Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and
and 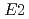 cross sections of the
cross sections of the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction at
O reaction at 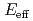
 1.2 MeV using pulsed
1.2 MeV using pulsed  beams
beamsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Fujimoto, Shinya*; Segawa, Mariko; Mishima, Kenji*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Igashira, Masayuki*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1269, p.283 - 288, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of
O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of 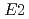 cross section to
cross section to  one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed
one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed  beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the
beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the  -ray from the
-ray from the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction with high statistics. We determined the
O reaction with high statistics. We determined the  and
and 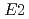 cross section down to
cross section down to 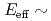 1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
 Os,
Os,  Os, and
Os, and 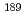 Os and the Re-Os chronology
Os and the Re-Os chronologySegawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Goriely, S.*; Koning, A.*; Hilaire, S.*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1016, p.448 - 450, 2008/05
 Re-
Re- Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of
Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of  Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,
Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,  Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of
Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of  Os. Secondly,
Os. Secondly,  Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of
Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of  Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for
Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and 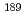 Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for
Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for  Os off the ground state of
Os off the ground state of  Os to its 9.75 keV first excited state in the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV.
Os to its 9.75 keV first excited state in the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV.
 Os,
Os,  Os, and
Os, and 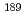 Os for the Re-Os chronology
Os for the Re-Os chronologySegawa, Mariko; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Goriely, S.*; Koning, A.*; Hilaire, S.*
Physical Review C, 76(2), p.022802_1 - 022802_5, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.66(Physics, Nuclear)Discrete as well as continuum  -ray energy spectra from the neutron capture by
-ray energy spectra from the neutron capture by  Os,
Os,  Os, and
Os, and 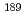 Os have been taken for the first time at 5
Os have been taken for the first time at 5  En
En  90 keV by an anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The detection of a weak discrete
90 keV by an anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The detection of a weak discrete  -ray, about 0.5% of total
-ray, about 0.5% of total  -ray strength, demonstrates the high sensitivity of the present measurement. The energy spectra enabled us to accurately determine the reaction cross sections with a small systematic uncertainty. Based on the new cross sections, we re-estimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F
-ray strength, demonstrates the high sensitivity of the present measurement. The energy spectra enabled us to accurately determine the reaction cross sections with a small systematic uncertainty. Based on the new cross sections, we re-estimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F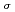 for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in
for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in  Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the Galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the Galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Goriely, S.*; Koning, A.*; Hilaire, S.*
no journal, ,
The  Re nucleus is known to be a good chronometer to derive the stellar duration of the r-process nuceosyntheis and deduce the age of universe. However, there are several problems inherent to this chronometer. In order to solve these problems, one must know both the production and depletion rates (via the excited state as well as the ground state) of
Re nucleus is known to be a good chronometer to derive the stellar duration of the r-process nuceosyntheis and deduce the age of universe. However, there are several problems inherent to this chronometer. In order to solve these problems, one must know both the production and depletion rates (via the excited state as well as the ground state) of  Os and inelastic scattering cross section off the ground state (J
Os and inelastic scattering cross section off the ground state (J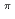 = 1/2
= 1/2 ) of
) of  Os to its excited 10 keV state (J
Os to its excited 10 keV state (J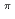 = 3/2
= 3/2 ) are needed. Hence, in the present study we aimed to accurately measure the neutron capture cross sections of
) are needed. Hence, in the present study we aimed to accurately measure the neutron capture cross sections of  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and 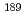 Os, and the inelastic scattering cross section for
Os, and the inelastic scattering cross section for  Os for neutrons between 10 and 90 keV by developing a new experimental method.
Os for neutrons between 10 and 90 keV by developing a new experimental method.
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Makii, Hiroyuki*; Mishima, Kenji*; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Nakayoshi, Akira*; Ota, Takeshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Re-
Re- Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of
Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of  Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,
Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,  Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of
Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of  Os. Secondly,
Os. Secondly,  Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of
Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of  Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for
Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and 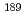 Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for
Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for  Os off the ground state of
Os off the ground state of  Os to its 9.75-keV first excited statein the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV. The measurements of the neutron capture reactions have been carried out by detecting a prompt
Os to its 9.75-keV first excited statein the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV. The measurements of the neutron capture reactions have been carried out by detecting a prompt  -ray by means fan anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The (n, n') reaction cross section for
-ray by means fan anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The (n, n') reaction cross section for  Os has been measured with use of four
Os has been measured with use of four  Li-glass scintillation detectors. Based on these new capture cross sections, we reestimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in
Li-glass scintillation detectors. Based on these new capture cross sections, we reestimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in  Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
 C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction at E
O reaction at E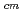 = 1.2 and 1.5 MeV using pulsed
= 1.2 and 1.5 MeV using pulsed  beam
beamMakii, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Segawa, Mariko; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*
no journal, ,
The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of He-burning. However the cross section at the stellar temperature still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the cross section ratio,
O reaction plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of He-burning. However the cross section at the stellar temperature still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the cross section ratio, 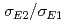 . In order to make a precise measurement of the
. In order to make a precise measurement of the 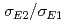 , we have installed a new measurement system of the
, we have installed a new measurement system of the  -ray angular distributions of the
-ray angular distributions of the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction. In this experiment, we used high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers to detect
O reaction. In this experiment, we used high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers to detect  -rays from the reaction with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed
-rays from the reaction with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed  beams, and the monitoring system of the target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutrons and could clearly detect the
beams, and the monitoring system of the target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutrons and could clearly detect the  -ray from the reaction with high statistics. We determined the E1 and E2 cross section down to E
-ray from the reaction with high statistics. We determined the E1 and E2 cross section down to E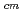 = 1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
= 1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.