Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagasawa, Makoto*; Shimizu, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Tokunaga, Kohei; Mukai, Hiroki*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemical Geology, 670, p.122431_1 - 122431_25, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.42(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Yamada, Masako*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Bourgeois, D.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Langmuir, 40(46), p.24257 - 24271, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Microscopic structures in liquid-liquid extraction, such as structuration between extractants or extracted complexes in bulk organic phases and at interfaces, can influence macroscopic phenomena, such as the distribution behavior of solutes, including extraction efficiency, selectivity, and phase separation of the organic phase. In this study, we correlated the macroscopic behavior of the extraction of Zr(IV) ions from nitric acid solutions with microscopic structural information in order to understand at the molecular level the key factors contributing to the higher metal ion extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system comprising fluorous phosphate (TFP) in perfluorohexane as compared to the analogous organic extraction system comprising organic phosphate (THP) in n-hexane. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure, neutron reflectometry, and small-angle neutron scattering revealed the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion, the accumulation of extractant molecules at the interface, and the structuration of extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase, respectively. In the fluorous extraction system, extractant aggregates with were formed after contact with nitric acid. In contrast, in the organic extraction system, only extractant dimers were formed. We speculate that differences in the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion and the structuration of the extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase contribute to the high Zr(IV) extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system. In particular, the size of the aggregates hardly changed with increasing Zr(IV) concentration in the fluorous phase, which may be closely related to the absence of phase splitting in the fluorous extraction system.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10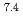 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.*; Shariful, I. M.*; Eljamal, R.*; Bensaida, K.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tokunaga, Kohei; Eljamal, O.*
Advanced Materials Letters (Internet), 14(2), p.23021721_1 - 23021721_10, 2023/04
 bimetallic Ni/Fe
bimetallic Ni/Fe nanoparticles; Implications towards Tc(VII) removal
nanoparticles; Implications towards Tc(VII) removalMaamoun, I.; Tokunaga, Kohei; Dohi, Terumi; Kanno, Futoshi*; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, O.*; Tanaka, Kazuya
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 2, p.1142823_1 - 1142823_17, 2023/03
Recently, the rapid development of nuclear power technologies and the continuous energy demand around the world exhibited massive amounts of contaminated water with radionuclides. Technetium-99 ( Tc) is one of the long-lived radionuclides with a highly mobile anionic form (Tc(VII)) in aqueous solutions. Hence, the rapid and efficient Tc(VII) removal from radioactive water has emerged as a challenging issue. In this work, bimetallic nickel/iron nanoparticles (Ni/Fe
Tc) is one of the long-lived radionuclides with a highly mobile anionic form (Tc(VII)) in aqueous solutions. Hence, the rapid and efficient Tc(VII) removal from radioactive water has emerged as a challenging issue. In this work, bimetallic nickel/iron nanoparticles (Ni/Fe ) were prepared to enhance the immobilization of rhenium (Re(VII)) from aqueous solutions, as the surrogate of Tc(VII).
) were prepared to enhance the immobilization of rhenium (Re(VII)) from aqueous solutions, as the surrogate of Tc(VII).
Tokunaga, Kohei
Hosha Kagaku, (47), p.20 - 23, 2023/03
no abstracts in English

 -, SeO
-, SeO
 -, and SeO
-, and SeO
 -coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphate
-coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphateTokunaga, Kohei; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(8), p.3166 - 3175, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.52(Engineering, Environmental)Coprecipitation of radionuclides with barite has been studied to remove radionuclides from radioactive liquid waste because of its excellent removal efficiency; however, little information exists concerning the stability of the ions coprecipitated with barite. This study systematically investigated the stability of iodate, selenite, and selenate coprecipitated with barite via leaching tests. These oxyanions were gradually leached from the oxyanion-bearing barite into ultrapure water over time. Leaching of the oxyanions significantly increased in leaching solutions containing NaCl (pH5.3), NaNO (pH5.9), and Na
(pH5.9), and Na SO
SO (pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH
(pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH PO
PO solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO
solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 23, p.14 - 19, 2023/00
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 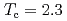 K for
K for 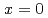 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 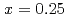 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 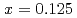 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 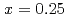 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 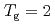 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 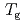 with a
with a 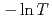 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
Ueda, Yuki; Eguchi, Ayano; Tokunaga, Kohei; Kikuchi, Kei*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Naganawa, Hirochika
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 61(19), p.6640 - 6649, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.94(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English
 Cs
CsUchiyama, Yusuke*; Tokunaga, Natsuki*; Azuma, Kohei*; Kamidaira, Yuki; Tsumune, Daisuke*; Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Yamada, Masatoshi*; Tateda, Yutaka*; Ishimaru, Takashi*; Ito, Yukari*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 816, p.151573_1 - 151573_13, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.04(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi
Chemosphere, 266, p.129104_1 - 129104_10, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:59.45(Environmental Sciences)Radioactive iodine ( I) is of great concern owing to its high mobility in the environment and long-term radiotoxicity, but there is a lack of effective techniques for removing iodate (IO
I) is of great concern owing to its high mobility in the environment and long-term radiotoxicity, but there is a lack of effective techniques for removing iodate (IO
 ) from aqueous solution. The aim of this study is to develop a new technique for removing radioactive iodate from contaminated solution by using barite (BaSO
) from aqueous solution. The aim of this study is to develop a new technique for removing radioactive iodate from contaminated solution by using barite (BaSO ). In the present study, we examined the coprecipitation mechanism of iodate by barite at the molecular level for determining optimum conditions for iodate removal. The results showed that iodate was effectively removed from aqueous solution by coprecipitation, even in the presence of competitive anions in solution. Comparing our method with previous studies, iodate removal efficiency by barite was determined to be about two orders of magnitude greater than that by hydrotalcite-like layered double hydroxide at Cl
). In the present study, we examined the coprecipitation mechanism of iodate by barite at the molecular level for determining optimum conditions for iodate removal. The results showed that iodate was effectively removed from aqueous solution by coprecipitation, even in the presence of competitive anions in solution. Comparing our method with previous studies, iodate removal efficiency by barite was determined to be about two orders of magnitude greater than that by hydrotalcite-like layered double hydroxide at Cl concentration of 10 mmol L
concentration of 10 mmol L . Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis indicated that incorporated iodate was strongly bound in the crystal lattice of barite by substituting the sulfate site in the structure when the iodine concentration was low. The charge compensation problem from the IO
. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis indicated that incorporated iodate was strongly bound in the crystal lattice of barite by substituting the sulfate site in the structure when the iodine concentration was low. The charge compensation problem from the IO
 substitution in SO
substitution in SO
 site is achieved by the substitution of Na
site is achieved by the substitution of Na -IO
-IO
 pairs at the nearest Ba
pairs at the nearest Ba site. Therefore, considering high removal efficiency and strong binding of iodate in barite, coprecipitation with barite is a promising material for removing radioactive iodate from various aqueous solutions contaminated with iodate.
site. Therefore, considering high removal efficiency and strong binding of iodate in barite, coprecipitation with barite is a promising material for removing radioactive iodate from various aqueous solutions contaminated with iodate.
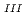 from nitrate media; Comparison with a conventional organic phosphate
from nitrate media; Comparison with a conventional organic phosphateUeda, Yuki; Kikuchi, Kei*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Tanaka, Kazuya; Okamura, Hiroyuki
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 39(5-6), p.491 - 511, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 production from methane decomposition by fullerene at low temperature
production from methane decomposition by fullerene at low temperatureTokunaga, Tomoharu*; Kuno, Kohei*; Kawakami, Takumi*; Yamamoto, Takahisa*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45(28), p.14347 - 14353, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:10.60(Chemistry, Physical)To understand the catalytic behavior of graphite and carbon black with mainly 6-membered rings with sp bonds for H
bonds for H production by CH
production by CH decomposition, fullerenes with 6-membered rings and also those comprising 5- and 7-membered rings with sp
decomposition, fullerenes with 6-membered rings and also those comprising 5- and 7-membered rings with sp bonds was investigated using gas chromatography, XPS and TEM analysis. From these analysis, it is anticipated that the ring structures without 6-membered rings in carbon materials with sp
bonds was investigated using gas chromatography, XPS and TEM analysis. From these analysis, it is anticipated that the ring structures without 6-membered rings in carbon materials with sp bonding contribute to the catalytic behavior for CH
bonding contribute to the catalytic behavior for CH decomposition at a low temperature of 400
decomposition at a low temperature of 400 C.
C.
Tokunaga, Kohei; Kozai, Naofumi; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 359, p.307 - 315, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:70.46(Engineering, Environmental)In the present study, we looked at the removal efficiency of Sr by using barite (BaSO ) under various experimental conditions to develop techniques for the direct removal of Sr from seawater. The uptake of Sr by barite was found to be dependent on pH, saturation state, and [Ba
) under various experimental conditions to develop techniques for the direct removal of Sr from seawater. The uptake of Sr by barite was found to be dependent on pH, saturation state, and [Ba ]/[SO
]/[SO
 ] ratio in initial aqueous solution, showing that most of the aqueous Sr can be removed from the aqueous solution by adjusting these parameters. However, the effects of ionic strength and competitive ions were negligible, suggesting the effectiveness of its application to removal of Sr from seawater. Batch experiments were also conducted in a seawater system, and a rather high removal efficiency of Sr from seawater (more than 90%) was achieved. Considering its high removal and retention efficiency of Sr in seawater systems, barite is a reliable material for the removal of Sr from seawater.
] ratio in initial aqueous solution, showing that most of the aqueous Sr can be removed from the aqueous solution by adjusting these parameters. However, the effects of ionic strength and competitive ions were negligible, suggesting the effectiveness of its application to removal of Sr from seawater. Batch experiments were also conducted in a seawater system, and a rather high removal efficiency of Sr from seawater (more than 90%) was achieved. Considering its high removal and retention efficiency of Sr in seawater systems, barite is a reliable material for the removal of Sr from seawater.
Tokunaga, Kohei*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Environmental Science & Technology, 51(16), p.9194 - 9201, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:80.64(Engineering, Environmental)In the present study, we explore a new application of barite (BaSO ) as a sequestering phase for selenite (Se(IV)) and selenate (Se(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions due to the low solubility and high stability of barite. The uptake of Se(IV) and Se(VI) during coprecipitation with barite was investigated through batch experiments to understand the factors controlling effective removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from polluted water to barite. The uptake of Se(IV) by barite is dependent on pH, coexistent calcium ion, and sulfate concentration in the initial solution, possibly due to their effects on the chemical affinity and structural similarity. On the other hand, the uptake of Se(VI) by barite was strongly dependent on sulfate concentration in the initial solution, which is only related to the structural similarity. This study provides a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove Se(IV) and Se(VI) from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) under optimized experimental parameters.
) as a sequestering phase for selenite (Se(IV)) and selenate (Se(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions due to the low solubility and high stability of barite. The uptake of Se(IV) and Se(VI) during coprecipitation with barite was investigated through batch experiments to understand the factors controlling effective removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from polluted water to barite. The uptake of Se(IV) by barite is dependent on pH, coexistent calcium ion, and sulfate concentration in the initial solution, possibly due to their effects on the chemical affinity and structural similarity. On the other hand, the uptake of Se(VI) by barite was strongly dependent on sulfate concentration in the initial solution, which is only related to the structural similarity. This study provides a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove Se(IV) and Se(VI) from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) under optimized experimental parameters.
 -MnO
-MnO in NaCl solution
in NaCl solutionTanaka, Kazuya; Tanaka, Masato*; Watanabe, Naoko*; Tokunaga, Kohei*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemical Geology, 460, p.130 - 137, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:36.62(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Pd is highly accumulated in ferromanganese nodules and crusts relative to its concentration in seawater but the mechanism by which Pd(II) is incorporated remains poorly understood. We investigated the local coordination structure of Pd(II) adsorbed on  -MnO
-MnO , using X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analyses indicated that Pd was adsorbed on
, using X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analyses indicated that Pd was adsorbed on  -MnO
-MnO through ligand exchange, from Cl coordination to O coordination. Furthermore, curve fitting of EXAFS spectra demonstrated the formation of two different inner-sphere complexes, bidentate-mononuclear and bidentate-binuclear complexes, and this finding was supported by density functional theory calculations. The formation of inner-sphere complexes is reasonable given the relatively large distribution coefficients obtained from adsorption experiments.
through ligand exchange, from Cl coordination to O coordination. Furthermore, curve fitting of EXAFS spectra demonstrated the formation of two different inner-sphere complexes, bidentate-mononuclear and bidentate-binuclear complexes, and this finding was supported by density functional theory calculations. The formation of inner-sphere complexes is reasonable given the relatively large distribution coefficients obtained from adsorption experiments.

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; et al.
no journal, ,
In heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn , slight Zn substitutions for In atoms induce antiferromagnetism, while slight Ni substitutions for Co atoms suppress superconductivity. The both substituted CeCoIn
, slight Zn substitutions for In atoms induce antiferromagnetism, while slight Ni substitutions for Co atoms suppress superconductivity. The both substituted CeCoIn exhibit non- fermi-liquid behaviors near the phase boundaries which have been detected by magnetization and specific heat measurements. We have performed NMR experiments in these systems to investigate the microscopic effects by substituents. We will discuss about the spin fluctuations near the boundaries by NMR relaxation rates.
exhibit non- fermi-liquid behaviors near the phase boundaries which have been detected by magnetization and specific heat measurements. We have performed NMR experiments in these systems to investigate the microscopic effects by substituents. We will discuss about the spin fluctuations near the boundaries by NMR relaxation rates.
Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
no journal, ,
In the present study, we explore a new application of barite as a sequestering phase for radioactive oxyanions, such as selenium-79, technetium-99, and iodine-129, from aqueous solutions. Barite is a common phase in many geological environments, and it can be used to remove toxic and/or radioactive elements from aqueous solutions, but it has not been widely used in environmental studies. This study mainly describes the mechanisms of selenite and selenate distribution between barite and water, thus providing a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove these ions from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) using the optimized experimental parameters examined here.