Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
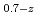 Pu
Pu Am
Am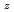 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sugimoto, Masatoshi*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Hino, Tetsushi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101156_1 - 101156_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)In current nuclear fuel cycle systems, to reduce the amount of high-level radioactive waste, minor actinides (MAs) bearing MOX fuel is one option for burning MAs using fast reactor. However, the effects of Am content in fuel on thermal conductivity are unclear because there are no experimental data on thermal conductivity of high Am bearing MOX fuel. In this study, The thermal conductivities of near stoichiometric (U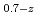 Pu
Pu Am
Am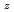 )O
)O solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT)
solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT) ) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U
) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U and Am
and Am . B values were independent of Am content.
. B values were independent of Am content.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Onishi, Takashi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Katsuyama, Kozo; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 536, p.152119_1 - 152119_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to obtain the release rate coefficients from fuels for fast reactors (FRs), heating tests and the subsequent analyses of the fission products (FPs) and actinides that are released were carried out using samples of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel pellets irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo. Three heating tests targeting temperatures of 2773, 2973 and 3173 K were conducted using an FP release behavior test apparatus equipped with a high-frequency induction furnace and solid FP sampling systems consisting of a thermal gradient tube (TGT) and filters. Irradiated fuel pellets were placed into a tungsten crucible, then loaded into the induction furnace. The temperature was raised continuously at a heating rate of 10 K/s to the targeted temperature and maintained for 500 s in a flowing argon gas atmosphere. The FPs and actinides released from the MOX fuels and deposited in the TGT and filters were quantified by gamma-ray spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis. Based on the analysis, the release rates of radionuclides from MOX fuels for FR were obtained and compared with literature data for light water reactor (LWR) fuels. The release rate coefficients of FPs obtained in this study were found to be similar to or lower than the literature values for LWR fuels. It was also found that the release rate coefficient data for actinides were within the range of variation of literature values for LWR fuels.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
JAEA-Testing 2014-001, 29 Pages, 2014/05
The penetration tests with solution containing radioactive nuclides were experimented to understand basic data for floor and wall materials of Fukushima Daiichi reactor buildings. The solution prepared from irradiated fuels was used as solution containing radioactive nuclides. The solution was applied to surface of epoxy paint, dried concrete and mortar used as specimens. Dose-rate profiles of direction of depth were given by radiation measurement and grinding of the specimens. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for epoxy paint specimens were not clearly observed and the penetration depths would be within 0.4 mm. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for dried concrete specimens proceeded. The penetration rates were substantially decreased when 16 days have elapsed from start. The dose rates of penetrated dried concrete specimens were reduced to background by grinding-2.0 mm.  -ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
-ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Miwa, Shuhei; Sato, Isamu; Hirosawa, Takashi; Sekine, Shinichi; Seki, Takayuki*; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Obayashi, Hiroshi; Koyama, Shinichi
JAEA-Research 2013-022, 62 Pages, 2014/01
In order to establish the method for heating tests focused on the fission product release resulting from the high temperature chemical interaction between fuel and cladding material and to obtain the novel data on fission product release behaviors, the heating test was carried out with irradiate MOX fuel pellet and cladding.
Tokoro, Daishiro*; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro
no journal, ,
Fire-extinguishing test of fire extinguishants composed of graphite on burning lithium has been performed, and the results were compared with the performance of the previous report (sodium chloride). The reaction products and the products after the water/alcohol cleaning were analyzed by using X-ray diffraction meter.
Kondo, Hiroo; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Iuchi, Hiroshi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Kanemura, Takuji; Ida, Mizuho; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Wakai, Eiichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA) for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) were started from July 2007 under an international agreement called ITER Broader Approach. As a major Japanese activity, EVEDA Li test loop (ELTL) to simulate hydraulic and impurity conditions of IFMIF has already designed and is under construction, in which feasibility of hydraulic stability of the liquid Li target, the purification systems of hot traps are major key issues to be validated in this loop. This presentation focuses on the engineering design of the ELTL, and its construction and commissioning.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Kanayama, Fumihiko; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Koyama, Shinichi; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Fukushima, Mineo; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kosuke; Miwa, Shuhei; Sato, Isamu; Hirosawa, Takashi; Sekine, Shinichi; Obayashi, Hiroshi; Koyama, Shinichi; Seki, Takayuki*; Tokoro, Daishiro*
no journal, ,
In order to develop the heating method for both fuel pellet and cladding, irradiated MOX fuel together with Zry-2 cladding were heated by using source term evaluation equipment.
Sato, Isamu; Hirosawa, Takashi; Miwa, Shuhei; Tanaka, Kosuke; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Seki, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
Fuel pellets irradiated in the advanced thermal reactor, "FUGEN", were heated using a high frequency induction fuenace, and then the release and residue behavior of fission products were observed.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Kanayama, Fumihiko; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Koyama, Shinichi; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Fukushima, Mineo; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Isozaki, Ryosuke; Katsuyama, Kozo; Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu; Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Hayashi, Takehiro; Tokoro, Daishiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Isamu; Onishi, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Ishigamori, Toshio*; Seki, Takayuki*; Shinada, Masanori*; et al.
no journal, ,
As a material simulating FP, CsI was heated and evaporated to be decomposited on the surface of a tube having a temperature gradient. Gaseous B O
O made by heating it at higher temperature was react with CsI decomposited on the surface, and then the boron effects for decomposition and migration behavior of Cs and I were observed. Consequently, it was indicated that boron vapor could strip decomposited CsI to make it gaseous species again and then the guseous CsI could move to the colder position.
made by heating it at higher temperature was react with CsI decomposited on the surface, and then the boron effects for decomposition and migration behavior of Cs and I were observed. Consequently, it was indicated that boron vapor could strip decomposited CsI to make it gaseous species again and then the guseous CsI could move to the colder position.
Iwasaki, Maho; Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Amaya, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Seki, Takayuki*; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu; Hirosawa, Takashi; Onishi, Takashi; Suto, Mitsuo; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Seki, Takayuki*; Shinada, Masanori*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to evaluate chemical forms of deposited fission products,  ray spectrometry, macroscopic observation, XRD, ICP-MS analysis were performed in the specimens of sampling parts after a heating test of a fuel which was irradiated at FUGEN.
ray spectrometry, macroscopic observation, XRD, ICP-MS analysis were performed in the specimens of sampling parts after a heating test of a fuel which was irradiated at FUGEN.
Hirosawa, Takashi; Sato, Isamu; Tanaka, Kosuke; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Ishigamori, Toshio*; Seki, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
In order to demonstrate severe accident condition on BWR, FP gas release test device was alternated to be used under oxidizing atmosphere. As a result, it is confirmed that the oxidation reaction of tungsten part was inhibited under high temperature.
Ishikawa, Takashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Onishi, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Takashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Ishikawa, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Katsuyama, Kozo; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Onishi, Takashi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Katsuyama, Kozo; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
Fractional release rate was evaluated based on the results of chemical analysis of sampling parts on which released nuclides were deposited during the over-heating test of irradiated fuels in a fast reactor.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Seki, Takayuki; Oka, Hiroshi; Matsuda, Tetsushi*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Sekioka, Ken*; Tokoro, Daishiro*
no journal, ,
The outline and main results of "Study on the physical properties of non-stoichiometric oxide fuels with high minor actinide contents", entrusted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan are presented.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Onishi, Takashi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Katsuyama, Kozo; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to obtain the release rate coefficients from fuels for fast reactors, heating tests and the subsequent analyses of the fission products (FPs) and actinides released were carried out using samples of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel pellets irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo. Three heating tests targeting temperatures of 2773, 2973 and 3173 K were conducted using an FP release behavior test apparatus equipped with a high frequency induction furnace and solid FP sampling systems consisting of a thermal gradient tube (TGT) and filters. Irradiated fuel pellets were placed into a tungsten crucible, then loaded into the induction furnace. The temperature was raised continuously at a heating rate of 10 K/s to the targeted temperature and maintained for 500 s in a flowing argon gas atmosphere. The FPs and actinides released from the MOX fuels and deposited in TGT and filters were quantified by  -ray spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis. Based on the analysis, the release rates of radionuclides from MOX fuels for FR were obtained and compared with literature data for light water reactor (LWR) fuels. The release rate coefficients of FPs obtained in this study were found to be similar to or lower than the literature values for LWR fuels. It was also found that the data of release rate coefficient for actinides were within the range of variation of literature values for LWR fuels.
-ray spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis. Based on the analysis, the release rates of radionuclides from MOX fuels for FR were obtained and compared with literature data for light water reactor (LWR) fuels. The release rate coefficients of FPs obtained in this study were found to be similar to or lower than the literature values for LWR fuels. It was also found that the data of release rate coefficient for actinides were within the range of variation of literature values for LWR fuels.