Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Takuro*; Fukuoka, Masafumi*; Toda, Kanako*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Niwano, Yuma*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Kobayashi, Natsuko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; et al.
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 4(8), p.3579 - 3586, 2024/08
Nozaki, Mikito*; Terashima, Daiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(SM), p.SMMA07_1 - SMMA07_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.83(Physics, Applied)AlGaN/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures were fabricated by low-power inductively coupled plasma reactive ion etching and chemical vapor deposition of SiO dielectrics on the etched surfaces, and they were systematically investigated by physical and electrical characterizations in an effort to develop a low-damage recessed gate process. The comprehensive research demonstrates the significant advantages of the proposed low-damage recessed gate process for fabricating next-generation AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFET devices.
dielectrics on the etched surfaces, and they were systematically investigated by physical and electrical characterizations in an effort to develop a low-damage recessed gate process. The comprehensive research demonstrates the significant advantages of the proposed low-damage recessed gate process for fabricating next-generation AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFET devices.
 /AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistors
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistorsWatanabe, Kenta*; Terashima, Daiki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA03_1 - 06KA03_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:46.31(Physics, Applied)The advantage of SiO /AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO , AlON and Al
, AlON and Al O
O single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
Saito, Takumi*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Terashima, Motoki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(4), p.444 - 451, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Humic substances (HSs) are ubiquitous in various environments including deep underground and play an important role in the speciation and mobility of radionuclides. The binding of Eu , a chemical homologue of trivalent actinide ions, to HSs isolated from sedimentary groundwater at -250 m below the surface was studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy combined with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) as a function of pH and salt concentration. PARAFAC modeling reveals the presence of multiple factors that corresponds to different Eu
, a chemical homologue of trivalent actinide ions, to HSs isolated from sedimentary groundwater at -250 m below the surface was studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy combined with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) as a function of pH and salt concentration. PARAFAC modeling reveals the presence of multiple factors that corresponds to different Eu species. These factors resemble those observed for Eu
species. These factors resemble those observed for Eu binding to HSs from surface environments; however, detailed comparison shows that there are some particularities in Eu
binding to HSs from surface environments; however, detailed comparison shows that there are some particularities in Eu binding to the deep groundwater HSs. The distribution coefficients (
binding to the deep groundwater HSs. The distribution coefficients ( ) of Eu
) of Eu binding to the HSs calculated from the PARAFAC modeling exhibits a rather strong salt effect. At 0.01 M NaClO
binding to the HSs calculated from the PARAFAC modeling exhibits a rather strong salt effect. At 0.01 M NaClO the
the  values are relatively large and comparable to those to the surface HSs; they are decreaed at 0.1 M NaClO
values are relatively large and comparable to those to the surface HSs; they are decreaed at 0.1 M NaClO by more than an order of the magnitude. The
by more than an order of the magnitude. The  values are larger for humic acid fraction of the deep underground HSs than fulvic acid over the entire range of pH and salt concentration investigated in this study.
values are larger for humic acid fraction of the deep underground HSs than fulvic acid over the entire range of pH and salt concentration investigated in this study.
 -YbAlB
-YbAlB at high magnetic fields
at high magnetic fieldsTerashima, Taku*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Shintaro*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(11), p.114715_1 - 114715_4, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Saito, Takumi; Terashima, Motoki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nagao, Seiya*; Fujitake, Nobuhide*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Environmental Science; Processes & Impacts, 17(8), p.1386 - 1395, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:29.79(Chemistry, Analytical)The deep groundwater HSs were different from surface HSs, having high aliphaticities, sulfur contents, and small molecular sizes. The amounts of their acidic functional groups were comparable to or slightly larger than those of surface HSs; however, the magnitude of Cu binding to the deep groundwater HSs was smaller. The NICA-Donnan model attributed this to the binding of Cu
binding to the deep groundwater HSs was smaller. The NICA-Donnan model attributed this to the binding of Cu to chemically homogeneous carboxylic-type sites via mono-dentate coordination at relatively low pH. The binding mode tended to shift to multi-dentate coordination with carboxylic-type and probably more heterogeneous alcoholic hydroxide-type groups at higher pH. This study shows the particularity of the deep groundwater HSs in terms of their physicochemical and ion-binding properties, compared with surface HSs.
to chemically homogeneous carboxylic-type sites via mono-dentate coordination at relatively low pH. The binding mode tended to shift to multi-dentate coordination with carboxylic-type and probably more heterogeneous alcoholic hydroxide-type groups at higher pH. This study shows the particularity of the deep groundwater HSs in terms of their physicochemical and ion-binding properties, compared with surface HSs.
 -YbAl
-YbAl Fe
Fe B
B (
(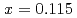 ) at low temperatures and high magnetic fields
) at low temperatures and high magnetic fieldsTerashima, Taku*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Shintaro*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 592(1), p.012020_1 - 012020_6, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.62(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Valence fluctuation phenomena in rare-earth intermetallic compounds have attracted attention because the quantum criticality of the valence transition has been proposed theoretically. Recently, it was found that  -YbAlB
-YbAlB shows quantum criticality without tuning and has a strong mixed-valence state. In this study, we measured the magnetization curve and X-ray magnetoabsorption in
shows quantum criticality without tuning and has a strong mixed-valence state. In this study, we measured the magnetization curve and X-ray magnetoabsorption in  -YbAl
-YbAl Fe
Fe B
B (
(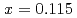 ), which is a locally isostructural polymorph of
), which is a locally isostructural polymorph of  -YbAlB
-YbAlB . The magnetization and X-ray experiments were performed in fields up to 55 and 40 T, respectively. A small increase in the Yb valence was observed at fields where the magnetization curve exhibited a change in slope.
. The magnetization and X-ray experiments were performed in fields up to 55 and 40 T, respectively. A small increase in the Yb valence was observed at fields where the magnetization curve exhibited a change in slope.
Saito, Takumi; Terashima, Motoki; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
Redox properties of humic substances extracted from deep sedimentary groundwater was investigated by cyclic voltammetry and bulk electrolysis with a mediator organic molecule. Reversible current-potential curves were observed with the mediator, although electrode reaction of humic substances are slow in general. The redox capacities of various humic substances exhibited positive correlation with their aromaticity; those of deep groundwater humic substances were appreciably smaller than those of surface humic substances.
Terashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi; Ishii, Tomoko*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /AlGaN interface property deposited by PECVD
/AlGaN interface property deposited by PECVDTerashima, Daiki*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Shih, H.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
Impact of input power and substrate temperature of SiO deposition by plasma-enhanced CVD on SiO
deposition by plasma-enhanced CVD on SiO /AlGaN interface was investigated by means of electrical characterization of MOS capacitors. Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy revealed that Ga oxide component on AlGaN surface increases with increasing input power of PECVD. MOS capacitors with SiO
/AlGaN interface was investigated by means of electrical characterization of MOS capacitors. Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy revealed that Ga oxide component on AlGaN surface increases with increasing input power of PECVD. MOS capacitors with SiO gate insulator deposited at low input power shows relatively better SiO
gate insulator deposited at low input power shows relatively better SiO /AlGaN interface quality, despite degraded interface quality for the sample with SiO
/AlGaN interface quality, despite degraded interface quality for the sample with SiO deposited at high input power. These results suggest that AlGaN surface oxidation during oxide deposition should be controlled to obtain good interface property.
deposited at high input power. These results suggest that AlGaN surface oxidation during oxide deposition should be controlled to obtain good interface property.
 /AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFET
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETWatanabe, Kenta*; Terashima, Daiki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
The advantage of SiO /AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO , AlON and Al
, AlON and Al O
O single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
Saito, Takumi*; Terashima, Motoki
no journal, ,
Humic substances (HSs) are ubiquitous in various environments and play an important role for the fate of pollutants. Deep underground environment is not an exception, although physicochemical and ion-binding properties of HSs there are largely unknown due to difficulties of their extraction. Based on limited studies on deep underground HSs, it has been recognized that they are distinctive from their counterparts in surface or shallow sub-surface environments. Thus, we have been studying humic and fulvic acids extracted from sedimentary groundwater at -250 m below ground surface at the Horonobe underground research laboratory, JAEA, including their chemical compositions, size distributions, spectroscopic properties, and ion bindings. The aim of this talk is to demonstrate similarities and differences between the Horonobe HSs and surface HSs.
Terashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi*; Ishii, Tomoko*; Ito, Miki*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kimuro, Shingo*; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Nagao, Seiya*; Saito, Takumi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Terashima, Motoki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi*; Ito, Miki*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 binding by dissolved organic matters in groundwater
binding by dissolved organic matters in groundwaterTerashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Endo, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Takuro*; Saito, Takumi*; Toda, Kanako*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Terashima, Motoki; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Kobayashi, Natsuko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*
no journal, ,
Cs-137 dispersed by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident deposited in Fukushima area, that are not decontaminated in mountainous areas, may migrate through river water to animals and plants. Most of Cs-137 in river are fixed in clay minerals, but there are some Cs that can be easily desorbed, named as labile components. It has been suggested that labile components affect the bioavailability of Cs-137. In this study, the labile Cs-137 was sampled in situ from upstream to downstream in several rivers of Fukushima using a passive sampler called diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). Sampling was conducted at a different season in addition to the previous studies.
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Terashima, Motoki; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; et al.
no journal, ,
We demonstrated a method of  Sr measurement in small pieces of hard tissues with radioactivity measurement or ICP-MS measurement. Interference elements of the measurements were removed by chemical separation. We could determine
Sr measurement in small pieces of hard tissues with radioactivity measurement or ICP-MS measurement. Interference elements of the measurements were removed by chemical separation. We could determine  Sr in 0.1 g of hard tissues by radioactivity measurement method and ICP-MS method. Limit of detection of the ICP-MS method was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. The ICP-MS method is adequate method for distribution analysis of
Sr in 0.1 g of hard tissues by radioactivity measurement method and ICP-MS method. Limit of detection of the ICP-MS method was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. The ICP-MS method is adequate method for distribution analysis of  Sr in the hard tissues.
Sr in the hard tissues.
Nakagawa, Taichi; Suzuki, Reika*; Matsueda, Makoto; Terashima, Motoki; Horita, Takuma; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi*; Iijima, Kazuki; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,