to Applied Geochemistry focusing on the theme of the special issue.
Yu, Q.*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tanaka, Kazuya; Sasaki, Keiko*
Chemical Geology, 470, p.141 - 151, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:54.72(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In this work, the Cs retention onto two types of Mn oxide was investigated. We found that Todorokite has sorption sites with a higher selectivity for Cs than birnessite. When the initial Cs concentration was 10 mol/L for the sorption experiments, approximately 34% of the sorbed Cs was residual in the todorokite after the extraction using 1 M NaCl and NH
mol/L for the sorption experiments, approximately 34% of the sorbed Cs was residual in the todorokite after the extraction using 1 M NaCl and NH Cl; this value was much higher than the results for the Cs-sorbed birnessite. These results strongly suggest that todorokite contributes to the fixation of radioactive Cs in soils.
Cl; this value was much higher than the results for the Cs-sorbed birnessite. These results strongly suggest that todorokite contributes to the fixation of radioactive Cs in soils.
 high energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy
high energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopyCui, Y.-T.*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Hatanaka, Tatsuya*; Nakamura, Naoki*; Ando, Masaki*; Yoshida, Toshihiko*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Oji, Hiroshi*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.1482_1 - 1482_8, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:48.90(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko
Applied Geochemistry, 78, p.279 - 286, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.06(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This study examined the rate constant for the U(VI) reduction process by three flavin analogues, which are redox-active biomolecules secreted from anaerobic bacteria, to elucidate their substituent group effect on the U(VI) reduction rate by electrochemical methods. The formation of the U(IV) was monitored by UV-vis spectrometry in the presence of the flavins. The rate constant for the U(VI) reduction by the flavins was determined. The apparent reduction potential of U(VI) increased about 0.2 V in the presence of the mediators, which strongly suggests that the biological electron mediator makes the U(VI) reduction possible even under more oxidative conditions.
Deguchi, Akira*; Umeki, Hiroyuki*; Ueda, Hiroyoshi*; Miyamoto, Yoichi; Shibata, Masahiro; Naito, Morimasa; Tanaka, Toshihiko*
LBNL-1006984 (Internet), p.12_1 - 12_22, 2016/12
The H12 report demonstrated the feasibility of safe and technically reliable geological disposal in 1999. The Government of Japan re-evaluated the geological disposal program in terms of technical feasibility based on state-of-the-art geosciences and implementation process, because more than 10 years have passed from H12 and the Great Earthquake and nuclear accident have increased public concern regarding nuclear issues and natural hazards to cause accidents at nuclear facilities. Following the re-evaluation, the Government concluded further to promote geological disposal program, and thus the Basic Policy for Final Disposal was revised in 2015 including a new approach to siting process with identification of "Scientifically Preferable Areas". NUMO and relevant research organizations such as JAEA have been carrying out R and D activities to increase technical reliability for geological disposal. NUMO has started to develop a generic safety case.
 and O
and O /H
/H O adsorption revealed by in situ XAFS and hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
O adsorption revealed by in situ XAFS and hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyCui, Y.*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Hatanaka, Tatsuya*; Nakamura, Naoki*; Ando, Masaki*; Yoshida, Toshihiko*; Ikenaga, Eiji*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Li, R.*; et al.
ECS Transactions, 72(8), p.131 - 136, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.47(Electrochemistry)Yu, Q.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tani, Yukinori*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 174, p.1 - 12, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:58.30(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Although microorganisms possess high sorption capability for lanthanides (Lns), their biological response affecting Lns migration is unclear. We investigated the effects of microbial activity on transformation of Lns by contact of Lns with Aeremonium strictum under metabolically active condition with Mn(II). A biomolecule that specifically complex to Ce(IV) was found to be released from the fungal cell, facilitating the desorption of Ce(IV) from Mn oxide. This biomolecule was not associated with any other trivalent Lns or Fe, which differed from those non-nuclide-specific organic substances released from resting cells, as reported previously.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Jiang, M.*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Yu, Q.; Tanaka, Kazuya; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Xia, X.*; Yange, K.*; et al.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 163, p.1 - 13, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:58.56(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The association of Ce(III) with the microbial cell surface and the formation of Ce phosphate nano-particles are responsible for suppressing the oxidation of Ce(III) to Ce(IV) in the mixtures.
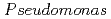 sp. strain NGY-1
sp. strain NGY-1Tanaka, Kazuya*; Yu, Q.; Sasaki, Keiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Geomicrobiology Journal, 30(10), p.874 - 885, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:40.57(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English