Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Eguchi, Yuta; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/07
In order to investigate the basic neutronics characteristics of the accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS), JAEA has a plan to construct a new critical assembly in the J-PARC project, Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). This study aims to evaluate the natural cooling characteristics of TEF-P core which has large decay heat by minor actinide (MA) fuel, and to achieve a design that does not damage the core and the fuels during the failure of the core cooling system. In the evaluation of the TEF-P core temperature, empty rectangular lattice tube outer of the core has a significant effect on the heat transfer characteristics. The experiments by using the mockup device were performed to validate the heat transfer coefficient and experimental results were obtained. By using the obtained experimental results, the three-dimensional heat transfer analysis of TEF-P core were performed, and the maximum core temperature was obtained, 294 C. This result shows TEF-P core temperature would be less than 327
C. This result shows TEF-P core temperature would be less than 327 C that the design criterion of temperature.
C that the design criterion of temperature.
Tazawa, Yujiro; Nishihara, Kenji; Sugawara, Takanori; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Eguchi, Yuta; Kikuchi, Masashi*; Inoue, Akira*
JAEA-Technology 2016-029, 52 Pages, 2016/12
Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) planned in the J-PARC project uses minor actinide (MA) fuels in the experiments. These MA fuels are highly-radioactive, so the fuel handling equipment in TEF-P is necessary to be designed as remote-handling system. This report summarizes fabrication and test results of the testing equipment for fuel loading that is one of components of the testing equipment for remote-handling of MA fuels. The testing equipment which had a remote-handling system for fuel loading was fabricated. And the test in combination with the mock-up core was performed. Through the test, it was confirmed to load/take the dummy fuel pin to/from the mock-up core without failure. It was shown that the concept design of the fuel loading equipment of TEF-P was reasonable.
Eguchi, Yuta; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inoue, Akira; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
JAEA-Technology 2015-052, 34 Pages, 2016/03
Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) planned in the J-PARC project uses minor actinide (MA) fuel which has large decay heat. So it is necessary to consider the increase of the core temperature when the core cooling system is stopped. This change of the core temperature was evaluated by thermal conduction analysis. It was found that the impact of thermal insulation in the empty rectangular lattice matrix area was large. So it is necessary to verify reliability and accuracy of heat transfer effect used in this area. Testing equipment was fabricated to verify the accuracy of calculation model for the empty lattice matrix which was the free convection model of sealed fluid. By using this equipment, thermal distribution and one dimensional heat flow through the lattice were measured. It was observed that the actual equivalent thermal conductivity in the lattice was larger than the free convection model. It was also confirmed that the insertion of the aluminum block into the empty lattice could achieve the higher equivalent thermal conductivity. These results could be the useful data for the thermal conduction analysis.
Nishihara, Kenji; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inoue, Akira; Sugawara, Takanori; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Obayashi, Hironari; Yamaguchi, Kazushi; Kikuchi, Masashi*
JAEA-Technology 2015-051, 47 Pages, 2016/03
This report summarizes fabrication and test results of a testing equipment for fuel cooling that is a component of the testing equipment for remote-handling of highly-radioactive MA fuels in the transmutation physics experimental facility (TEF-P) planned in the J-PARC. Evaluation formula of pressure drop and temperature increase used in the design of TEF-P was validated by the test, and, feasibility of cooling concept was confirmed.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Tazawa, Yujiro*; Tachibana, Yukio; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
FAPIG, (190), p.20 - 24, 2015/07
In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat in HTGRs must be removed by radiation, thermal conduction and natural convection. Passive heat removal performance is of primary concern for enhancing inherent safety features of HTGRs. Therefore, the thermal hydraulic analyses for normal operation and a loss of forced cooling accident are conducted by using thermal hydraulic CFD code. And further, a multi-hole type fuel block of MHTGR is also modeled and the flow and heat transfer characteristics are compared with a pin-in-block type fuel block.
Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Tazawa, Yujiro; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2014-044, 59 Pages, 2015/03
Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) planned in the J-PARC is a critical assembly with low thermal output and it will treat large amount of highly-radioactive minor actinide (MA) fuels in the experiments. Handling of the MA fuels in each stage of storage, transport and loading/unloading to the core was conceptually investigated, then, criticality, dose and cooling performance were assessed. For the criticality, it was shown that the effective multiplication factors in each step, storage, transport and loading, were sufficiently lower than 1.0. For the dose, the dose for workers will be reduced by installing remote handling devices to treat the MA fuels. For the cooling performance, it was found that the temperature of the core would be kept low in the normal operation. On the other hand, in the case which the air conditioning or the blower for the core stopped for long period, it was shown that there would be a possibility of the MA fuel failure.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tazawa, Yujiro; Aihara, Jun; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Goto, Minoru; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2013-017, 71 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has started a conceptual design of a 50 MWt small-sized high temperature gas cooled reactor (HTGR) for steam supply and electricity generation (HTR50S). Though the safety design of HTR50S was determined based on that of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) for the early deployment of HTR50S, the shutdown cooling system, which is the forced cooling heat removal system, was categorized as non-safety class to optimize the protection to provide the highest level of safety that can reasonably be achieved, and the vessel cooling system, which is categorized as the safety class system, was designed as a passive safety features. The preliminary safety analysis of HTR50S for the rupture of co-axial hot gas duct in primary cooling system and the tube rupture of steam generator was conducted to confirm the adequacy of the safety design. It was confirmed that the analysis results satisfied the acceptance criteria.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Yan, X.; Sumita, Junya; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Tazawa, Yujiro; Noguchi, Hiroki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Technology 2013-016, 176 Pages, 2013/09
JAEA has started a conceptual design of a 50MWt small-sized high temperature gas cooled reactor for steam supply and electricity generation (HTR50S), which is a first-of-kind of the commercial plant or a demonstration plant of a small-sized HTGR system for steam supply to the industries and district heating and electricity generation by a steam turbine. The plant design of HTR50S for the steam supply and electricity generation was performed based on the plant specification and the requirements for each system taking into account for the increase of the reactor outlet coolant temperature from 750 C to 900
C to 900 C and the installation of IHX. The technical feasibility of HTR50S was confirmed because the designed systems satisfies the design requirements. The conceptual plant layout was also determined. This paper provides the summary of the plan design and technical feasibility of HTR50S.
C and the installation of IHX. The technical feasibility of HTR50S was confirmed because the designed systems satisfies the design requirements. The conceptual plant layout was also determined. This paper provides the summary of the plan design and technical feasibility of HTR50S.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tazawa, Yujiro; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2013-015, 68 Pages, 2013/06
In present study, requirements in order to design, construct and operate hydrogen production plants coupled to HTGRs under conventional chemical plant standards are identified. In addition, design considerations for safety design of nuclear facility are suggested. Furthermore, feasibility of proposed safety design and design considerations are clarified.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Goto, Minoru; Yan, X.; Sumita, Junya; Tazawa, Yujiro*; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Aihara, Jun; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Fukaya, Yuji; et al.
International Journal of Nuclear Energy, 2013, p.918567_1 - 918567_18, 2013/00
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted a conceptual design of a 50 MWt small-sized high temperature gas cooled reactor (HTGR) for multiple heat applications, named HTR50S, with the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 750  C and 900
C and 900  C. It is first-of-a-kind of the commercial plant or a demonstration plant of a small-sized HTGR system to deploy it in developing countries in the 2020s. The design concept of HTR50S is to satisfy the user requirements for multipurpose heat application, to upgrade its performance compared to that of HTTR without significant R&D utilizing the knowledge obtained by the HTTR design and operation, and to fulfill the high level of safety by utilizing the inherent features of HTGR and a passive decay heat removal system.
C. It is first-of-a-kind of the commercial plant or a demonstration plant of a small-sized HTGR system to deploy it in developing countries in the 2020s. The design concept of HTR50S is to satisfy the user requirements for multipurpose heat application, to upgrade its performance compared to that of HTTR without significant R&D utilizing the knowledge obtained by the HTTR design and operation, and to fulfill the high level of safety by utilizing the inherent features of HTGR and a passive decay heat removal system.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Nakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/10
Passive heat removal performance of the reactor vessel cavity cooling system (RCCS) is of primary concern for enhanced inherent safety of HTGR. In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat must be removed by radiation and natural convection of RCCS. Thus thermal hydraulic analysis of reactor internals and RCCS is powerful means for evaluation of the heat removal performance of RCCS. The thermal hydraulic analyses using CFD computation tools are conducted for normal operation of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and are compared to the temperature distribution of measured data. The calculated temperatures on outer faces of the permanent side reflector (PSR) blocks are in fair agreement with measured data. The transient analysis for decay heat removal mode in HTTR is also conducted.
 C high temperature gas-cooled reactor
C high temperature gas-cooled reactorNakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The conceptual core design study of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is performed. The major specifications are 600 MW thermal output, 950 C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release,
C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release, 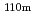 Ag and
Ag and  Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tazawa, Yujiro; Yan, X.; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of ASME 2011 Small Modular Reactors Symposium (SMR 2011) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/09
JAEA has started a conceptual design of a small-sized HTGR for steam supply and power generation (HTR50S), of which reactor power is 50 MWt and the reactor outlet temperature is 750 C, to deploy the HTGR in developing countries at an early date (i.e., in the 2030s). The major specifications of the HTR50S were determined based on its design philosophy, which is to upgrade its performance and to reduce the cost by utilizing the knowledge obtained by the HTTR operation and the GTHTR300 design. The system design of HTR50s was performed to offer the capability of electricity generation, cogeneration of electricity and steam for a district heating and industries. The market potential for the small-sized HTGR in the developing countries was evaluated for the application of the electricity, process heat, district heating and pure water production. It was confirmed that there is enough market potential for the small-sized HTGR in the developing countries.
C, to deploy the HTGR in developing countries at an early date (i.e., in the 2030s). The major specifications of the HTR50S were determined based on its design philosophy, which is to upgrade its performance and to reduce the cost by utilizing the knowledge obtained by the HTTR operation and the GTHTR300 design. The system design of HTR50s was performed to offer the capability of electricity generation, cogeneration of electricity and steam for a district heating and industries. The market potential for the small-sized HTGR in the developing countries was evaluated for the application of the electricity, process heat, district heating and pure water production. It was confirmed that there is enough market potential for the small-sized HTGR in the developing countries.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tazawa, Yujiro; Yan, X.; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Technology 2011-013, 67 Pages, 2011/06
In the present study, major specifications of a small-sized HTGR system (HTR50S) aiming to deploy in developing countries in 2030s are investigated. In addition, technology to be demonstrated (e.g. increasing power density, reduction of the number of uranium enrichment in the fuel, increasing the burn up, side-by-side arrangement between the reactor pressure vessel and the steam generator) are identified. Also, a system design of HTR50S which offers the capability of electricity generation, cogeneration of electricity and steam for a district heating and industries, is performed. Furthermore, a market size for small-sized HTGR systems are estimated.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tazawa, Yujiro; Sakaba, Nariaki; Tachibana, Yukio
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 133(2), p.022902_1 - 022902_8, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.95(Engineering, Mechanical)A practical safety evaluation method, which enables to design, construct and operate hydrogen production plants under conventional chemical plant standards, is proposed. An event identification for the HTTR-IS nuclear hydrogen production system is conducted in order to select abnormal events which would change the scenario and quantitative results of the evaluation items from the existing HTTR safety evaluation. In addition, a safety analysis is performed for the identified events. The results of safety analysis for the identified five Anticipated Operational Occurrences and three Accidents show that evaluation items do not exceed the acceptance criteria during the scenario. In addition, the increase of peak fuel temperature is small in the most severe case, and therefore the reactor core was not damaged and cooled sufficiently.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tazawa, Yujiro; Sakaba, Nariaki; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Technology 2010-012, 65 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is planning to demonstrate hydrogen production by thermochemical water-splitting IS process utilizing heat from the high-temperature gas-cooled reactor HTTR (HTTR-IS system). The previous study identified that the HTTR modification due to the coupling of hydrogen production plant requires an additional safety review since the scenario and quantitative values of the evaluation items would be altered from the original HTTR safety review. Hence, preliminary safety analyses are conducted by using the system analysis code. Calculation results showed that evaluation items such as a coolant pressure, temperatures of heat transfer tubes at the pressure boundary, etc., did not exceed allowable value. Also, the peak fuel temperature also did not exceed allowable value and therefore the reactor core was not damaged and cooled sufficiently.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tazawa, Yujiro; Sakaba, Nariaki; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/05
In the present study, a practical safety evaluation method, which enables to design, construct and operate hydrogen production plants under conventional chemical plant standards, is proposed. An event identification for the HTTR-IS nuclear hydrogen production system is conducted in order to select abnormal events which would change the scenario and quantitative results of the evaluation items from the existing HTTR safety evaluation. In addition, a safety analysis is performed for the identified events. The results of safety analysis for the indentified five AOOs and three ACDs show that evaluation items such as a primary cooling system pressure, temperatures of heat transfer tubes at pressure boundary, etc., do not exceed the acceptance criteria during the scenario. In addition, the increase of peak fuel temperature is small in the most severe case, and therefore the reactor core was not damaged and cooled sufficiently.
Takei, Hayanori; Ouchi, Nobuo; Sasa, Toshinobu; Hamaguchi, Dai; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Kurata, Yuji; Nishihara, Kenji; Obayashi, Hironari; Saito, Shigeru; Sugawara, Takanori; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Research Applications and Utilization of Accelerators (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/05
JAEA has been promoting the research and development (R&D) on accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS) as a dedicated system for the transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides. The ADS proposed by JAEA is a lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) cooled, tank-type subcritical reactor with a thermal power of 800 MW driven by a superconducting linac. The R&D activities can be divided into two categories: one is the design study and technical development for a future large-scale ADS, and the other is the experimental programme at the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) under the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) project. As for the design study of the future ADS, the reliability of the accelerator is being investigated based on the data analysis of existing linac facilities. As for the technical development of the superconducting linac, fabrication and tests of prototype cryomodule were carried out, and its good performance was demonstrated. As for the TEF development, design study including experimental device to handle minor actinide fuels is being conducted.
Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2008-093, 56 Pages, 2009/03
As HTGR hydrogen production systems, such as HTTR-IS system or GTHTR300C currently being developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency, consists of nuclear reactor and chemical plant, which are without a precedent in the world, safety design philosophy and regulatory framework should be newly developed. In this report, phenomena to be considered and events to be postulated in the safety evaluation of the HTGR hydrogen production systems were investigated and basic principles to establish acceptance criteria for the explosion and toxic gas release accidents were provided. Especially for the explosion accident, quantitative criteria to the reactor building are proposed with relating sample calculation results. It is necessary to treat abnormal events occurred in the hydrogen production system as external events to the nuclear plant in order to classify the hydrogen production system as no-nuclear facility and basic policy to meet such requirement was also provided.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Kenji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sugawara, Takanori; Iwanaga, Kohei; Kikuchi, Kenji; Kurata, Yuji; Takei, Hayanori; Saito, Shigeru; et al.
Proceedings of 5th International Workshop on the Utilisation and Reliability of High Power Proton Accelerators (HPPA-5), p.387 - 399, 2008/04
JAEA has been promoting the research and development on accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS) as a dedicated system for the transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides. The ADS proposed by JAEA is a lead-bismuth eutectic cooled, tank-type subcritical reactor with the thermal power of 800 MWth driven by a 30 MW superconducting linac. As for the design study of the future ADS, reduction of the maximum temperature of fuel claddings and verification of the feasibility of the beam window are under way. As for the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) of the J-PARC project, design study including experimental device to deal with minor actinide fuels is being conducted. To facilitate the research and development on ADS, a common road map is necessary to be shared by international communities. The TEF program can play an important role in such an international context as an experimental platform to conduct basic and flexible experiments.