Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Chiu, I.-H. ; Terada, Kentaro*; Osawa, Takahito; Park, C.*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*
Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 58(9), p.1333 - 1344, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:93.95(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Chiu, I.-H. ; Terada, Kentaro*; Osawa, Takahito; Park, C.*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012004_1 - 012004_6, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.2(Physics, Applied)In the last decade, non-destructive elemental analysis using negative muon beams advanced significantly. This method can be used to determine the elemental composition of bulk materials without causing damage. In this study, we performed a negative muon irradiation experiment for a Northwest Africa 482 lunar meteorite (NWA482), which was installed in a stainless steel analysis chamber. The analysis chamber was filled with helium gas to suppress the background signals caused by air-scattering muons. The muonic X-rays from Al, Fe, Ca, Mg, Si, and O in the samples were detected using six high-purity germanium semiconductor detectors arranged around the analysis chamber. To correct the X-ray self-absorption effect of the samples, a Monte-Carlo simulation using Geant4 toolkit was used. Based on the quantitative analysis for muonic X-ray measurement with the correction application from the simulation, we successfully investigated the analytical sensitivity of each element in meteorites based on the NWA482 data.
Terada, Kentaro*; Sato, Akira*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kawashima, Yoshitaka*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yoshida, Go*; Kawai, Yosuke*; Osawa, Takahito; Tachibana, Shogo*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.15478_1 - 15478_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:68.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Electron- or X-ray-induced characteristic X-ray analysis has been widely used to determine chemical compositions of materials in vast research fields. In recent years, analysis of characteristic X-rays from muonic atoms, in which a muon is captured, has attracted attention because both a muon beam and a muon-induced characteristic X-ray have high transmission abilities. Here we report the first non-destructive elemental analysis of a carbonaceous chondrite using one of the world-leading intense direct current muon beam source (MuSIC; MUon Science Innovative Channel). We successfully detected characteristic muonic X-rays of Mg, Si, Fe, O, S and C from Jbilet Winselwan CM chondrite, of which carbon content is about 2 wt percent, and the obtained elemental abundance pattern was consistent with that of CM chondrites.
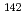 Nd and stellar neutron capture cross sections
Nd and stellar neutron capture cross sectionsKatabuchi, Tatsuya*; Matsuhashi, Taihei*; Terada, Kazushi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Hirose, Kentaro; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Hara, Kaoru*; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(3), p.037603_1 - 037603_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.7(Physics, Nuclear)Terada, Kentaro*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Osawa, Takahito; Tachibana, Shogo*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kubo, Kenya*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsuchiyama, Akira*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 4, p.5072_1 - 5072_6, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:82.6(Multidisciplinary Sciences)After the discovery of X-ray by Rontgen, mankind got a new eye to see through things. This fluoroscopy, so-called X-ray radiography that gives the density distribution of the inside of an object, has been applied to the vast research field such as natural/material/medical sciences, industry and technology. The recent development on the intense pulsed muon source at J-PARC MUSE (rate of 106 cps for 60 MeV/c) enabled us to pioneer a new frontier of analytical sciences. Here we report on a non-destructive elemental analysis by using muon capture. Controlling muon's momentum from 32.5 to 57.5 MeV/c. we successfully demonstrated a depth-profile analysis of light elements from several mm-thick layered materials, and non-destructive bulk analyses of meteorites containing organics. Now it is a beginning to utilize a new eye, muon radiography.
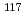 Sn
Sn using ANNRI-NaI(Tl) spectrometer at J-PARC
using ANNRI-NaI(Tl) spectrometer at J-PARCHirose, Kentaro; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; Oshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-002, p.173 - 178, 2013/10
Yamasaki, Satoshi*; Terada, Toru*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Shimizu, Kentaro*; Sarai, Akinori*
Nucleic Acids Research, 40(17), p.e129_1 - e129_7, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:44.94(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Yamasaki, Satoshi*; Terada, Toru*; Shimizu, Kentaro*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Sarai, Akinori*
Nucleic Acids Research, 37(20), p.e135_1 - e135_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:15.1(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Terada, Kentaro*; Ito, Katsunori*; Hidaka, Hiroshi*; Yoshida, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Aoki, Wako*; Williams, I. S.*
New Astronomy Reviews, 50(7-8), p.582 - 586, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Europium isotopic composition could be a good probe to investigate the neutron capture process in Asymptotic Giant Branch stars (AGB stars) and/or supernovae, because the  Sm and
Sm and 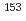 Sm branchings are sensitive to the neutron densities and temperature. Here, we report Eu isotopic analyses of single SiC grains from primitive meteorites using the sensitive high resolution ion microprobe. The results are compared with Eu isotopic ratios predicted from the s-process model of AGB stars. The observed Eu isotopic composition of SiC grains place constraints on s-process conditions such as the temperature and neutron densities in AGB stars.
Sm branchings are sensitive to the neutron densities and temperature. Here, we report Eu isotopic analyses of single SiC grains from primitive meteorites using the sensitive high resolution ion microprobe. The results are compared with Eu isotopic ratios predicted from the s-process model of AGB stars. The observed Eu isotopic composition of SiC grains place constraints on s-process conditions such as the temperature and neutron densities in AGB stars.
Sato, Satoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Hori, Junichi; Verzilov, Y. M.; Klix, A.; Wada, Masayuki*; Terada, Yasuaki*; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Morimoto, Yuichi*; Nishitani, Takeo
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.527 - 530, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.16(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hori, Junichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Wada, Masayuki*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Morimoto, Yuichi*; Terada, Yasuaki; Klix, A.; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 63-64, p.271 - 276, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to the waste management method and the safety design of future D-T fusion reactor, it is important to consider the radioactivity productions via not only primary neutron reactions but also sequential charged particle reactions (SCPR). Especially, on the surface of a coolant channel many recoiled protons are generated by the neutron irradiation with coolant water, so it is apprehensive that the undesirable radioactive nuclide production yields via SCPR are enhanced. In this work, the laminated sample pieces of fusion material foils (V, Fe, W, Ti, Pb, Cu) were made and attached on a polyethylene board to simulate water flowing inside a coolant channel. They were irradiated with D-T neutrons. The effective radioactivity cross section and the depth distribution of the radioactivity production yields due to SCPR were obtained for each material. On the other hand, the estimated values were compared with the experimental ones.
Terada, Yasuaki*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Sato, Satoshi; Wada, Masayuki*; Klix, A.; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Hori, Junichi; Nishitani, Takeo
JAERI-Research 2002-019, 70 Pages, 2002/10
D-T neutron irradiation experiments have been carried out with a F82H-containing breeding blanket mock-up of a fusion in order to investigate the activation characteristics of F82H low activation stainless steel. We have measured reaction rates producing 54Mn, 56Mn, 51Cr and 187W in foils of F82H, chromium and tungsten. MCNP calculations were done with evaluated nuclear data from the JENDL-3.2 and the FENDL/E-2.0 files and the results were compared with the measured values. The comparison shows that by using the current data files the reaction rates obtained from the calculations will be overestimated by up to 10-20% for 54Mn, 56Mn and 51Cr, up to 30-40% for 187W, respectively. The calculated values for tungsten are different with the evaluated nuclear data library, which shows that the neutron capture cross sections of tungsten have discrepancy in the resonance region for each nuclear data libraries.
 Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO breeding blanket experiments with D-T neutrons
breeding blanket experiments with D-T neutronsKlix, A.; Ochiai, Kentaro; Terada, Yasuaki; Morimoto, Yuichi*; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Hori, Junichi; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Science and Technology, 41(3, Part2), p.1040 - 1043, 2002/05
 Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO is one of the candidate materials for the breeding blanket of the fusion DEMO reactor. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the tritium production performance and estimate the accuracy of the measurement method. The JAERI Fusion Neutronics Source (FNS) group has carried out experiments with breeding blanket mock-ups composed of layers of beryllium, ferritic steel F82H and enriched Li
is one of the candidate materials for the breeding blanket of the fusion DEMO reactor. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the tritium production performance and estimate the accuracy of the measurement method. The JAERI Fusion Neutronics Source (FNS) group has carried out experiments with breeding blanket mock-ups composed of layers of beryllium, ferritic steel F82H and enriched Li TiO
TiO . Pellets of enriched Li
. Pellets of enriched Li TiO
TiO with a diameter of 12mm and a thickness of 2mm were used as detectors inside the tritium breeding layer. After irradiation, the pellets were dissolved and the tritium activity in the sample solution was measured by liquid scintillation counting. The experimentally obtained tritium production profile in the lithium titanate layer agreed well with MCNP calculations within the estimated error of the measured values (10%). The calculation-experiment ratio was close to one for all samples. Tritium loss from the pellet during storage time (a few days) was experimentally found to be negligible.
with a diameter of 12mm and a thickness of 2mm were used as detectors inside the tritium breeding layer. After irradiation, the pellets were dissolved and the tritium activity in the sample solution was measured by liquid scintillation counting. The experimentally obtained tritium production profile in the lithium titanate layer agreed well with MCNP calculations within the estimated error of the measured values (10%). The calculation-experiment ratio was close to one for all samples. Tritium loss from the pellet during storage time (a few days) was experimentally found to be negligible.
Yamasaki, Satoshi*; Fukui, Kazuhiko*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Shimizu, Kentaro*; Sarai, Akinori*; Terada, Toru*
no journal, ,
Yamasaki, Satoshi*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Shimizu, Kentaro*; Sarai, Akinori*; Terada, Toru*
no journal, ,
Yamasaki, Satoshi*; Terada, Toru*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Shimizu, Kentaro*; Sarai, Akinori*
no journal, ,
 using ANNRI-NaI(Tl) detector at J-PARC
using ANNRI-NaI(Tl) detector at J-PARCHirose, Kentaro; Oshima, Masumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Toh, Yosuke; Nakamura, Shoji; Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishimura, Akihiko; Ito, Fuyumi; Terada, Takaya; Tomiyoshi, Kentaro; Oka, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English