Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ono, Masato; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.235 - 242, 2025/05
 Md produced in the
Md produced in the  He +
He +  Es reaction
Es reactionNishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Kean, K. R.*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Chiera, N. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(4), p.044609_1 - 044609_12, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Taguchi, Miki*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Ozawa, Satoru*; Hasegawa, Ryuichi*; Morimitsu, Yuma*; Kawaguchi, Daisuke*; Yamamoto, Satoru*; Tanaka, Keiji*
Polymer Journal, 7 Pages, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Polymer Science)Morishita, Yuki; Sagawa, Naoki; Fujisawa, Makoto; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Sasano, Makoto*; Hayashi, Masateru*; Tanaka, Hiroki*
Radiation Measurements, 181, p.107371_1 - 107371_5, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of different types of radiation on a high-resolution alpha imager developed using an electron multiplying charge-coupled device (EMCCD) camera were investigated. This imager was originally developed to visualize alpha particles from Pu oxide particles at decommissioning sites. Other types of radiation such as beta particles, gamma rays, and neutrons are also present. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of these background radiations on the imager and to develop a method to discriminate between alpha particles and other types of radiation. When measuring gamma rays, and neutrons, the sensor of the EMCCD camera generated high intensity signals due to gamma rays and neutrons. These radiations were identified by image processing. The image values were binarized and the findContours function was applied to count the number of alpha particle spots. The results showed that alpha and gamma (neutron) radiation can be discriminated by using differences in intensity. This method will be useful for visualizing alpha particles at decommissioning sites.
Liu, Y.*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Shundo, Atsuomi*; Kawaguchi, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Keiji*; Aoki, Hiroyuki
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8 Pages, 2025/00
Sato, Yuki; Kakuto, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Takayuki*; Shimano, Hiroyuki*
European Physical Journal; Special Topics, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sugimoto, Chihiro; Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 95, p.98 - 107, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical) -H
-H O system using deep neural network
O system using deep neural networkTanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Myagmarjav, O.; Ono, Masato; Sugimoto, Chihiro
Chemical Engineering Science, 299, p.120479_1 - 120479_11, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Chemical)We developed a deep neural network method to predict the composition of the iodine-sulfur process of thermochemical water-splitting hydrogen production using measurable properties. Unlike conventional titration analysis, this approach allows a quick understanding of fluid composition, providing essential information for controlling operating conditions. This study focused on the HI-I -H
-H O three-component system within the IS process. Using Gibbs phase rule, the DNN model was constructed using online measurable parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and density, as input conditions. The model was trained with experimental data, and the structural parameters were tuned. Composition prediction using actual trend data demonstrated good correlation with titration analysis measurements. Furthermore, the local interpretable model-agnostic explanations method was incorporated to gain insights into the significance of input parameters for compositions from the DNN model, providing valuable information on crucial parameters for effective composition control.
O three-component system within the IS process. Using Gibbs phase rule, the DNN model was constructed using online measurable parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and density, as input conditions. The model was trained with experimental data, and the structural parameters were tuned. Composition prediction using actual trend data demonstrated good correlation with titration analysis measurements. Furthermore, the local interpretable model-agnostic explanations method was incorporated to gain insights into the significance of input parameters for compositions from the DNN model, providing valuable information on crucial parameters for effective composition control.
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 19(11), p.1888 - 1894, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Ishikawa, Akihisa; Tanaka, Hiroki*; Nakamura, Satoshi*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Tanagami, Yuki*; Uritani, Akira*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 65(6), p.765 - 775, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biology)Hayakawa, Satoshi*; Hagiwara, Hiroyuki*; Imamura, Akira*; Onoda, Yuichi; Tanaka, Masaaki; Nakamura, Hironori*
Proceedings of 13th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS13) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/11
In a sodium-cooled fast reactor, a cover gas region filled with argon gas is located above the sodium pool in the main vessel to prevent the hot sodium from contacting the structures. This region involves heat transportation by natural convection of the cover gas, radiation among liquid surface and structures, and sodium phase change between mist and vapor. In this study, the numerical evaluation method has been developed with a commercial CFD code, Fluent, incorporating the sodium mist transport and growth models, and the radiation scattering model. Simulations of a laboratory scale test with a cylindrical cover gas region was carried out for the validation of the method and showed that the temperature distribution and sodium mist concentration in the cover gas region are in good agreements with the test results. A simulation of a pool-type sodium cooled fast reactor has also conducted and the basic aspect of physical phenomena taking place in the cover gas region were evaluated.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Futagami, Satoshi; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ota, Hirokazu*; Ogata, Takanari*; Wozniak, N.*; Shemon, E.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
To enhance the accuracy of the safety evaluations in sodium-cooled fast reactors, it is necessary to develop a method to realistically evaluate the reactivity caused by core deformation. In this regard, Japan and the United States jointly conducted a benchmark analysis of thermal bowing experiments of a single duct of Joyo-type fuel assembly. The aim was to confirm the validity of the core bowing analysis codes. Comparisons of analysis and test results revealed that the core bowing analysis codes used by both countries were able to reasonably predict the axial distribution of horizontal duct displacement of a single duct due to thermal bowing and the contact load on the duct pad.
Wozniak, N.*; Shemon, E.*; Feng, B.*; Ohgama, Kazuya; Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Futagami, Satoshi; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ota, Hirokazu*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
To enhance the accuracy of the safety evaluations in sodium-cooled fast reactors, it is necessary to develop a method to realistically evaluate the reactivity caused by core deformation. In this regard, Japan and the United States jointly conducted a benchmark analysis of thermal bowing experiments using multiple ducts of Joyo-type fuel assembly. The aim was to confirm the validity of the core bowing analysis codes. Comparisons of analysis and test results revealed that the core bowing analysis codes used by both countries were able to reasonably predict the thermal bowing of a row of assemblies.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Arakawa, Masato*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Kida, Takumitsu*; Tokumitsu, Katsuhisa*; Tanaka, Ryo*; et al.
Langmuir, 40(30), p.15758 - 15766, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kawano, Masayuki*; Morimitsu, Yuma*; Liu, Y.*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Kawaguchi, Daisuke*; Yamamoto, Satoru*; Tanaka, Keiji*
Macromolecules, 57(14), p.6625 - 6633, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Polymer Science)Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2776, p.012009_1 - 012009_9, 2024/06
Kimuro, Shingo; Taneichi, Yayoi; Iwata, Hajime; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kitamura, Akira; Tachi, Yukio; Tanaka, Takeru*; Hirano, Kana*; Hieda, Manami*; Miyabe, Shunsuke*; et al.
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 53(6), p.854 - 868, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Sato, Yuki; Kakuto, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Takayuki*; Shimano, Hiroyuki*; Morohashi, Yuko; Hatakeyama, Tomoyoshi*; Nakajima, Junsaku; Ishiyama, Masahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1063, p.169300_1 - 169300_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:86.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10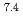 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.