Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Katsutoshi*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Shimokawa, Takashi*; Imai, Takashi*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Kando, Masaki
Journal of Radiation Research, 56(4), p.633 - 638, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.21(Biology)While X-ray laser is expected to be widely applied to biomedical studies, this has not been achieved to date and its biological effects such as DNA damage have not been evaluated. As a first step for its biological application, we developed a culture cell irradiation system using laser-plasma soft X-ray laser and investigated whether the soft X-ray laser is able to induce the DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) in living cells or not. The human adenocarcimona cell line A549 was irradiated with the soft X-ray laser at a photon energy of 89 eV and then the repair focus formation of the DSBs was assessed by immunofluorescence staining with anti-phosphorylated DNA-PKcs antibody. As a result, the phosphorylated DNA-PKcs foci were clearly identified even with just a single shot of the soft X-ray laser. In this study, we successfully demonstrated for the first time that soft X-ray laser at 89 eV induced the DNA double strand breaks in living cells.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.301 - 306, 2011/12
Temporal sequences of physical and physicochemical stage of actions in biological systems irradiated with energetic radiation take place with in the order of picoseconds. The short duration of laser produced plasma source could be used as a new source in contrast to conventional X-ray sources in investigating the mechanism of the affect of radiation on biological cells. We have started to develop a focused X-ray beam irradiation system for use in studying radiobiological effects on cells, and demonstrated a preliminary study of radiation effect on culture cells irradiated with laser produced plasma Ka X-rays and the X-ray laser.
Yogo, Akifumi; Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Maeda, Takuya*; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko*; Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(10), p.106401_1 - 106401_7, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.43(Physics, Applied)Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, C, 130(10), p.1800 - 1805, 2010/10
no abstracts in English
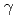 -H2AX and phosphorylated ATM focus formation in cancer cells after laser plasma X irradiation
-H2AX and phosphorylated ATM focus formation in cancer cells after laser plasma X irradiationSato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Okano, Yasuaki*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
Radiation Research, 174(4), p.436 - 445, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:47.49(Biology)Usefulness of laser-plasma X-ray pulse for medical and radiation biological studies was investigated and compared with that of conventional sources such as those obtained from a linear accelerator. A cell irradiation system was developed which uses Copper-K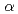 (8 keV) lines from an ultra-short high intensity laser to produce plasma. The absorbed dose of the 8 keV laser-plasma X-ray pulse was accurately estimated with Gafchromic EBT film. When the cells were irradiated with approximately 2 Gy of laser plasma X-ray, the circular regions on
(8 keV) lines from an ultra-short high intensity laser to produce plasma. The absorbed dose of the 8 keV laser-plasma X-ray pulse was accurately estimated with Gafchromic EBT film. When the cells were irradiated with approximately 2 Gy of laser plasma X-ray, the circular regions on 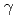 -H2AX positive cells could be clearly identified. Moreover, the number of
-H2AX positive cells could be clearly identified. Moreover, the number of 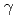 -H2AX and phosphorylated ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) foci induced by 8 keV laser plasma X-ray were comparable to those induced by 4MV X-ray. These results indicate that the laser plasma X-ray source can be useful for radiation biological studies.
-H2AX and phosphorylated ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) foci induced by 8 keV laser plasma X-ray were comparable to those induced by 4MV X-ray. These results indicate that the laser plasma X-ray source can be useful for radiation biological studies.
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Imaoka, Tatsuhiko*; Masunaga, Shinichiro*; Ogata, Toshiyuki*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kato, Takamitsu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Onishi, Takeo*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(4), p.365 - 383, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:124 Percentile:91.08(Biology) X-ray probe in radiation biology
X-ray probe in radiation biologyNishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 81(2), p.026107_1 - 026107_3, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:66.38(Instruments & Instrumentation)An X-ray generation and exposure system dedicated for radiation biology is developed. An X-ray pulse of 8.0 keV in energy as short as 1 ps is generated with a fs-laser pulse, and sample cells are irradiated through a specially designed cell dish with a silicon nitride membrane. DNA double-strand breaks in a nucleus of a human caner cell are caused by X-ray irradiation, and similar DNA breaks are obtained to those with the conventional X-ray source. This result demonstrates feasibility of radiobiological study with a single burst of X-rays shining on a single cell specimen.
Yogo, Akifumi; Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Mori, Michiaki; Teshima, Teruki*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Murakami, Masao*; Demizu, Yusuke*; Akagi, Takashi*; Nagayama, Shinichi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 94(18), p.181502_1 - 181502_3, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:113 Percentile:94.56(Physics, Applied)Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Maeda, Takuya; Mori, Michiaki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Maeda, Takuya; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Mori, Michiaki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Okano, Yasuaki*; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
Recently, high energy, monochromatic X-rays emanating from laser-produced plasma (LPP) are attracting much attention as a new radiation source indispensable for high energy density physics, bioscience, and material sciences. Aiming at these applications, we have been improving performances of Ka lines emitted from and soft X-ray lasers. The monochromaticity is particularly important when X-rays are handled with a narrow-band optics or used to selectively excite a specific material involved in matters. In addition, time-duration of such sources is typically an order of pico-second, and it could be comparable or even shorter than recovery time of radiatively-damaged biological cell, so that the LPP source can be a new source for investigating the mechanisms of irradiation survival and death of biological cells. We propose to develop an ultrashort, intense X-ray microbeam system to study the radiobiological effect and the bystander effect.
Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Matsuura, Nariaki*
no journal, ,
Recently, the bystander effect induced by ionizing radiation has been reported by many researchers. Many signal transducers such as reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, molecules involved in mitochondrial functions, and inflammatory cytokines were associated with the bystander effect. Whole phenomenon of the bystander effect must be clarified to understand the apparatus of the radiation effects on the cells. The laser plasma X-ray source has suitable features for this study. To elucidate the bystander effects, we have developed the microbeam system using a laser plasma X-ray, and the feasibilities in the radiation biology have been evaluated. In this research, we report that p53 function is associated with the bystander effect.
Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*
no journal, ,
Techniques for generating high energy bright short-pulse Ka X-rays have been rapidly developed in recent progress made in utilizing intense ultrashort laser pulses. The soft X-ray laser is also generated from the laser-produced plasma. A highly spatial coherent XRL is generated by the oscillator-amplifier configuration with two targets. Use of X-ray focusing optics has resulted in focused X-ray beams of submicron spot size being achieved in soft and hard X-ray regions. The short duration of laser produced plasma source could be used as a new source in contrast to conventional X-ray sources in investigating the mechanism of the affect of radiation on biological cells. We have started to develop a focused X-ray beam irradiation system for use in studying radiobiological effects on cells, and demonstrated a preliminary study of radiation effect on culture cells irradiated with the X-ray laser and laser produced plasma Ka X-rays.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Okano, Yasuaki*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
We have started to develop a laser plasma X-ray microbeam irradiation system, and demonstrated a preliminary study of the cell survival and  -H2AX focus formation in the culture cells irradiated with laser-produced plasma X-ray.
-H2AX focus formation in the culture cells irradiated with laser-produced plasma X-ray.
Sato, Katsutoshi; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yogo, Akifumi; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Teshima, Teruki*; Daido, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi; Ishino, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kado, Masataka; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
A dedicated radiation biologyn X-ray generation and exposure system has been dedicated for radiation biology is developed. An X-ray pulse of 8.0 keV in energy X-ray pulses is generated with an fs-laser pulse were used to irradiate, and sample cells are irradiated through a custom-made culture dish with a silicon nitride membrane. The X-ray irradiation resulted in DNA double-strand breaks in thea nucleus of a culture cell are caused by X-ray irradiation that were, and similar DNA breaks are obtained to those obtained with athe conventional X-ray source, thus. This result demonstrating thees feasibility of radiobiological studiesy utilizing with a single burst of X-rays focused shining on a single cell specimens.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Tanaka, Momoko; Sato, Katsutoshi; Yamamoto, Minoru; Oba, Toshiyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
Recent Progress in the development of laser-driven plasma soft X-ray laser (XRL) and the applications are presented. In the source development, TOPAZ laser using Nd:glass zigzag slab amplifiers with 10 J, 0.1 Hz repetition-rate routinely provides the fully spatial coherent X-ray laser at 13.9 nm for the applications. The bright, coherent, and picoseconds X-ray pulse can be used in a variety of applications such as X-ray speckle measurement and interferometer for probing materials, diffraction imaging, nano-scale fabrication, radiation biology, and so on. In order to extend the use of XRLs, now we are constructing new XRL beam lines for the optical pump and XRL probe experiment.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
Techniques for generating high energy bright short-pulse Ka X-rays have been rapidly developed in recent progress made in utilizing intense ultrashort laser pulses. The soft X-ray laser (XRL) is also generated from the Laser-Produced Plasma (LPP). A highly spatial coherent XRL is generated by the oscillator-amplifier configuration with two targets. Use of X-ray focusing optics has resulted in focused X-ray beams of submicron spot size being achieved in soft and hard X-ray regions. The short duration of laser produced plasma source could be used as a new source in contrast to conventional X-ray sources in investigating the mechanism of the affect of radiation on biological cells.
Yogo, Akifumi; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Mori, Michiaki; Teshima, Teruki*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Murakami, Masao*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
In this work, we demonstrate the irradiation effect of laser accelerated protons induced on human lung cancer cells. In-vitro A549 cells are irradiated with a proton dose of 20 Gy, resulting in a distinct formation of  -H2AX foci as an indicator of DNA double-strand breaks. This is the first result showing that laser-driven ion beams can generate a lethal effect on cancer cells.
-H2AX foci as an indicator of DNA double-strand breaks. This is the first result showing that laser-driven ion beams can generate a lethal effect on cancer cells.