Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakamoto, Tetsuo*; Morita, Masato*; Kanenari, Keita*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Saito, Kosuke*; Ohashi, Masaya*; Kato, Kotaro*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Kawai, Toshihide*; et al.
Analytical Sciences, 34(11), p.1265 - 1270, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.86(Chemistry, Analytical)Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; Hirose, Ryoichi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 106(12), p.121109_1 - 121109_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.60(Physics, Applied)Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Ohashi, Hayato*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 7(8), p.086202_1 - 086202_4, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:74.22(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate high conversion efficiency for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) emission at 6.5-6.7 nm from multiple laser beam-produced one-dimensional spherical plasmas. Multiply charged-state ions produce strong resonance emission lines, which combine to yield intense unresolved transition arrays in Gd, Tb, and Mo. The maximum in-band EUV conversion efficiency was observed to be 0.8%, which is one of the highest values ever reported due to the reduction of plasma expansion loss.
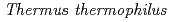
Horie, Akira*; Tomita, Takeo*; Saiki, Asako*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Taka, Hikari*; Mineki, Reiko*; Fujimura, Tsutomu*; Nishiyama, Chiharu*; Kuzuyama, Tomohisa*; Nishiyama, Makoto*
Nature Chemical Biology, 5(9), p.673 - 679, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:67.47(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)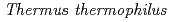
Yoshida, Ayako*; Tomita, Takeo*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Fushinobu, Shinya*; Kuzuyama, Tomohisa*; Nishiyama, Makoto*
FEBS Journal, 276(11), p.3124 - 3136, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:30.27(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Tomita, Hideki*; Saito, Kosuke*; Ohashi, Masaya*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Kato, Kotaro*; Suzuki, So*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Morita, Masato*; Sakamoto, Tetsuo*; Kanenari, Keita*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakada, Naoki*; Takada, Eiji*; Isobe, Mitsutaka*; Ogawa, Kunihiro*; Nishitani, Takeo*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sato, Satoshi; Kawarabayashi, Jun*
no journal, ,
In order to measure the profile of the neutron generation in LHD at NIFS, we have developed the directional fast neutron detector based on scintillating optical fibers by using the forward direction of the probability of the recoil proton generation by the neutron and the scintillating optical fibers. We have enhanced the directional quality by optimizing the configuration of the scintillating optical fibers. In case 14 MeV neutrons were incident to the detector, we calculated the number of the energy deposition events with the energy of more than threshold value by PHITS. In case they were incident to the detector parallel, the number of the events at the rear part lessened due to the self-shielding. Even if the scintillating optical fiber was shortened, the angular dependency was not so changed. In case it was thin downed, it was found that the angular dependency was enhanced. We performed the neutron measurement experiment by using the developed detector and the DT neutron source at JAEA/FNS. The angular dependencies by the experiment were worse than those by the calculation. It is thought to be causally related to the high sensitivity to the  -ray of the detector. In the future, we will redesign the detector for the neutron and
-ray of the detector. In the future, we will redesign the detector for the neutron and  -ray field in LHD.
-ray field in LHD.