Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (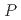
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 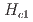 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 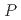 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Oba, Yojiro; Terada, Noriki*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Okubo, Tadakatsu*; Shinohara, Takenao
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.9184_1 - 9184_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.21(Multidisciplinary Sciences) studied by polarized and unpolarized neutron diffraction
studied by polarized and unpolarized neutron diffractionTerada, Noriki*; Qureshi, N.*; Stunault, A.*; Enderle, M.*; Ouladdiaf, B.*; Colin, C. V.*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Orlandi, F.*; Miyahara, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(8), p.085131_1 - 085131_7, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Terada, Noriki*; Qureshi, N.*; Chapon, L. C.*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Nature Communications (Internet), 9, p.4368_1 - 4368_9, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.54(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Oba, Yojiro; Terada, Noriki*; Watanabe, Norimichi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.15516_1 - 15516_8, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.01(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English

Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Kikkawa, Akiko*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*
Physical Review B, 93(8), p.081104_1 - 081104_5, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed neutron diffraction experiments under high pressures and high magnetic fields using a single crystal of the multiferroic compound TbMnO in order to clarify the mechanism associated with pressure/magnetic-field-induced giant ferroelectric polarization. We found that the E-type ordering of Mn spins induces giant ferroelectric polarization over all the parameter regions investigated, through an exchange striction mechanism. Furthermore, we propose that the polarization is reduced by polar ordering of the Tb moments in a zero magnetic field and is enhanced via the field-induced transition from polar to nonpolar Tb orderings at 2T.
in order to clarify the mechanism associated with pressure/magnetic-field-induced giant ferroelectric polarization. We found that the E-type ordering of Mn spins induces giant ferroelectric polarization over all the parameter regions investigated, through an exchange striction mechanism. Furthermore, we propose that the polarization is reduced by polar ordering of the Tb moments in a zero magnetic field and is enhanced via the field-induced transition from polar to nonpolar Tb orderings at 2T.

Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Radaelli, P. G.*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*
Physical Review B, 89(22), p.220403_1 - 220403_6, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:73.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the pressure effect on the magnetic orderings in the strongly frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO , by using neutron diffraction experiments under hydrostatic pressure. The main result is elucidation of the pressure-temperature magnetic phase diagram, consisting of the fourmagnetic phases including two polar ones. In particular, in the 3 GPa
, by using neutron diffraction experiments under hydrostatic pressure. The main result is elucidation of the pressure-temperature magnetic phase diagram, consisting of the fourmagnetic phases including two polar ones. In particular, in the 3 GPa  P
P  4 GPa pressure range, the ICM2 phase with the proper screw magnetic ordering stabilized. This polar phase is almost identical to the ferroelectric incommensurate (FEIC) phase induced by either a magnetic field or chemical doping. Furthermore, above 4 GPa, a new low-symmetry phase ICM3 is realized. This is unique for the family of delafossite multiferroics and implies an admixture of both cycloidal and proper screw spin configurations. The sequence of the observed magnetic phases with changing pressure might be attributed to pressure suppression of the monoclinic lattice distortions responsible for releasing the spin frustration in the system.
4 GPa pressure range, the ICM2 phase with the proper screw magnetic ordering stabilized. This polar phase is almost identical to the ferroelectric incommensurate (FEIC) phase induced by either a magnetic field or chemical doping. Furthermore, above 4 GPa, a new low-symmetry phase ICM3 is realized. This is unique for the family of delafossite multiferroics and implies an admixture of both cycloidal and proper screw spin configurations. The sequence of the observed magnetic phases with changing pressure might be attributed to pressure suppression of the monoclinic lattice distortions responsible for releasing the spin frustration in the system.

Terada, Noriki*; Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Metoki, Naoto
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1905 - 1909, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated magnetic and nonmagnetic impurity substitution effects on magnetic ordering of a frustrated isosceles triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuMnO by means of the magnetic neutron diffraction measurements on Cu(Mn
by means of the magnetic neutron diffraction measurements on Cu(Mn Ga
Ga )O
)O . While the magnetic wave vector of the magnetic ground state of "magnetically" substituted Cu(Mn
. While the magnetic wave vector of the magnetic ground state of "magnetically" substituted Cu(Mn Cu
Cu )O
)O with x = 0:04 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 0), that in the "nonmagnetically" substituted Cu(Mn
with x = 0:04 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 0), that in the "nonmagnetically" substituted Cu(Mn Ga
Ga )O
)O with y =0.05, 0.15 and 0.20 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 1/2) that is identical to that of pure CuMnO
with y =0.05, 0.15 and 0.20 is Q = (-1/2 1/2 1/2) that is identical to that of pure CuMnO . We discuss an influence of magnetic or nonmagnetic impurity substitution on the magnetic ordering of CuMnO
. We discuss an influence of magnetic or nonmagnetic impurity substitution on the magnetic ordering of CuMnO , by comparing the results of Cu(Mn
, by comparing the results of Cu(Mn Ga
Ga )O
)O with Cu(Mn
with Cu(Mn Cux)O
Cux)O .
.
 Ga
Ga O
O (
( = 0, 0.018)
= 0, 0.018)Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Takahashi, Keiichiro*; Yoshitomi, Keisuke*; Masuda, Kazuya*; Kaneko, Chikafumi*; Homma, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kosaka, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094710_1 - 094710_8, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:64.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Ga
Ga O
O (x =0, 0.018)
(x =0, 0.018)Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Takahashi, Keiichiro*; Yoshitomi, Keisuke*; Masuda, Kazuya*; Kaneko, Chikafumi*; Homma, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kosaka, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094710_1 - 094710_8, 2012/09
 as seen via inelastic neutron scattering
as seen via inelastic neutron scatteringNakajima, Taro*; Suno, Azusa*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Terada, Noriki*; Kimura, Shojiro*; Kaneko, Koji; Yamauchi, Hiroki
Physical Review B, 84(18), p.184401_1 - 184401_7, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:76.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Terada, Noriki*; Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Metoki, Naoto; Igawa, Naoki; Oyama, Kenji*
Physical Review B, 84(6), p.064432_1 - 064432_8, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:56.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the magnetic correlations of the isosceles triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuMnO . Above
. Above 
 , the magnetic correlations are characterized by a two-dimensional (2D) short-range correlation. Below
, the magnetic correlations are characterized by a two-dimensional (2D) short-range correlation. Below 
 , the magnetic structures have been identified to be collinear with the magnetic moments almost parallel to the
, the magnetic structures have been identified to be collinear with the magnetic moments almost parallel to the 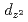 orbitals. The stacking sequence along the
orbitals. The stacking sequence along the  direction is changed from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic by atomic disorder. We find that the second-nearest-neighbor interlayer interaction plays an important role for the magnetic stacking along the
direction is changed from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic by atomic disorder. We find that the second-nearest-neighbor interlayer interaction plays an important role for the magnetic stacking along the  axis. The magnetic excitation below
axis. The magnetic excitation below 
 is characterized by collective spin-wave excitation with an energy gap of 6 meV from the three-dimensional long-range magnetic order and by spin-liquid-like 2D excitation, indicated by specific heat.
is characterized by collective spin-wave excitation with an energy gap of 6 meV from the three-dimensional long-range magnetic order and by spin-liquid-like 2D excitation, indicated by specific heat.

Terada, Noriki*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Kitazawa, Hideaki*
Physical Review B, 83(2), p.020403_1 - 020403_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in observing pressure-suppressed magnetic long-range ordering (LRO) in the triangular-lattice antiferromagnet CuFeO , using neutron-diffraction experiments under an isotropic pressure. The magnetic LRO of the four-sublattice ground state under ambient pressure in CuFeO
, using neutron-diffraction experiments under an isotropic pressure. The magnetic LRO of the four-sublattice ground state under ambient pressure in CuFeO almost disappears at the high pressure of 7.9 GPa, and is replaced by an incommensurate order with temperature-independent wave number of (0.192 0.192 1.5). The incommensurate wave number observed at 7.9 GPa corresponds to that observed just above the temperature at which lattice distortion and magnetic LRO simultaneously occur under ambient pressure. Therefore, the long-range magnetic ordering disappears because the high pressure suppressed the lattice distortion that otherwise relieves spin frustration and leads the spin system to LRO.
almost disappears at the high pressure of 7.9 GPa, and is replaced by an incommensurate order with temperature-independent wave number of (0.192 0.192 1.5). The incommensurate wave number observed at 7.9 GPa corresponds to that observed just above the temperature at which lattice distortion and magnetic LRO simultaneously occur under ambient pressure. Therefore, the long-range magnetic ordering disappears because the high pressure suppressed the lattice distortion that otherwise relieves spin frustration and leads the spin system to LRO.
 Al
Al
Inami, Toshiya; Terada, Noriki*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Sakai, Osamu*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 200, p.032022_1 - 032022_4, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ga
Ga O
O
Terada, Noriki*; Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Matsuda, Masaaki; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Tanaka, Yoshihito*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 211(1), p.012005_1 - 012005_6, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.67(Physics, Applied) Al
Al
Inami, Toshiya; Terada, Noriki*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Sakai, Osamu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(8), p.084713_1 - 084713_5, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:61.72(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Inami, Toshiya; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Terada, Noriki*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 150, p.042069_1 - 042069_4, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:60.48(Thermodynamics) Al
Al O
O
Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Inami, Toshiya; Terada, Noriki*; Osumi, Hiroyuki*; Prokes, K.*; Podlesnyak, A.*
Physical Review B, 78(2), p.024106_1 - 024106_10, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:77.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ga
Ga O
O by means of CRYOPAD and RXS
by means of CRYOPAD and RXSKaneko, Chikafumi*; Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Terada, Noriki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Tanaka, Yoshikazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Inami, Toshiya; Terada, Noriki*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English