Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maekawa, Akihiro*; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Fan, S.*; Fukuda, Miho*; Nasu, Koki*; Taniguchi, Keisuke*
KEK Proceedings 2024-6, p.7 - 12, 2024/12
no abstracts in English
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:75.48(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
 layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O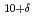 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopyIdeta, Shinichiro*; Johnston, S.*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Mori, Michiyasu; Anzai, Hiroaki*; Ino, Akihiro*; Arita, Masashi*; Namatame, Hirofumi*; Taniguchi, Masaki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.217004_1 - 217004_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:71.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) irradiation
irradiationYukawa, Takuji*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo 2016 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.359 - 362, 2016/05
The immersion tests of pure titanium were carried out in aqueous solution containing carbonate/bicarbonate with 50 mM-chloride ion under gamma irradiation. The effect of pH on general corrosion rate of titanium were studied. The experimental results showed that the concentration of hydrogen preoxide was increased with pH, and the corrosion rate increased with the hydrogen preoxide concentration. The corrosion rate in pH12 and 13 were 5 to10 times larger than those under unirradiated conditions.
Fumon, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Ippei*; Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; Okuda, Shuichi*; Taniguchi, Ryoichi*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-8), p.203 - 206, 2008/12
We developed an apparatus for electron irradiation and in-situ current-voltage (I-V) characteristics measurements for space solar cells. The apparatus was interfaced to an electron linear accelerator at Radiation Research Center of Osaka Prefecture University. By using this apparatus, the electron irradiation with the energies from 6 MeV to 12 MeV can be performed at various temperatures from -196  C to 100
C to 100  C. In-situ I-V characteristic measurements are also possible at the temperature from -196
C. In-situ I-V characteristic measurements are also possible at the temperature from -196  C to 100
C to 100  C. As a first demonstration using this apparatus, we performed two experiments. First, I-V characteristics of a Si solar cell were measured at room temperature and at low temperature. Secondly, the Si solar cell was irradiated with 10 MeV electrons and I-V characteristics were measured at room temperature. The experimental result was compared with those for 1 MeV electron irradiation and 10 MeV proton irradiation.
C. As a first demonstration using this apparatus, we performed two experiments. First, I-V characteristics of a Si solar cell were measured at room temperature and at low temperature. Secondly, the Si solar cell was irradiated with 10 MeV electrons and I-V characteristics were measured at room temperature. The experimental result was compared with those for 1 MeV electron irradiation and 10 MeV proton irradiation.
 N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction as a
N reaction as a  -ray intensity standard up to 11 MeV
-ray intensity standard up to 11 MeVMiyazaki, Itaru*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Takayama, Hirokazu*; Kasaishi, Masafumi*; Tojo, Akinori*; Furuta, Masataka*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Suematsu, Osamu*; Narasaki, Hiromichi*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(6), p.481 - 486, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)The intensities of the prompt  rays from the
rays from the  N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C
N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C D
D N
N ) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of
) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of  -ray energy.
-ray energy.
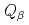 measurements of
measurements of 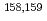 Pm,
Pm, 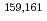 Sm,
Sm, 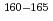 Eu,
Eu, 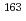 Gd and
Gd and 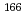 Tb using a total absorption BGO detector
Tb using a total absorption BGO detectorHayashi, Hiroaki*; Akita, Yukinori*; Suematsu, Osamu*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 34(4), p.363 - 370, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.88(Physics, Nuclear)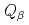 values of
values of 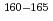 Eu and
Eu and 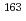 Gd were measured for the first time using a total absorption BGO detector, and the data of
Gd were measured for the first time using a total absorption BGO detector, and the data of 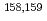 Pm,
Pm, 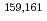 Sm, and
Sm, and 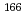 Tb obtained previously were reanalyzed. These nuclei were produced by the proton-induced fission of
Tb obtained previously were reanalyzed. These nuclei were produced by the proton-induced fission of  U at the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility, and separated from the reaction products using an on-line isotope separator. The deduced mass excesses and two-neutron separation energies were compared with those of atomic mass evaluations and theoretical predictions.
U at the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility, and separated from the reaction products using an on-line isotope separator. The deduced mass excesses and two-neutron separation energies were compared with those of atomic mass evaluations and theoretical predictions.
Nakagawa, Sho*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kitagawa, Michiharu*; Oshima, Ryuichiro*; Tobita, Toru; Taniguchi, Ryoichi*; Suzuki, Masahide; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.397 - 401, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:35.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)Supersaturated Fe-1.2wt.%Cu alloys were irradiated with 200-MeV Xe and 200-MeV Au ions at elevated temperatures. To make an irradiated region and an unirradiated region in a specimen, a masking plate was put on the specimen during the irradiation. After the irradiation, the hardness was measured by using a conventional microhardness tester or a nano-indenter. We have found that the hardness only in irradiated region increases by the irradiation. The boundary of irradiated and unirradiated regions can be clearly identified by the difference in hardness. The present result implies that swift heavy ion irradiation can be used for the local modification of hardness in supersaturated alloys.
Miyazaki, Itaru*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Kawade, Kiyoshi*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Harada, Hideo
JNC TY8400 2005-002, 40 Pages, 2005/06
Accurate cross section data for the neutron capture of long-lived fission products (LLFP) are needed for developing a nuclear transmutation technology which reduces radioactive wastes by transmuting nuclides that have half-lives of as long as a few million years to other nuclides that have much shorter half-lives. There are some nuclides, whose cross sections cannot be measured in activation method. Utilization of prompt gamma-rays is expected to solve this problem. The aim of present study was twofold: (i) to measure emission probabilities of the high energy gamma-ray, up to 10MeV, emitted from  N(
N( )
) N reaction, which are usually used as standards, in order to improve their accuracies and (ii) to develop a measurement method for neutron capture cross sections by using prompt gamma-rays. Emission probabilities of principal prompt gamma-rays from
N reaction, which are usually used as standards, in order to improve their accuracies and (ii) to develop a measurement method for neutron capture cross sections by using prompt gamma-rays. Emission probabilities of principal prompt gamma-rays from  N(
N( )
) N reaction were determined with 0.2-0.9% errors. For ten nuclides,
N reaction were determined with 0.2-0.9% errors. For ten nuclides,  Na,
Na,  Al,
Al, 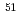 V,
V,  Mn,
Mn,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Cu,
Cu, 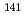 Pr,
Pr,  W, and
W, and  Au capture cross sections were measured by using prompt gamma-rays and gamma-rays following b-decay. By comparing both cross section values, it was found that emission probabilities of prompt gamma-rays reported in the literatures were systematically larger than those inferred from the cross sections that were determined in activation methods. The cross section of a
Au capture cross sections were measured by using prompt gamma-rays and gamma-rays following b-decay. By comparing both cross section values, it was found that emission probabilities of prompt gamma-rays reported in the literatures were systematically larger than those inferred from the cross sections that were determined in activation methods. The cross section of a 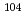 Pd(
Pd( )
)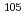 Pd reaction at thermal energy was measured. Considering transmutation of the nuclide, the cross section of
Pd reaction at thermal energy was measured. Considering transmutation of the nuclide, the cross section of 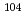 Pd(
Pd( ), which is an isotope of palladium, is also necessary. A lower limit of the cross section was determined with 6% accuracy. Additionally, a method of estimating an upper limit was examined by noting similarity of nuclear structures to the neighboring nuclides. It was estimated that the observed lower limit of emission probabilities correspond to 79% of the cross section.
), which is an isotope of palladium, is also necessary. A lower limit of the cross section was determined with 6% accuracy. Additionally, a method of estimating an upper limit was examined by noting similarity of nuclear structures to the neighboring nuclides. It was estimated that the observed lower limit of emission probabilities correspond to 79% of the cross section.
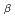 determination of neutron-rich isotope
determination of neutron-rich isotope  La with a total absorption detector
La with a total absorption detectorShibata, Michihiro*; Shindo, Terumasa*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Kojima, Yasuaki*; Kawade, Kiyoshi*; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Kawase, Yoichi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 71(5), p.1401 - 1402, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.49(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
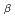 determination without the knowledge of the decay scheme
determination without the knowledge of the decay schemeShibata, Michihiro*; Kojima, Yasuaki*; Uno, H.*; Kawade, Kiyoshi*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Kawase, Yoichi*; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 459(3), p.581 - 585, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:86.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Kitamura, Akihiro; Machida, Masahiko; Suzuki, Masahiro; Omori, Takazumi; Taniguchi, Tatsuro; Ide, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Sato, Akira*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Mori, Yoshiharu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sonoda, Shinya*; Takada, Atsushi*; Tanimori, Toru*; Tsuda, Masaya*; Tahara, Keisuke*; Kobayashi, Koichiro*; Tanigaki, Minoru*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Nakayama, Hiromasa; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed an Electron Tracking Compton Camera (ETCC), which provides a well-defined Point Spread Function (PSF) by reconstructing a direction of each gamma as a point and realizes simultaneous measurement of brightness and spectrum of MeV gamma-rays. Here, we present the results of the gamma-imaging-spectroscopy with ETCC tested at the research reactor at the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University.
Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Kitamura, Akihiro; Omori, Takazumi; Taniguchi, Tatsuro; Ide, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
In this report, we present the validation results of the radiation source inverse estimation computation method and the effectiveness evaluation method of the "estimation system of radiation sources and dose rates" developed by JAEA. As for the validation test, the JMTR was used as the evaluation site, and the results of radiation source inverse estimation computations were compared with measured data. As a result, it was confirmed that the hot spot could be estimated approximately well. As for the effectiveness evaluation, the test field to be established at the NARREC and at the JMTR were used as the evaluation sites, and the effectiveness evaluation items such as the functions of each tool and the process of the system were summarized.