Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMRMatsumura, Hiroki*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 13 of others*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nagasawa, Makoto*; Shimizu, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Tokunaga, Kohei; Mukai, Hiroki*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemical Geology, 670, p.122431_1 - 122431_25, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)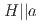 in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 11 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10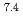 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(14), p.L140502_1 - L140502_6, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The normal-conducting state of the superconductor UTe is studied by entropy analysis for magnetic fields along the
is studied by entropy analysis for magnetic fields along the  -axis, obtained from magnetization using the relation
-axis, obtained from magnetization using the relation 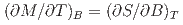 . We observe a strong increase in entropy with magnetic field due to metamagnetic fluctuations (spatially uniform,
. We observe a strong increase in entropy with magnetic field due to metamagnetic fluctuations (spatially uniform, 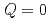 ). The field dependence is well described by the Hertz-Millis-Moriya theory for quantum criticality of itinerant metamagnetism. Notably, the lower bound of the quantum-critical region coincides well with the position of the minimum in the superconducting transition temperature
). The field dependence is well described by the Hertz-Millis-Moriya theory for quantum criticality of itinerant metamagnetism. Notably, the lower bound of the quantum-critical region coincides well with the position of the minimum in the superconducting transition temperature 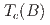 . Hence, our results suggest that
. Hence, our results suggest that 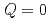 fluctuations reinforce the superconductivity.
fluctuations reinforce the superconductivity.
Hagihara, Koji*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Harjo, S.; Tokunaga, Toko*; Yamamoto, Kazuki*; Sugita, Mika*; Aoyama, Kairi*; Gong, W.; Nishimoto, Soya*
International Journal of Plasticity, 173, p.103865_1 - 103865_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:98.62(Engineering, Mechanical)
Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Aoki, Dai*; Knebel, G.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(22), p.226503_1 - 226503_7, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:85.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Yanase, Yoichi*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(14), p.144502_1 - 144502_5, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:68.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The vortex dynamics in the spin-triplet superconductor, UTe , are studied by measuring the DC electrical resistivity with currents along the
, are studied by measuring the DC electrical resistivity with currents along the  -axis under magnetic fields along the
-axis under magnetic fields along the  -axis. Surprisingly, we have discovered an island region of low critical current deep inside the superconducting (SC) state, well below the SC upper critical field, attributed to a weakening of vortex pinning. Notably, this region coincides with the recently proposed intermediate-field SC state. We discuss the possibility of nonsingular vortices in the intermediate state, where SC order parameter does not vanish entirely in the vortex cores due to the mixing of multiple SC components.
-axis. Surprisingly, we have discovered an island region of low critical current deep inside the superconducting (SC) state, well below the SC upper critical field, attributed to a weakening of vortex pinning. Notably, this region coincides with the recently proposed intermediate-field SC state. We discuss the possibility of nonsingular vortices in the intermediate state, where SC order parameter does not vanish entirely in the vortex cores due to the mixing of multiple SC components.
 Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Kinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Matsumura, Hiroki*; Hori, Fumiya*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 9(30), p.2736_1 - 2736_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:89.65(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 -axis knight shift on UTe
-axis knight shift on UTe with
with  = 2.1 K
= 2.1 KMatsumura, Hiroki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(6), p.063701_1 - 063701_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:98.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Nakamine, Genki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(5), p.053702_1 - 053702_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:75.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary) along hard magnetic axis
along hard magnetic axisSakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review Letters, 130(19), p.196002_1 - 196002_6, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:95.70(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The superconducting (SC) phase diagram in uranium ditelluride is explored under magnetic fields ( ) along the hard magnetic
) along the hard magnetic  -axis using a high-quality single crystal with
-axis using a high-quality single crystal with  = 2.1 K. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the
= 2.1 K. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the 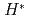 of
of 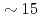 T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near
T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near 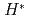 , indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
, indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
Maamoun, I.; Falyouna, O.*; Shariful, I. M.*; Eljamal, R.*; Bensaida, K.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tokunaga, Kohei; Eljamal, O.*
Advanced Materials Letters (Internet), 14(2), p.23021721_1 - 23021721_10, 2023/04
Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 78(5), p.267 - 272, 2023/04
no abstracts in English
 bimetallic Ni/Fe
bimetallic Ni/Fe nanoparticles; Implications towards Tc(VII) removal
nanoparticles; Implications towards Tc(VII) removalMaamoun, I.; Tokunaga, Kohei; Dohi, Terumi; Kanno, Futoshi*; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, O.*; Tanaka, Kazuya
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 2, p.1142823_1 - 1142823_17, 2023/03
Recently, the rapid development of nuclear power technologies and the continuous energy demand around the world exhibited massive amounts of contaminated water with radionuclides. Technetium-99 ( Tc) is one of the long-lived radionuclides with a highly mobile anionic form (Tc(VII)) in aqueous solutions. Hence, the rapid and efficient Tc(VII) removal from radioactive water has emerged as a challenging issue. In this work, bimetallic nickel/iron nanoparticles (Ni/Fe
Tc) is one of the long-lived radionuclides with a highly mobile anionic form (Tc(VII)) in aqueous solutions. Hence, the rapid and efficient Tc(VII) removal from radioactive water has emerged as a challenging issue. In this work, bimetallic nickel/iron nanoparticles (Ni/Fe ) were prepared to enhance the immobilization of rhenium (Re(VII)) from aqueous solutions, as the surrogate of Tc(VII).
) were prepared to enhance the immobilization of rhenium (Re(VII)) from aqueous solutions, as the surrogate of Tc(VII).
 Te
Te
Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(3), p.034704_1 - 034704_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:50.64(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the physical properties of a single crystal of uranium telluride U Te
Te . We have confirmed that U
. We have confirmed that U Te
Te crystallizes in the hexagonal structure with three nonequivalent crystallographic uranium sites. The paramagnetic moments are estimated to be approximately 1
crystallizes in the hexagonal structure with three nonequivalent crystallographic uranium sites. The paramagnetic moments are estimated to be approximately 1 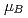 per the uranium site, assuming a uniform moment on all the sites. A ferromagnetic phase transition occurs at
per the uranium site, assuming a uniform moment on all the sites. A ferromagnetic phase transition occurs at  = 48 K, where the in-plane magnetization increases sharply, whereas the out of-plane component does not increase significantly. With decreasing temperature further below
= 48 K, where the in-plane magnetization increases sharply, whereas the out of-plane component does not increase significantly. With decreasing temperature further below  under field-cooling conditions, the out-of-plane component increases rapidly around T
under field-cooling conditions, the out-of-plane component increases rapidly around T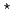 = 26 K. In contrast, the in-plane component hardly changes at T
= 26 K. In contrast, the in-plane component hardly changes at T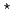 . Specific heat measurement indicates no
. Specific heat measurement indicates no  -type anomaly around T
-type anomaly around T , so this is a cross-over suggesting a reorientation of the ordering moments or successive magnetic ordering on the part of the multiple uranium sites.
, so this is a cross-over suggesting a reorientation of the ordering moments or successive magnetic ordering on the part of the multiple uranium sites.

 -, SeO
-, SeO
 -, and SeO
-, and SeO
 -coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphate
-coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphateTokunaga, Kohei; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(8), p.3166 - 3175, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.75(Engineering, Environmental)Coprecipitation of radionuclides with barite has been studied to remove radionuclides from radioactive liquid waste because of its excellent removal efficiency; however, little information exists concerning the stability of the ions coprecipitated with barite. This study systematically investigated the stability of iodate, selenite, and selenate coprecipitated with barite via leaching tests. These oxyanions were gradually leached from the oxyanion-bearing barite into ultrapure water over time. Leaching of the oxyanions significantly increased in leaching solutions containing NaCl (pH5.3), NaNO (pH5.9), and Na
(pH5.9), and Na SO
SO (pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH
(pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH PO
PO solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO
solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
 induced by magnetic field
induced by magnetic fieldKinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(6), p.L060502_1 - L060502_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:91.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)