Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya*; Kushida, Noriyuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Kim, G.; Takemiya, Hiroshi
High Performance Computing on Vector Systems 2011, p.107 - 117, 2012/01
no abstracts in English
Kim, G.; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya*; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.634 - 638, 2011/10
We developed grid-enabled application of full-scale 3D vibration simulator for an entire nuclear power plant on simple orchestration application framework (SOAF). The simulator is an analysis system to study seismic response of a whole digitalized nuclear power plant. In the simulator, components of a power plant are treated in hierarchical manner so that large components are grouped at primary level and small components such as pipes at secondary level. Boundary condition data are transferred from the primary level to the secondary level. SOAF provides functionality to enable users to simply define the data transfer in pipelined scenario which is technically difficult to realize using the existing grid technology. In this paper, we discuss technical issues of the realization of pipelined scenario on grid and demonstrate effectiveness of SOAF by analysis of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor of JAEA using grid-enabled application implementing SOAF.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya*; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.591 - 597, 2011/10
By integrating simulation codes which simulate physical process or part of nuclear energy facility, large-scale and detailed simulation can be carried out. Such integrated simulations require several weeks or months of CPU times. Avoiding unscheduled outage of computers or network, we have developed fault-tolerant mechanism for cooperative execution of the codes. The mechanism covers abnormal end of jobs on supercomputers and error of file transfers. When the computer causes unexpected outage, the mechanism tries to submit job of simulation to alternative computer. Furthermore, by comparison the size of the files between before and after transfer, the mechanism detects error of the transfer. In the fault-tolerant mechanism, because the relations between the jobs and the file transfers are connected, we can decide an execution order of the codes by the definition of file flow. Therefore we can operate integrated simulations in which the codes are executed sequentially or concurrently.
Tashiro, Toru*; Tatekawa, Takayuki
Numerical Simulations of Physical and Engineering Processes, p.301 - 318, 2011/09
The behavior of a self-gravitating system (SGS) is described using the equilibrium statistical mechanics. Although the behavior of the system is analytically solved for the spherically symmetric system, it is known that mass density in the central region and/or total mass of the system sometimes diverges. King model which is derived by modification of the statistical mechanics can explain the distribution without these difficulties. We construct a theory which can explain the dynamics toward the special steady state described by the King model. SGSs require quite long time for relaxation. Furthermore, we must compute interaction of all particle pairs. By these reasons, we require huge computation power for numerical simulation of the evolution of SGS. So we have applied special-purpose processor for computation of the interaction. From the numerical simulations of SGS, we have confirmed that our theory is appropriate for description of realistic density distribution.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Mizuno, Shuntaro*
Dark Energy; Theories, Developments, and Implications, p.241 - 294, 2010/10
Suzuki, Yoshio; Kushida, Noriyuki; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya; Caniou, Y.*; Guivarch, R.*; Dayde, M.*; Ramet, P.*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2010/10
The "Research and Development of International Matrix-Solver Prediction System (REDIMPS)" project, which is founded by the Strategic Japanese-French Cooperative Program on "Information and Communications Technology including Computer Science" with CNRS and JST, aims at improving the "Test for Large System of Equations (TLSE)" sparse linear algebra expert system by establishing an international grid computing environment between Japan and France. Here, we have established the interoperable environment between French and Japanese grid middleware (DIET and AEGIS), and have confirmed that TLSE can rely on this French and Japanese interoperable environment for researchers to select a matrix-solver suitable to their each application program. By this study, we proposed to the French and Japanese researchers the environment in which they can obtain useful information for the improvement of their application program.
Kim, G.; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2010/10
Full-Scale 3D vibration simulator for an entire nuclear power plant is a seismic response analysis system for a whole digitalized nuclear power plant. In the system, boundary data from large components are used as input data of small components. To make a whole simulation efficient, we introduced pipeline method in which the data were transferred each time step running all components simulations in parallel. In the realization of the method on grid, since there were no existing grid technologies to sufficiently support the method for a long time, we developed simple orchestration application framework (SOAF) and using the SOAF, we performed seismic response analysis of a test reactor of JAEA and succeeded simulation for a week.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2010/10
In the nuclear field, various large-scale integrated simulations which cannot be executed with single job have been developed to reveal physical and engineering phenomena. Such integrated simulations are accomplished by coupling several simulation codes, each of which is charge of each physical process or each engineering part of whole system. Fault-tolerant (FT) mechanism is very important to run such simulations on the error-prone environment such as Grid. We developed functions of error detection, job re-submission, and file re-transfer and integrated them as a FT mechanism. Our test run of integrated nuclear energy application showed that the FT mechanism sustained the long run of the application by recovering the job failure automatically.
Kino, Chiaki; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya; Kim, G.; Suzuki, Yoshio; Araya, Fumimasa; Nishida, Akemi; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2010/10
In the present study, we have developed a new control system for application integration with the fault-tolerant API (FT-API). The system treats an application as a task which consists of one job and multiple file transfer. Firstly, each task designates a computer to submit a job using a scheduler associated to the job. Secondly, all files which are necessary to execute the job are gathered in the computer using FT-API for file transfer. Finally, the job is submitted using FT-API for job execution. If the computer is outage, the task designates a new computer, gathers necessary files and submits a new job. Each scheduler, file transfer and job condition can be flexibly defined in XML. This time, we applied the system to fluid-structure interaction analysis simulation. The result indicates that the system enables a user to easily execute multi-scale and multi-physics simulation using application integration.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Kim, G.; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
High Performance Computing on Vector Systems 2010, p.107 - 120, 2010/09
In the atomic field, by integrating various simulation codes which were installed on distributed computers, large-scale and detailed simulations which aim explication of complicated phenomena. However integration of each simulation codes and cooperative operation of the integrated codes make heavy burden for researchers. We have developed the Simple Orchestration Application Framework (SOAF) to cooperatively control simulation codes on remote computers from a client PC. SOAF enables researchers to cooperatively execute various codes on grid infrastructure by only describing a configuration file including the information of execution codes and file flows among them. SOAF does not need substantial modification of the simulation codes. By using SOAF, we successfully execute four plasma simulation codes included in the "Burning Plasma Integrated Code" according to the scenario described in the configuration file.
Tashiro, Toru*; Tatekawa, Takayuki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 79(6), p.063001_1 - 063001_4, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We derive the non-Maxwellian distribution of self-gravitating  -body systems around the core by a model based on the random process with the additive and the multiplicative noise. The number density can be obtained through the steady state solution of the Fokker-Planck equation corresponding to the random process. We exhibit that the number density becomes equal to that of the King model around the core by adjusting the friction coefficient and the intensity of the multiplicative noise. We also show that our model can be applied in the system which has a heavier particle. Moreover, we confirm the validity of our model by comparing with our numerical simulation.
-body systems around the core by a model based on the random process with the additive and the multiplicative noise. The number density can be obtained through the steady state solution of the Fokker-Planck equation corresponding to the random process. We exhibit that the number density becomes equal to that of the King model around the core by adjusting the friction coefficient and the intensity of the multiplicative noise. We also show that our model can be applied in the system which has a heavier particle. Moreover, we confirm the validity of our model by comparing with our numerical simulation.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Kim, G.; Kino, Chiaki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Teshima, Naoya; Hayashi, Sachiko*; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Nakajima, Norihiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu, 15(2), p.1051 - 1054, 2010/05
We have developed the Atomic Energy Grid InfraStructure (AEGIS) for establishing computational infrastructure for nuclear field. In this R&D we have inherited the knowledge and skills in ITBL Infrastructure developed in the national project ITBL (Information Technology Based Laboratory), which aims at establishment of virtual research environment where supercomputers and data bases are connected by network. Here we have focused on two issues: improvements of safety and usability. For the safety, we have made the authentication mechanism double with both the personal certification and the machine certification. For the usability, we have developed the grid-enabled client API to use grid functions on a user terminal. By those R&Ds, we have successfully contributed to various nuclear researches, such as "full scale 3D vibration simulator for an entire nuclear power plant", "simulation for predicting quake-proof capability of nuclear power plants", and so on.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya; Kim, G.; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Iba, Katsuyuki*
Proceedings of 3rd International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization (CSO 2010), p.322 - 326, 2010/05
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Kim, G.; Kino, Chiaki; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
FUJITSU Fuamirikai Rombunshu (Internet), 19 Pages, 2010/03
We have introduced about the framework to make the integration of large and complicated simulation such as a proof strength simulation of nuclear power plants and a control simulation of nuclear fusion plasma which codes are installed to distributed computers. We able to carry out detailed simulations by integrating various simulation methods with development of simulation technique. However it becomes a burden to control the integration of each simulation code for researchers. We have noticed that the execution scenarios of each code in cooperated simulation are roughly categorized to workflow type, pipeline type, and conditional branch type. Then we have developed the framework in which just write those patterns in a configuration file and achieve the cooperative execution of element codes without substantial modification of simulation codes.
Kim, G.; Nakajima, Kohei*; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Kim, G.; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Kushida, Noriyuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Teshima, Naoya*; Fujibayashi, Kenichi*; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kim, G.; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya*; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
So far, we have developed Full-scale 3D vibration simulator for an Entire Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) which is simulation platform to analyze seismic response of a whole NPP. In this work, we introduced pipelined data-transfer scenario in which boundary condition data between NPP components are transferred each time step from large components to small ones and developed grid-enabled application to perform this simulation using various HPC resources. In doing so, we confronted two problems; first, how to realize the scenario on grid and second, to automate simulation restarting. As solution of these problems, we used Simple Orchestration Application Framework (SOAF) which enabled the introduced scenario to be realized in easy and simple way for a long-time. Using the SOAF, we developed grid-enable application and succeeded seismic analysis simulation of a test reactor in the scenario for about a week. In this symposium, the details of all of this work will be presented.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Sakagami, Masaaki*; Taruya, Atsushi*; Okamura, Takashi*; Ruffo, S.*
no journal, ,
We will discuss relaxation processes toward thermal equilibrium in the long-range interacting system by N-body simulations. In the early stage of its evolution, the system visits quasi-equilibrium state where the value of physical quantities such as mean kinetic energy are different from equilibrium ones. Then it gradually evolves toward thermal equilibrium. We find that this transient states can be described by the polytrope which is given by the one-particle distribution of the energy  ,
, 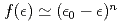 , only when the system has the negative specific heat. The relaxation processes are characterized by increase of index n to infinity which corresponds the Boltzmann distribution. For dynamical evolution, we are trying to accelerate N-body simulations with General-Purpose computation on Graphics Processing Units (GPGPU). GPGPU can accelerate the computation of 2-body interactions.
, only when the system has the negative specific heat. The relaxation processes are characterized by increase of index n to infinity which corresponds the Boltzmann distribution. For dynamical evolution, we are trying to accelerate N-body simulations with General-Purpose computation on Graphics Processing Units (GPGPU). GPGPU can accelerate the computation of 2-body interactions.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Teshima, Naoya*; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English