Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 835, p.119 - 135, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:63.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)A magnetic alloy loaded cavity is used to generate multi-harmonic rf voltage in J-PARC RCS. However, a vacuum tube operation analysis under the multi-harmonic driving is very complicated because many variables should be solved with a self consistency. At the conventional operation analysis, a hand work by tracing the constant current curve of the tube was performed, or an appropriate single harmonic wave form was assumed. We have developed a numerical analysis code which calculates the vacuum tube operation automatically and it realizes the multi-harmonic vacuum tube operation analysis. The code is verified at the high power beam acceleration test and we confirm the calculation results are consistent with the measurement ones. We can calculate the vacuum tube operation precisely by using the code, and it will contribute to improving the quality of the beam in the high intensity proton synchrotron.
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '16) (Internet), p.3443 - 3445, 2016/06
The J-PARC RCS accelerates 2 bunches at the harmonic number 2. The major Fourier component of the beam current is even harmonics. However, the odd harmonics grow under some conditions even though they are very small amplitude at the beginning. Particle tracking simulation suggests that the displacement and the deformation of the bunch are caused by the odd harmonics, it is synchronized with the potential distortion, and it results in the beam instability. We describe the particle tracking simulation results for the odd harmonic beam loading effect in the RCS.
Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.196 - 200, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the J-PARC synchrotrons, Magnetic Alloy (MA) cores loaded RF cavities are employed to achieve a high field gradient. We are successful to increase the shunt impedance of the MA cores for the Main Ring synchrotron RF cavities by applying a transverse magnetic field during annealing. The shunt impedances of the cores with transverse field annealing are around 50% higher than the cores without one. By applying the transverse magnetic field during annealing, the magnetization processes occur by mainly magnetization rotations, and consequently the core loss is reduced and the relative complex permeability shows an excellent frequency behavior. The MA core shunt impedance is increased by those improvements of the magnetic properties.
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Ezura, Eiji*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Omori, Chihiro*; Schnase, A.*; Shimada, Taihei; Takagi, Akira*; Takata, Koji*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.012015_1 - 012015_6, 2015/09
The J-PARC MR provides a coasting proton beam for nuclear physics experiments by slow extraction. The longitudinal emittance should be enlarged until the MR flat top to mitigate the microwave instability. We have investigated a Phase Modulation (PM) method by using a High Frequency Cavity (HFC) to increase the emittance. We have performed extensive simulation studies to find the appropriate parameters of the PM through the particle tracking simulation. We found that the effective HFC frequency has linear dependence with the PM frequency, where the emittance is smoothly enlarged. Furthermore, we found that the required HFC voltage is inverse proportional to the square root of the duration time of the PM. These PM properties will be used for the design of the HFC. We describe the particle tracking simulation results of controlled emittance blow-up by the PM.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Hotchi, Hideaki; Schnase, A.*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 18(9), p.091004_1 - 091004_8, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.74(Physics, Nuclear)The RCS in the J-PARC was originally designed to accelerate two high intensity bunches, while some of neutron experiments in the MLF and a muon experiment using MR beams require a single bunch operation mode. The beam intensity in the single bunch operation has been limited by longitudinal beam losses due to the rf bucket distortions by the wake voltage of the odd harmonics in the wide band MA cavities. We installed an additional rf feedforward system to compensate the wake voltages of the odd harmonics (h=1,3,5). The longitudinal beam losses during the single bunch acceleration disappeared with feedforward for the odd harmonics. We also confirmed that the beam quality in the single bunch acceleration are similar to that of the normal operation with two bunches. Thus, high intensity single bunch acceleration at the intensity of 2.3 10
10 protons per bunch has been achieved in the J-PARC RCS.
protons per bunch has been achieved in the J-PARC RCS.
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Omori, Chihiro*; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1008 - 1012, 2015/09
A harmonic number of J-PARC RCS is two, and when all RF buckets are filled with bunches, the major parts of the beam Fourier components are the even harmonics. However, the particle tracking simulation suggests that the odd harmonics promote asymmetry on each bunch shape and they rapidly increase under some conditions. When the asymmetry becomes larger and larger monotonously, it causes severe beam loss. Furthermore, although the odd harmonics remain small amplitude, an amplitude modulation of them makes a beam halo and causes small beam loss. We describe the particle tracking simulation results to investigate the odd harmonics.
Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1096 - 1110, 2015/09
We are successful in increasing the shunt impedance of the MA cores by applying a transverse magnetic field during annealing. In this paper, we discuss the effects of transverse field annealing on the MA core shunt impedance by comparing two kinds of MA cores, those are the FT3M core that is annealed without any magnetic fields and the FT3L core that is annealed with a transverse magnetic field. We also discuss the shunt impedance of the MA core when the magnetization processes are governed by ideal magnetization rotations. To understand the ribbon thickness and the permeability dependences of the shunt impedance intuitively, we represent the shunt impedance as the resistance of the closed rectangular loop through which the eddy current flows.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Shimada, Taihei; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.639 - 642, 2015/09
In the J-PARC RCS, magnetic alloy (MA) loaded rf cavities are employed to achieve a high accelerating voltage and to realize the dual harmonic operation, where a single cavity is driven by the fundamental accelerating rf and the second harmonic. The cavity is driven by a class-AB push-pull tetrode amplifier. R&D for a high power balun to mitigate the unbalanced output voltages of two tubes is undergoing. The balun is a rf transformer, which consists of a MA core and high voltage cables. In application to the RCS rf system, the maximum rf voltage is very high in the order of 15kV and suppression of corona dischages is a key. We presentthe techniques to suppress corona discharges. Also, the R&D status of cooling of the MA core and cables.
Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1037 - 1041, 2014/10
J-PARC 3 GeV RCS and Main Ring (MR) employ RF cavities loaded with Magnetic Alloy (MA) cores. The RF cavities in RCS employ un-cut cores and the RF cavities in MR employ cut cores to increase the Q-value. In this paper, we discuss the magnetic characteristics of cut cores. At first, we show the fundamental magnetic characteristics of cut core and the influence of leakage magnetic field. Next, we discuss the relation between Rp of un-cut core and cut core. At last, we show what parameters are effective to increase the cut core Rp. Rp is a key parameter to achieve a high field gradient for increasing the beam power.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Shimada, Taihei; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1122 - 1126, 2014/10
In the J-PARC RCS, magnetic alloy (MA) loaded rf cavities are employed to achieve a high accelerating voltage and to realize the dual harmonic operation, where a single cavity is driven by the fundamental accelerating rf and the second harmonic. The cavity is driven by a class-AB push-pull tetrode amplifier. In the dual harmonic operation, the output voltages of two tubes are unbalanced. By the unbalanced output voltage, we observe an increase of screen grid current of one of the tubes, and power consumption of the cavity tanks are also unbalanced. To balance the output voltage, high power baluns using MA cores are under development. We present the design of the baluns and test results using the RCS rf system.
Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Takata, Koji*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 749, p.84 - 89, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have been developing high shunt impedance Magnetic Alloy (MA) cores. The MA core shunt impedance is a key parameter to achieve a higher field gradient for increasing a beam power. We increase the MA core shunt impedance by two different ways. One way is applying an external magnetic field during annealing to increase the MA core magnetic properties. The other way is using thinner ribbons to reduce the eddy current. In this paper, we discuss the latter way.
Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.217 - 220, 2014/06
J-PARC RCS and MR employ RF cavities loaded with Magnetic Alloy (MA) cores. To achieve the high shunt impedance, we measured the shunt impedance with changing the core filling factor, ribbon thickness, and magnetization process. The shunt impedance was reduced in despite of the filling factor increase because the strong winding tension deteriorate the magnetic property. The MA core with thin ribbons and the MA core that is magnetized by a rotation process show high permeability in the accelerating frequency region, and those MA cores show the high shunt impedance consequently.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Schnase, A.; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Shimada, Taihei; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*
Proceedings of 1st International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2012) (Internet), p.63 - 65, 2013/06
Wall current monitors (WCM) for RF system commissioning are installed in the J-PARC synchrotrons, the RCS and the MR. The WCM signals are used for diagnosis to adjust the RF system parameters. For the diagnosis, the WCM signals are taken by an oscilloscope with the revolution clock signal generated by the LLRF control system, and slices of the WCM waveform with lengths of the revolution periods are generated. By stacking the slices, one can get a mountain plot, which shows motions of bunches and variations of the bunch shapes. Also, time variations of the bunching factor, which are important for acceleration of high intensity proton beams, are obtained. The harmonic analysis is performed on the WCM signal and the cavity voltage monitor signal. By using complex amplitudes of them, one can calculate the impedance seen by the beam. The RF parameters for high intensity beams have been successfully adjusted by using these analyses.
Shimada, Taihei; Nomura, Masahiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '13) (Internet), p.2750 - 2752, 2013/06
no abstracts in English
Nomura, Masahiro; Schnase, A.*; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '13) (Internet), p.2747 - 2749, 2013/06
During the development of Magnetic Alloy (MA) cores for RF cavities, the core shunt impedance was increased by lowering a core winding tension to improve the electrical insulation between MA ribbon layers. The lower winding tension reduced the core filling factor. The core shunt impedance might be reduced according to the core filling factor reduction. We study the influence of improving the electrical insulation and lowering the core winding tension on the core shunt impedance.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.*; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*
Proceedings of 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '13) (Internet), p.2540 - 2542, 2013/06
Beam loading compensation is indispensable to accelerate high intensity proton beams in the J-PARC MR. The MA-loaded rf cavities in the MR are driven by the single harmonic (h = 9) rf signals, while the cavity frequency response covers also the neighbor harmonics (h = 8, 10). The wake voltage induced by the beam consists of the three harmonics (h = 8, 9, 10). We employ the rf feedforward method to compensate the beam loading of these harmonics. The full-digital feedforward system was developed for the MR. We have successfully commissioned the feedforward patterns for all of eight cavities by using high intensity beams with 1.0 10
10 ppp. We present the commissioning results. The impedance seen by the beam is reduced and the longitudinal oscillations due to the beam loading are reduced. By the beam loading compensation, high power beam operation at the beam power of 200 kW has been achieved.
ppp. We present the commissioning results. The impedance seen by the beam is reduced and the longitudinal oscillations due to the beam loading are reduced. By the beam loading compensation, high power beam operation at the beam power of 200 kW has been achieved.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.*; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 16(5), p.051002_1 - 051002_12, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.92(Physics, Nuclear)Beam loading compensation is a key for acceleration of a high intensity proton beam in the MR of J-PARC. Magnetic alloy loaded rf cavities with a Q value of 22 are used to achieve high accelerating voltages. The cavity is driven by a single harmonic (h = 9) rf signal while the cavity frequency response also covers the neighbor harmonics (h = 8, 10). Therefore the wake voltage induced by the high intensity beam consists of the three harmonics, h = 8, 9, 10. We employ the rf feedforward method to compensate the beam loading ofthese three harmonics (h = 8, 9, 10). The full-digital multiharmonic feedforward system was developed for the MR. The commissioning of the feedforward system has been performed by using high intensity beams with 1.0 10
10 protons per pulse. The longitudinal oscillations due to the beam loading are reduced. By the beam loading compensation, stable high power beam operation is achieved.
protons per pulse. The longitudinal oscillations due to the beam loading are reduced. By the beam loading compensation, stable high power beam operation is achieved.
Schnase, A.; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Omori, Chihiro*; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Toda, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshii, Masahito*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1204 - 1208, 2012/08
Shimada, Taihei; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Schnase, A.; Toda, Makoto*; Omori, Chihiro*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1143 - 1145, 2012/08
The RF cavities of J-PARC 3 GeV synchrotron use 198 MA cores. Buckling occurred in some cores since the operation starting on the October of 2007. We have measured the inner diameters of the cores as a part of the investigation to determine the cause of the buckling when the cavities were disassembled for maintenance. We noticed that deformations of the inner shapes of the cores related to its manufacturing process and that inner diameters change over year were not measured in the most of the cores without buckled cores. Furthermore, the effective manufacturing process of cores to avoid the buckling has be established. We are going to replace old type cores with new type cores in shutdown periods in summer every year.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.89 - 93, 2012/08
For acceleration of high intensity proton beam, it is important to compensate the beam loading due to the wake voltages in accelerating cavities. The Q-value of the magnetic-alloy cavity in the J-PARC MR is set to 22 to cover the frequency sweep of the accelerating harmonic (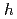 =9) without tuning bias loop. The cavity bandwidth also covers the neighbor harmonics (
=9) without tuning bias loop. The cavity bandwidth also covers the neighbor harmonics (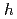 =8, 10). Thus, the wake voltage consists of the accelerating harmonic (
=8, 10). Thus, the wake voltage consists of the accelerating harmonic (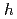 =9) and the neighbor harmonics (
=9) and the neighbor harmonics (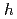 =8, 10). We employ the RF feedforward method to compensate the multiharmonic beam loading. The full-digital feedforward system has been developed for the MR. We present the commissioning results of the system with high intensity (1.0
=8, 10). We employ the RF feedforward method to compensate the multiharmonic beam loading. The full-digital feedforward system has been developed for the MR. We present the commissioning results of the system with high intensity (1.0 10
10 ppp) proton beams.
ppp) proton beams.